
The Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) is the largest transportation agency of the U.S. government and regulates all aspects of civil aviation in the country as well as over surrounding international waters. Its powers include air traffic management, certification of personnel and aircraft, setting standards for airports, and protection of U.S. assets during the launch or re-entry of commercial space vehicles. Powers over neighboring international waters were delegated to the FAA by authority of the International Civil Aviation Organization.
The Single European Sky (SES) is a European Commission initiative that seeks to reform the European air traffic management system through a series of actions carried out in four different levels with the aim of satisfying the needs of the European airspace in terms of capacity, safety, efficiency and environmental impact.

Air traffic control (ATC) is a service provided by ground-based air traffic controllers who direct aircraft on the ground and through controlled airspace, and can provide advisory services to aircraft in non-controlled airspace. The primary purpose of ATC worldwide is to prevent collisions, organize and expedite the flow of air traffic, and provide information and other support for pilots. In some countries, ATC plays a security or defensive role, or is operated by the military.
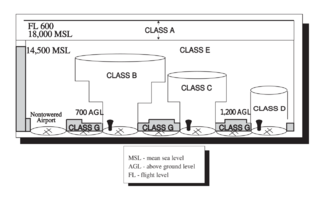
Airspace is the portion of the atmosphere controlled by a country above its territory, including its territorial waters or, more generally, any specific three-dimensional portion of the atmosphere. It is not the same as aerospace, which is the general term for Earth's atmosphere and the outer space in its vicinity.
NATS Holdings, formerly National Air Traffic Services and commonly referred to as NATS, is the main air navigation service provider in the United Kingdom. It inherited the traditions of UK air traffic control, which was the world's first air traffic control regime. It provides en-route air traffic control services to flights within the UK flight information regions and the Shanwick Oceanic Control Area, and provides air traffic control services to 14 UK airports.

ENAIRE is the air navigation manager in Spain and Western Sahara, certified for the provision of en route, approach and aerodrome control services. As a public corporate entity attached to the Ministry for Public Works, it is responsible for air traffic control, aeronautical information and the Communication, navigation and surveillance networks necessary so that air companies and their aircraft can fly safely, fluidly and in an orderly manner within Spanish airspace.

The European Organisation for the Safety of Air Navigation, commonly known as Eurocontrol, is an international organisation working to achieve safe and seamless air traffic management across Europe. Founded in 1960, Eurocontrol currently has 41 member states and is headquartered in Brussels, Belgium. It has several local sites as well, including R&D activities in Brétigny-sur-Orge, France, the Institute of Air Navigation Training (IANS) in Luxembourg, and the Maastricht Upper Area Control Centre (MUAC) in Maastricht, the Netherlands. The organisation employs approximately two thousand people, and operates with an annual budget in excess of half a billion Euro.

Airservices Australia is an Australian Government owned corporation, responsible for providing safe, secure, efficient and environmentally responsible services to the aviation industry within the Australian Flight Information Region (FIR). Some of Airservices responsibilities include air traffic control, airways navigation and communication facilities, publishing aeronautical data and airport rescue and fire-fighting services. Airservices Australia has international partnerships with ICAO, CANSO and IATA.

The Airports Authority of India or AAI is a statutory body, under the jurisdiction of Directorate General of Civil Aviation, Ministry of Civil Aviation, Government of India. It is responsible for creating, upgrading, maintaining and managing civil aviation infrastructure in India. It provides Communication Navigation Surveillance / Air Traffic Management (CNS/ATM) services over Indian airspace and adjoining oceanic areas. AAI is currently managing a total of 137 Airports, including 23 International Airports, 10 Customs Airports, 81 Domestic Airports and 23 Civil enclaves at Defense Airfields. AAI also has ground installations at all airports and 25 other locations to ensure safety of aircraft operations. AAI covers all major air-routes over Indian landmass via 29 Radar installations at 11 locations along with 700 VOR/DVOR installations co-located with Distance Measuring Equipment (DME). 52 runways are provided with Instrument landing system (ILS) installations with Night Landing Facilities at most of these airports and Automatic Message Switching System at 15 Airports.
In aviation, an air traffic service (ATS) is a service which regulates and assists aircraft in real-time to ensure their safe operations. In particular, ATS is to:
The Next Generation Air Transportation System (NextGen) is an ongoing modernization project of the United States National Airspace System (NAS). The U.S. Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) began work on NextGen improvements in 2007 and plans to have all major components in place by 2025.

The Federal Aviation Act of 1958 was an act of the United States Congress, signed by President Dwight D. Eisenhower, that created the Federal Aviation Agency and abolished its predecessor, the Civil Aeronautics Administration (CAA). The act empowered the FAA to oversee and regulate safety in the airline industry and the use of American airspace by both military aircraft and civilian aircraft.

The Directorate General of Civil Aviation (DGCA) is a statutory body of the Indian Central Government to regulate civil aviation in India. Formed under the Aircraft (Amendment) Bill, 2020, the DGCA investigates aviation accidents and incidents, maintains all regulations related to aviation and is responsible for issuance of licenses pertaining to aviation like PPL's, SPL's and CPL's in India. It is headquartered along Sri Aurobindo Marg, opposite Safdarjung Airport, in New Delhi. The Government of India is planning to replace the organisation with a Civil Aviation Authority (CAA), modelled on the lines of the American Federal Aviation Administration (FAA).

GCAA or Ghana Civil Aviation Authority is the national aviation authority and regulatory agency of the Republic of Ghana for air transportation in the country. It has its headquarters in Kotoka Airport in Accra.

The Civil Aviation Authority is the civil aviation authority in the special administrative region of Macau, China and is responsible for controlling and regulating air its traffic and airspace.
The Single European Sky ATM Research Joint Undertaking is a public-private partnership, established in 2007, responsible for the coordination and concentration of all European Union (EU) research and development activities in Air Traffic Management (ATM) as part of the SESAR programme. Initiated in 2004, the SESAR programme is the technological arm of the EU's Single European Sky initiative to integrate EU Member States' ATM systems. Founded by the EU and Eurocontrol, today the SESAR JU includes 19 members, representing over 100 organisations.

ENAV S.p.A. is an Italian company owned by the Ministry of Economy and Finances and managed by the Ministry of Infrastructure and Transport, through ENAC, the Italian Civil Aviation Authority. Together with the Italian Air Force, the company is responsible for the provision of air traffic services (ATS) and other air navigation services in Italy. As an air navigation service provider (ANSP) it is responsible for the provision of air traffic control service (ATCS), flight information service (FIS), aeronautical information service (AIS), and issuing of weather forecasts for the airports and the airspace under its responsibility. The company name ENAV was the former name of the public agency, acronym for "Ente Nazionale Assistenza al Volo". In 2001 the agency ENAV was transformed in ENAV S.p.A., a company owned by the Italian Treasury.

Estonian Air Navigation Services, abbreviated as EANS, is a modern, rapidly developing company operating under the auspices of the Ministry of Economic Affairs and Communications of the Republic of Estonia. It is a business entity, the major function of which is to provide services to air traffic in accordance with international standards as well as to ensure flight safety in Tallinn Flight Information Region. The sole owner of the company shares is the Republic of Estonia.
Karachi Area Control Centre is one of two Area Control Centers in Pakistan operated by the Pakistan Civil Aviation Authority and is based in Terminal 1 at Jinnah International Airport in Karachi. Karachi ACC air traffic controllers provide en route and terminal control services to aircraft in the Karachi Flight Information Region. The Karachi FIR airspace covers Pakistani airspace between the 30° North to 23° North. To the north is the Lahore FIR. To the east is the Delhi FIR. To the south is the Muscat FIR and to the west are the Tehran FIR and Kabul FIRs.

Lahore Area Control Centre is one of two Area Control Centers in Pakistan operated by the Pakistan Civil Aviation Authority and based at Allama Iqbal International Airport in Lahore. Lahore ACC air traffic controllers provide en route and terminal control services to aircraft in the Lahore Flight Information Region (FIR). The Lahore FIR airspace covers Pakistani airspace between the 30° North to 37° North. To the south is the Karachi FIR. To the north is the Urumqi FIR. To the east is the Delhi FIR. To the west is the Kabul FIR.














