Related Research Articles

Common law is the body of law created by judges and similar quasi-judicial tribunals by virtue of being stated in written opinions.

Roman law is the legal system of ancient Rome, including the legal developments spanning over a thousand years of jurisprudence, from the Twelve Tables, to the Corpus Juris Civilis ordered by Eastern Roman emperor Justinian I. Roman law forms the basic framework for civil law, the most widely used legal system today, and the terms are sometimes used synonymously. The historical importance of Roman law is reflected by the continued use of Latin legal terminology in many legal systems influenced by it, including common law.

The Napoleonic Code, officially the Civil Code of the French, is the French civil code established during the French Consulate in 1804 and still in force in France, although heavily and frequently amended since its inception. Although Napoleon himself was not directly involved in the drafting of the Code, as it was drafted by a commission of four eminent jurists, he chaired many of the commission's plenary sessions, and his support was crucial to its passage into law.

The Corpus JurisCivilis is the modern name for a collection of fundamental works in jurisprudence, enacted from 529 to 534 by order of Byzantine Emperor Justinian I. It is also sometimes referred to metonymically after one of its parts, the Code of Justinian.

Edward Livingston was an American jurist, statesman and slaveholder. He was an influential figure in the drafting of the Louisiana Civil Code of 1825, a civil code based largely on the Napoleonic Code. Livingston represented both New York and then Louisiana in Congress and served as the U.S. Secretary of State from 1831 to 1833 and Minister to France from 1833 to 1835 under President Andrew Jackson. He was also the 46th mayor of New York City.
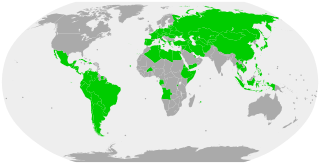
A civil code is a codification of private law relating to property, family, and obligations.
In law, codification is the process of collecting and restating the law of a jurisdiction in certain areas, usually by subject, forming a legal code, i.e. a codex (book) of law.

Legal history or the history of law is the study of how law has evolved and why it has changed. Legal history is closely connected to the development of civilisations and operates in the wider context of social history. Certain jurists and historians of legal process have seen legal history as the recording of the evolution of laws and the technical explanation of how these laws have evolved with the view of better understanding the origins of various legal concepts; some consider legal history a branch of intellectual history. Twentieth-century historians viewed legal history in a more contextualised manner – more in line with the thinking of social historians. They have looked at legal institutions as complex systems of rules, players and symbols and have seen these elements interact with society to change, adapt, resist or promote certain aspects of civil society. Such legal historians have tended to analyse case histories from the parameters of social-science inquiry, using statistical methods, analysing class distinctions among litigants, petitioners and other players in various legal processes. By analyzing case outcomes, transaction costs, and numbers of settled cases, they have begun an analysis of legal institutions, practices, procedures and briefs that gives a more complex picture of law and society than the study of jurisprudence, case law and civil codes can achieve.
Jus commune or ius commune is Latin for "common law" in certain jurisdictions. It is often used by civil law jurists to refer to those aspects of the civil law system's invariant legal principles, sometimes called "the law of the land" in English law. While the ius commune was a secure point of reference in continental European legal systems, in England it was not a point of reference at all. The phrase "the common law of the civil law systems" means those underlying laws that create a distinct legal system and are common to all its elements.

Civil law is a legal system originating in Italy and France that has been adopted in large parts of the world. Modern civil law stems mainly from the Napoleonic Code of the early 19th century, and it is a continuation of ancient Roman law. Its core principles are codified into a referable system, which serves as the primary source of law.
The legal origins theory claims that the two main legal traditions or origins, civil law and common law, crucially shape lawmaking and dispute adjudication and have not been reformed after the initial exogenous transplantation by Europeans. Therefore, they affect economic outcomes to date. According to the evidence reported by the initial proponents of such a theory, countries that received civil law would display today less secure investor rights, stricter regulation, and more inefficient governments and courts than those that inherited common law. These differences would reflect both a stronger historical emphasis of common law on private ordering and the higher adaptability of judge-made law.

David Dudley Field II was an American lawyer and law reformer who made major contributions to the development of American civil procedure. His greatest accomplishment was engineering the move away from common law pleading towards code pleading, which culminated in the enactment of the Field Code in 1850 by the state of New York.
In Scots law, jus relictae is the right of the surviving spouse in the moveable property of the deceased spouse. Jus relictae is the term used for a surviving wife, and jus relicti is the term used for a surviving husband. The similar right for any surviving children is referred to as legitim.

Norman Stephan Kinsella is an American patent attorney, author, and deontological anarcho-capitalist. His legal works have been published by Oxford University Press, Oceana Publications, Mises Institute, Quid Pro Books and others.

A code of law, also called a law code or legal code, is a systematic collection of statutes. It is a type of legislation that purports to exhaustively cover a complete system of laws or a particular area of law as it existed at the time the code was enacted, by a process of codification. Though the process and motivations for codification are similar in different common law and civil law systems, their usage is different.

François Xavier Martin, was a Franco-American lawyer and author, the first Attorney General of State of Louisiana, and longtime Justice of the Louisiana Supreme Court. Born in Marseille, he moved to Martinique in 1780, and then immigrated to North Carolina just before the end American Revolutionary War. He was appointed as Attorney General of the Territory of Orleans after the Louisiana Purchase; he also helped untangle layers of French and Spanish colonial law in the territory and subsequent state of Louisiana. His legal writing and reviews of cases was important to codification of Louisiana law in the 1820s.

Law in the state of Louisiana is based on a more diverse set of sources than the laws of the other 49 states of the United States. Private law—that is, substantive law between private sector parties, principally contracts and torts—has a civil law character, based on French and Spanish codes and ultimately Roman law, with some common law influences. Louisiana is the only state whose private legal system is based on civil law, rather than the traditional American common law. Louisiana's criminal law, however, does largely rest on common law. Louisiana's administrative law is generally similar to the administrative law of the federal government and other states. Louisiana's procedural law is generally in line with that of other U.S. states, which in turn is generally based on the U.S. Federal Rules of Civil Procedure.

The law of Sweden is a civil law system, whose essence is manifested in its dependence on statutory law. Sweden's civil law tradition, as in the rest of Europe, is founded upon Roman law as codified in the Corpus Juris Civilis, but as developed within German law, rather than upon the Napoleonic Code. But, over time Sweden along with the other Scandinavian countries have deviated significantly from their classical Roman and German models. Instead, the Scandinavian countries together with Finland, the Faroe Islands, Greenland, Åland (self-governing) and Iceland may be said to have a special "Nordic" version of jurisprudence that is neither a truly civil law system nor a part of the British-derived common law legal system.
Vernon Palmer (Vernon Valentine Palmer) is an American-born legal scholar, the Thomas Pickles Professor of Law at Tulane University Law School and the co-director of its Eason Weinmann Center of Comparative Law. He is a specialist in civil law and mixed jurisdiction legal studies, with a primary focus on the study of comparative international law.
References
- ↑ Parise, Agustín (2014). "Private Law in Louisiana: An Account of Civil Codes, Heritage, and Law Reform". In César Rivera, Julio (ed.). The Scope and Structure of Civil Codes. Ius Gentium: Comparative Perspectives on Law and Justice. Vol. 32. Springer. p. 453. doi:10.1007/978-94-007-7942-6. ISBN 978-94-007-7942-6. LCCN 2014930754.
- ↑ "How the Code Napoleon makes Louisiana law different". LA-Legal . Retrieved 2006-10-26.
- ↑ Official English title:: Digest of the Civil Laws now in Force in the Territory of Orleans, with Alterations and Amendments Adapted to its Present System of Government.
- ↑ Kinsella, Norman (1997). "A Civil Law to Common Law Dictionary" (PDF). KinsellaLaw.com. Archived from the original (PDF) on December 25, 2010. Retrieved December 7, 2010.