Related Research Articles

Domitian was Roman emperor from 81 to 96. The son of Vespasian and the younger brother of Titus, his two predecessors on the throne, he was the last member of the Flavian dynasty. Described as "a ruthless but efficient autocrat", his authoritarian style of ruling put him at sharp odds with the Senate, whose powers he drastically curtailed.

Galba was Roman emperor, ruling from AD 68 to 69. He was the first emperor in the Year of the Four Emperors and assumed the throne following Emperor Nero's suicide.

Nero Claudius Caesar Augustus Germanicus was a Roman emperor and the final emperor of the Julio-Claudian dynasty, reigning from AD 54 until his death in AD 68.

Otho was Roman emperor, ruling for three months from 15 January to 16 April 69. He was the second emperor of the Year of the Four Emperors.

Plutarch was a Greek Middle Platonist philosopher, historian, biographer, essayist, and priest at the Temple of Apollo in Delphi. He is known primarily for his Parallel Lives, a series of biographies of illustrious Greeks and Romans, and Moralia, a collection of essays and speeches. Upon becoming a Roman citizen, he was possibly named Lucius Mestrius Plutarchus.

Aulus Vitellius was Roman emperor for eight months, from 19 April to 20 December AD 69. Vitellius was proclaimed emperor following the quick succession of the previous emperors Galba and Otho, in a year of civil war known as the Year of the Four Emperors. Vitellius was the first to add the honorific cognomen Germanicus to his name instead of Caesar upon his accession. Like his predecessor, Otho, Vitellius attempted to rally public support to his cause by honoring and imitating Nero who remained popular in the empire.

Vespasian was Roman emperor from 69 to 79. The last emperor to reign in the Year of the Four Emperors, he founded the Flavian dynasty, which ruled the Empire for 27 years. His fiscal reforms and consolidation of the empire brought political stability and a vast building program.
AD 69 (LXIX) was a common year starting on Sunday of the Julian calendar. In the Roman Empire, it was known as the Year of the consulship of Galba and Vinius. The denomination AD 69 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Titus Caesar Vespasianus was Roman emperor from 79 to 81. A member of the Flavian dynasty, Titus succeeded his father Vespasian upon his death, becoming the first Roman emperor to succeed his biological father.

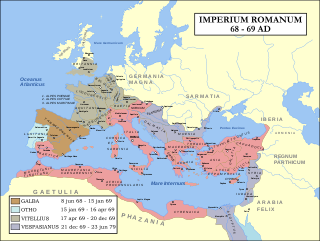
The Year of the Four Emperors, AD 69, was the first civil war of the Roman Empire, during which four emperors ruled in succession: Galba, Otho, Vitellius, and Vespasian. It is considered an important interval, marking the transition from the Julio-Claudians, the first imperial dynasty, to the Flavian dynasty. The period witnessed several rebellions and claimants, with shifting allegiances and widespread turmoil in Rome and the provinces.

The Flavian dynasty ruled the Roman Empire between AD 69 and 96, encompassing the reigns of Vespasian (69–79), and his two sons Titus (79–81) and Domitian (81–96). The Flavians rose to power during the civil war of 69, known as the Year of the Four Emperors. After Galba and Otho died in quick succession, Vitellius became emperor in mid 69. His claim to the throne was quickly challenged by legions stationed in the eastern provinces, who declared their commander Vespasian emperor in his place. The Second Battle of Bedriacum tilted the balance decisively in favour of the Flavian forces, who entered Rome on 20 December. The following day, the Roman Senate officially declared Vespasian emperor of the Roman Empire, thus commencing the Flavian dynasty. Although the dynasty proved to be short-lived, several significant historic, economic and military events took place during their reign.
Aulus Caecina Alienus was a Roman general active during the Year of the Four Emperors.

De vita Caesarum, commonly known as The Twelve Caesars, is a set of twelve biographies of Julius Caesar and the first 11 emperors of the Roman Empire written by Gaius Suetonius Tranquillus. The group are: Julius Caesar, Augustus, Tiberius, Caligula, Claudius, Nero, Galba, Otho, Vitellius, Vespasian, Titus, Domitian.
Titus Flavius T. f. T. n. Sabinus was a Roman politician and soldier. A native of Reate, he was the elder son of Titus Flavius Sabinus and Vespasia Polla, and brother of the Emperor Vespasian.
Marcus Cluvius Rufus was a Roman consul, senator, governor, and historian who was mentioned on several occasions by Tacitus, Suetonius, Cassius Dio, Josephus and Plutarch.
The gens Vitellia was a family of ancient Rome, which rose from obscurity in imperial times, and briefly held the Empire itself in AD 69. The first of this gens to obtain the consulship was Aulus Vitellius, uncle of the emperor Vitellius, in AD 32.

Nerva was a Roman emperor from 96 to 98. Nerva became emperor when aged almost 66, after a lifetime of imperial service under Nero and the succeeding rulers of the Flavian dynasty. Under Nero, he was a member of the imperial entourage and played a vital part in exposing the Pisonian conspiracy of 65. Later, as a loyalist to the Flavians, he attained consulships in 71 and 90 during the reigns of Vespasian and Domitian, respectively. On 19 September 96, Domitian was assassinated in a palace conspiracy involving members of the Praetorian Guard and several of his freedmen. On the same day, Nerva was declared emperor by the Roman Senate. As the new ruler of the Roman Empire, he vowed to restore liberties which had been curtailed during the autocratic government of Domitian.

The gens Antonia was a Roman family of great antiquity, with both patrician and plebeian branches. The first of the gens to achieve prominence was Titus Antonius Merenda, one of the second group of Decemviri called, in 450 BC, to help draft what became the Law of the Twelve Tables. The most prominent member of the gens was Marcus Antonius.
The gens Rubria was a plebeian family at ancient Rome. Members of this gens are first mentioned in the time of the Gracchi, but they did not rise to prominence until imperial times. The first of the Rubrii to obtain the consulship was Rubrius Gallus, some time before AD 68.

Vitellia was a Roman noblewoman, who was the daughter of the emperor Aulus Vitellius and was married to the Roman senator Decimus Valerius Asiaticus. A fictionalised Vitellia is a central character in the opera La clemenza di Tito by Mozart.