Related Research Articles
This article concerns the period 219 BC – 210 BC.

The gens Claudia, sometimes written Clodia, was one of the most prominent patrician houses at ancient Rome. The gens traced its origin to the earliest days of the Roman Republic. The first of the Claudii to obtain the consulship was Appius Claudius Sabinus Regillensis, in 495 BC, and from that time its members frequently held the highest offices of the state, both under the Republic and in imperial times.
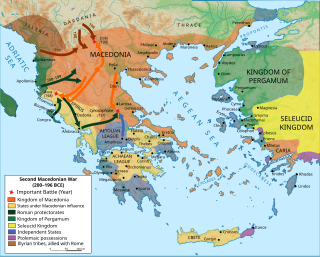
The Second Macedonian War was fought between Macedon, led by Philip V of Macedon, and Rome, allied with Pergamon and Rhodes. Philip was defeated and was forced to abandon all possessions in southern Greece, Thrace and Asia Minor. During their intervention, although the Romans declared the "freedom of the Greeks" against the rule from the Macedonian kingdom, the war marked a significant stage in increasing Roman intervention in the affairs of the eastern Mediterranean, which would eventually lead to Rome's conquest of the entire region.
The gens Sulpicia was one of the most ancient patrician families at ancient Rome, and produced a succession of distinguished men, from the foundation of the Republic to the imperial period. The first member of the gens who obtained the consulship was Servius Sulpicius Camerinus Cornutus, in 500 BC, only nine years after the expulsion of the Tarquins, and the last of the name who appears on the consular list was Sextus Sulpicius Tertullus in AD 158. Although originally patrician, the family also possessed plebeian members, some of whom may have been descended from freedmen of the gens.

The gens Furia, originally written Fusia, and sometimes found as Fouria on coins, was one of the most ancient and noble patrician houses at Rome. Its members held the highest offices of the state throughout the period of the Roman Republic. The first of the Furii to attain the consulship was Sextus Furius in 488 BC.
The Battle of Cremona was fought in 200 BC between the Roman Republic and Cisalpine Gaul. The Roman force was victorious.

Marcus Claudius Marcellus was Roman consul for the years 166 BC, for 155 BC, and for 152 BC.
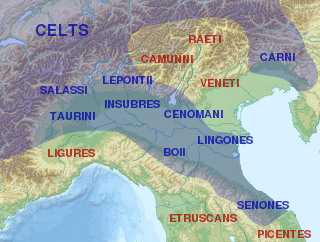
The Insubres or Insubri were an ancient Celtic population settled in Insubria, in what is now the Italian region of Lombardy. They were the founders of Mediolanum (Milan). Though completely Gaulish at the time of Roman conquest, they were the result of the fusion of pre-existing Ligurian and Celtic population with Gaulish tribes.
The gens Sempronia was one of the most ancient and noble houses of ancient Rome. Although the oldest branch of this gens was patrician, with Aulus Sempronius Atratinus obtaining the consulship in 497 BC, the thirteenth year of the Republic, but from the time of the Samnite Wars onward, most if not all of the Sempronii appearing in history were plebeians. Although the Sempronii were illustrious under the Republic, few of them attained any importance or notice in imperial times.

Quintus Caecilius Metellus was a pontiff in 216 BC, aedile of the plebeians in 209 BC, curule aedile in 208 BC, magister equitum in 207 BC, consul in 206 BC, dictator in 205 BC, proconsul of Bruttium in 204 BC, and an ambassador at the court of Philip V of Macedon in 185 BC.

The gens Postumia was a noble patrician family at ancient Rome. Throughout the history of the Republic, the Postumii frequently occupied the chief magistracies of the Roman state, beginning with Publius Postumius Tubertus, consul in 505 BC, the fifth year of the Republic. Although like much of the old Roman aristocracy, the Postumii faded for a time into obscurity under the Empire, individuals bearing the name of Postumius again filled a number of important offices from the second century AD to the end of the Western Empire.
The gens Atinia was a minor plebeian family at ancient Rome, which came to prominence during the late Republic. No members of this gens ever attained the consulship, although several were praetors in the early second century BC, beginning with Gaius Atinius Labeo 195.
The gens Cluvia was a plebeian family at ancient Rome, known from the later Republic, and early imperial times. The first member of the gens to achieve prominence was Gaius Cluvius Saxula, praetor in 175 and 173 BC.

Over the course of nearly four centuries, the Roman Republic fought a series of wars against various Celtic tribes, whom they collectively described as Galli, or Gauls. Among the principal Gallic peoples described as antagonists by Greek and Roman writers were the Senones, Insubres, Boii, and Gaesatae.
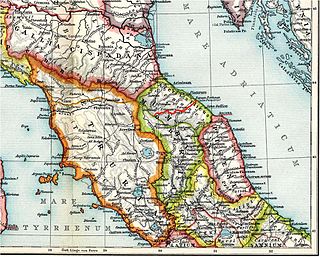
The Battle of Silva Litana was an ambush that took place in a forest 75 miles northwest of the Roman city of Ariminum during the Second Punic War in 216 BC. The Gallic Boii surprised and destroyed a Roman army under the consul-elect Lucius Postumius Albinus. Of 25,000 Romans, only 13 survived, with a few being taken prisoner by the Gauls. The corpse of Postumius was decapitated and his skull was made into a gilded ceremonial cup by the Boii. News of this military disaster probably reached Rome after the defeat at Cannae in the fall of 216 BC or the spring election of consuls for 215 BC, triggering a renewed panic. The Romans were compelled to postpone military operations against the Gauls until the conclusion of the Second Punic War, sending only two legions to guard against additional Gallic attacks. However, the Boii and Insubres did not attempt to exploit their victory. Cisalpine Gaul remained in relative peace until 207 BC, when Hasdrubal Barca arrived there with his army from Spain.
The siege of Mutina in 218 BC constitutes one of the first episodes of the Second Punic War. Hannibal's diplomacy in Cisalpine Gaul persuaded the Gallic Boii and Insubres tribes to revolt and drive the Roman colonists out of Piacenza (Placentia) and push them as far as Modena (Mutina), which was then besieged.
Gaius Aurelius Cotta was a Roman politician in the second century BC.
References
- ↑ Livy, History of Rome 27.2.
- ↑ Livy, History of Rome 31.10-11.
- ↑ Livy, History of Rome 31.21-22. Words taken from William Smith, A Dictionary of Greek and Roman Biography and Mythology, Volume 3, page 605.
- ↑ Edmonds, Cyrus (1891). The History of Rome, Volume 3 (1 ed.). London: George Bell & Sons. pp. 1369–1370. Retrieved 19 May 2015.
- ↑ Livy, History of Rome 33.37.