Related Research Articles
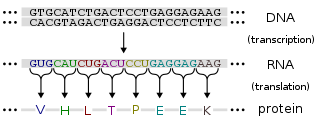
Protein production is the biotechnological process of generating a specific protein. It is typically achieved by the manipulation of gene expression in an organism such that it expresses large amounts of a recombinant gene. This includes the transcription of the recombinant DNA to messenger RNA (mRNA), the translation of mRNA into polypeptide chains, which are ultimately folded into functional proteins and may be targeted to specific subcellular or extracellular locations.

Lumbricus rubellus is a species of earthworm that is related to Lumbricus terrestris. It is usually reddish brown or reddish violet, iridescent dorsally, and pale yellow ventrally. They are usually about 25 millimetres (0.98 in) to 105 millimetres (4.1 in) in length, with around 95–120 segments. Their native distribution was mainland Europe and the British Isles, but they have currently spread worldwide in suitable habitats.

Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase is an enzyme in the lyase family used in the metabolic pathway of gluconeogenesis. It converts oxaloacetate into phosphoenolpyruvate and carbon dioxide.

Oxaloacetate decarboxylase is a carboxy-lyase involved in the conversion of oxaloacetate into pyruvate.

A serine/threonine protein kinase is a kinase enzyme, in particular a protein kinase, that phosphorylates the OH group of the amino-acid residues serine or threonine, which have similar side chains. At least 350 of the 500+ human protein kinases are serine/threonine kinases (STK).

Leucyl aminopeptidases are enzymes that preferentially catalyze the hydrolysis of leucine residues at the N-terminus of peptides and proteins. Other N-terminal residues can also be cleaved, however. LAPs have been found across superkingdoms. Identified LAPs include human LAP, bovine lens LAP, porcine LAP, Escherichia coli LAP, and the solanaceous-specific acidic LAP (LAP-A) in tomato.

Nattokinase is an enzyme extracted and purified from a Japanese food called nattō. Nattō is produced by fermentation by adding the bacterium Bacillus subtilisvar natto, which also produces the enzyme, to boiled soybeans. While other soy foods contain enzymes, it is only the nattō preparation that contains the specific nattokinase enzyme under the Japan Nattokinase Administration and Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare.

Glycine decarboxylase also known as glycine cleavage system P protein or glycine dehydrogenase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the GLDC gene.

Cyclooxygenase 1 (COX-1), also known as prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthase 1, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PTGS1 gene. In humans it is one of three cyclooxygenases.
In enzymology, a lipoyl(octanoyl) transferase (EC 2.3.1.181) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

Alcohol dehydrogenase [NADP+] also known as aldehyde reductase or aldo-keto reductase family 1 member A1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the AKR1A1 gene. AKR1A1 belongs to the aldo-keto reductase (AKR) superfamily. It catalyzes the NADPH-dependent reduction of a variety of aromatic and aliphatic aldehydes to their corresponding alcohols and catalyzes the reduction of mevaldate to mevalonic acid and of glyceraldehyde to glycerol. Mutations in the AKR1A1 gene has been found associated with non-Hodgkin's lymphoma.

Succinate-semialdehyde dehydrogenase, mitochondrial is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ALDH5A1 gene.

Dipeptidyl peptidase 8 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the DPP8 gene.

Zinc finger protein 24 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ZNF24 gene.
Di Long or Dilong extract is a medicinal preparation based on abdominal extracts from the earthworm species Lumbricus rubellus used in traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) for a wide variety of disorders, from convulsions and fevers to rheumatoid arthritis and blood stasis syndromes.

Acetyl-CoA carboxylase 2 also known as ACC-beta or ACC2 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ACACB gene.
Nepenthesin is an aspartic protease of plant origin that has so far been identified in the pitcher secretions of Nepenthes and in the leaves of Drosera peltata. It is similar to pepsin, but differs in that it also cleaves on either side of Asp residues and at Lys┼Arg. While more pH and temperature stable than porcine pepsin A, it is considerably less stable in urea or guanidine hydrochloride. It is the only known protein with such a stability profile.
Fibrolase is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
In the medical field of immunology, nanoCLAMP affinity reagents are recombinant 15 kD antibody mimetic proteins selected for tight, selective and gently reversible binding to target molecules. The nanoCLAMP scaffold is based on an IgG-like, thermostable carbohydrate binding module family 32 (CBM32) from a Clostridium perfringens hyaluronidase. The shape of nanoCLAMPs approximates a cylinder of approximately 4 nm in length and 2.5 nm in diameter, roughly the same size as a nanobody. nanoCLAMPs to specific targets are generated by varying the amino acid sequences and sometimes the length of three solvent exposed, adjacent loops that connect the beta strands making up the beta-sandwich fold, conferring binding affinity and specificity for the target.
References
- ↑ Hu, R. (2004). "Codon optimization, expression, and characterization of recombinant lumbrokinase in goat milk". Protein Expression and Purification. 37 (1): 83–8. doi:10.1016/j.pep.2004.05.018. PMID 15294284.
- 1 2 3 Mihara, Hisashi; Sumi, Hiroyuki; Yoneta, Tomoyuki; Mizumoto, Hideaki; Ikeda, Ryuzo; Seiki, Masao; Maruyama, Masugi (1991). "A novel fibrinolytic enzyme extracted from the earthworm, Lumbricus rubellus". The Japanese Journal of Physiology. 41 (3): 461–472. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.41.461 . PMID 1960890.
- ↑ Ge, T.; Sun, Z.; Fu, S.; Liang, G. (2005). "Cloning of thrombolytic enzyme (lumbrokinase) from earthworm and its expression in the yeast". Protein Expression and Purification. 42 (1): 20–8. doi:10.1016/j.pep.2005.04.005. PMID 15927482.