
Butterflies are insects in the macrolepidopteran clade Rhopalocera from the order Lepidoptera, which also includes moths. Adult butterflies have large, often brightly coloured wings, and conspicuous, fluttering flight. The group comprises the large superfamily Papilionoidea, which contains at least one former group, the skippers, and the most recent analyses suggest it also contains the moth-butterflies. Butterfly fossils date to the Paleocene, about 56 million years ago.

Libreville is the capital and largest city of Gabon. Occupying 65 square kilometres (25 sq mi) in the northwestern province of Estuaire, Libreville is a port on the Komo River, near the Gulf of Guinea. As of the 2013 census, its population was 703,904.

Jethro Tull was an English agriculturist from Berkshire who helped to bring about the British Agricultural Revolution. He perfected a horse-drawn seed drill in 1700 that economically sowed the seeds in neat rows, and later developed a horse-drawn hoe. Tull's methods were adopted by many landowners and helped to provide the basis for modern agriculture.

June Gloom is a California term for a weather pattern that results in cloudy, overcast skies with cool temperatures during the late spring and early summer. While it is most common in the month of June, it can occur in surrounding months, giving rise to other colloquialisms, such as "May Gray", "No-Sky July", and, rarely, "Fogust". Low-altitude stratus clouds form over the cool water of the California Current, and spread overnight into the coastal regions of Southern California. The overcast skies often are accompanied by fog and drizzle, though usually not rain. June Gloom usually clears up between mid-morning and early afternoon, depending on the strength of the marine layer, and gives way to sunny skies. On a strong June Gloom day, the clouds and fog may extend inland to the valleys and Inland Empire and may persist into the mid-afternoon or evening.

The Mulanje Massif, also known as Mount Mulanje, is a large inselberg in southern Malawi. Sapitwa Peak, the highest point on the massif at 3,002 m, is the highest point in Malawi. It lies 65 km east of Blantyre, rising sharply from the surrounding plains of Phalombe and the Mulanje district.

The blue duiker is a small antelope found in central, southern and eastern Africa. It is the smallest duiker. The species was first described by Swedish naturalist Carl Peter Thunberg in 1789. 12 subspecies are identified. The blue duiker reaches 32–41 centimetres (13–16 in) at the shoulder and weighs 3.5–9 kilograms (7.7–19.8 lb). Sexually dimorphic, the females are slightly larger than the males. The dark tail measures slightly above 10 centimetres (3.9 in). It has short, spiky horns, around 5 centimetres (2.0 in) long and hidden in hair tufts. The subspecies show a great degree of variation in their colouration. The blue duiker bears a significant resemblance to Maxwell's duiker.

Hákarl is a national dish of Iceland consisting of a Greenland shark or other sleeper shark that has been cured with a particular fermentation process and hung to dry for four to five months. It has a strong ammonia-rich smell and fishy taste, making hákarl an acquired taste.

Myrmecodia is a genus of epiphytic myrmecophytes, native to Southeast Asia, but also present in Indochina, Malaysia, the Southwest Pacific, the Philippines, Fiji, and extending south to Queensland and Cape York in Australia. It is one of five ant-plant genera in the family Rubiaceae, the others being Anthorrhiza, Hydnophytum, Myrmephytum, and Squamellaria.
The climate of San Diego, California is classified as a Mediterranean climate. The basic climate features hot, sunny, and dry summers, and cooler, wetter winters. However, San Diego is much more arid than typical Mediterranean climates, and winters are still dry compared with most other zones with this type of climate.

Wild Africa is a British nature documentary series created and produced by the BBC. It explores the natural history of the African continent. It was first transmitted on 7 November 2001 on BBC Two in the United Kingdom and comprises six episodes. Each concentrates on a particular environment. The producers use aerial photography and wildlife footage to show how natural phenomena such as seasonal changes influence the patterns of life. Wild Africa was produced by the BBC Natural History Unit and narrated by Fergal Keane.

The African sheath-tailed bat is a species of sac-winged bat in the family Emballonuridae found in Angola, Benin, the Central African Republic, the Republic of the Congo, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Ivory Coast, Djibouti, Eritrea, Ethiopia, Ghana, Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Kenya, Madagascar, Mozambique, Nigeria, Somalia, Sudan, Tanzania, Togo, Uganda, and Yemen. Its natural habitats are dry savanna, subsaharic shrubland, subtropical or tropical dry shrubland, caves, and hot deserts. It is threatened by habitat loss, although still ranked as least concern.

Bagheera kiplingi is a species of jumping spider found in Central America, including Mexico, Costa Rica, and Guatemala. It is the type species of the genus Bagheera, which includes three other species, including B. prosper. B. kiplingi is notable for its peculiar diet, which is mostly herbivorous. No other known species of omnivorous spider has such a markedly herbivorous diet.
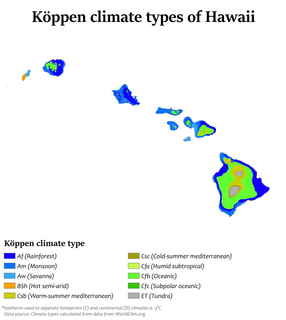
The American state of Hawaii, which covers the Hawaiian Islands, is tropical but it experiences many different climates, depending on altitude and surroundings. The island of Hawaii for example hosts 4 climate groups on a surface as small as 4,028 square miles (10,430 km2) according to the Köppen climate types: tropical, arid, temperate and polar. When counting also the Köppen sub-categories the island of Hawaii hosts 10 climate zones. The islands receive most rainfall from the trade winds on their north and east flanks as a result of orographic precipitation. Coastal areas are drier, especially the south and west side or leeward sides.

Anoplolepis custodiens, commonly known as the common pugnacious ant, is a species of ant in the genus Anoplolepis, native to central and southern Africa. Individual ants may come in a range of colors and sizes. Found in dry and cultivated areas, it is an important source of prey for some pangolins and aardvarks. Although generally aggressive, ants from other colonies of Anoplolepis custodiens are not attacked.

The Ndjili River is a river that flows from the south through the capital city of Kinshasa in the Democratic Republic of the Congo, where it joins the Congo River. It separates the districts of Tshangu and Mont Amba. The river gives its name to the Ndjili commune and to the Ndjili International Airport.

Montane ecosystems are found on the slopes of mountains. The alpine climate in these regions strongly affects the ecosystem because temperatures fall as elevation increases, causing the ecosystem to stratify. This stratification is a crucial factor in shaping plant community, biodiversity, metabolic processes and ecosystem dynamics for montane ecosystems. Dense montane forests are common at moderate elevations, due to moderate temperatures and high rainfall. At higher elevations, the climate is harsher, with lower temperatures and higher winds, preventing the growth of trees and causing the plant community to transition to montane grasslands, shrublands or alpine tundra. Due to the unique climate conditions of montane ecosystems, they contain increased numbers of endemic species. Montane ecosystems also exhibit variation in ecosystem services, which include carbon storage and water supply.

Lugbara cuisine is one of the meals of East Africa and the ancient Lado Enclave. The Lugbara people of northwestern Uganda and northeastern DR Congo eat not only vegetable dishes, but also animals like goats, cows plus ope (guineafowls) and catch insects like onya for food which is called nyaka in the standard Lugbara language used in Arua. Cassava flour sometimes mixed and mingled with millet or sorghum like posho or ugali is the staple food and is called enya(sa) [kalo or atap(a) in Ateso, fufu in West Africa] accompanied with a range of soup dishes. Rice, yams, potatoes and matoke are also eaten. Below is a list of some of the Lugbara-styled delicacies you can find in West Nile Restaurants, Ariwara Town, Arua Park in Kampala and many homes or cafeterias that cherish traditional Lugbara cuisine.
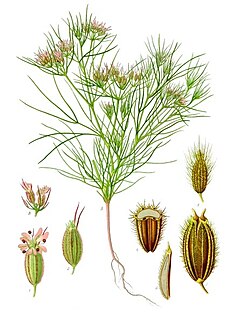
Cumin is a flowering plant in the family Apiaceae, native to a territory including the Middle East and stretching east to India. Its seeds – each one contained within a fruit, which is dried – are used in the cuisines of many cultures in both whole and ground form. Although cumin is thought to have uses in traditional medicine, there is no high-quality evidence that it is safe or effective as a therapeutic agent.

Mimetes capitulatus is an evergreen, upright, rounded shrub of about 2 m (7 ft) high, from the family Proteaceae. It has geyish green, lance- to egg-shaped leaves ending in a thickened tip. The flower heads and subtending leaves form a cylindric inflorescence, topped by ordinary, more or less upright leaves. Each primarily orange flowerhead contains 10–13 flowers with conspicuously scarlet styles, yellow under the narrow hourglass-like pollen presenter at its tip. Flowers can usually be found from mid-June till December, peaking in August. It is called conical pagoda in English and skraalstompie in Afrikaans.

Seattle has a temperate climate, classified in the Mediterranean zone by the main climatic classification but some sources put the city in the oceanic zone (Cfb). It has cool, wet winters and mild, relatively dry summers, covering characteristics of both. The climate is sometimes characterized as a "modified Mediterranean" climate because it is cooler and wetter than a "true" Mediterranean climate, but shares the characteristic dry summer. The city and environs are part of USDA hardiness zone 8b, with isolated coastal pockets falling under 9a.


















