
Tiglath-Pileser III was the king of the Neo-Assyrian Empire from 745 BC to his death in 727. One of the most prominent and historically significant Assyrian kings, Tiglath-Pileser ended a period of Assyrian stagnation, introduced numerous political and military reforms and more than doubled the lands under Assyrian control. Because of the massive expansion and centralization of Assyrian territory and establishment of a standing army, some researchers consider Tiglath-Pileser's reign to mark the true transition of Assyria into an empire. The reforms and methods of control introduced under Tiglath-Pileser laid the groundwork for policies enacted not only by later Assyrian kings but also by later empires for millennia after his death.

Menua, also rendered Meinua or Minua, was the fifth known king of Urartu from c. 810 BC to approximately 786 BC. In Armenian, Menua is rendered as Menua. The name Menua may be connected etymologically to the Ancient Greek names Minos and Minyas.

Argishti I, was the sixth known king of Urartu, reigning from 786 BC to 764 BC. He founded the citadel of Erebuni in 782 BC, which is the present capital of Armenia, Yerevan. Alternate transliterations of the name include Argishtis, Argisti, Argišti, and Argishtish. Although the name is usually rendered as Argišti, some scholars argue that Argisti is the most likely pronunciation. This is due to the belief that the Urartians used the cuneiform symbol š to voice an s-sound, as opposed to representing the digraph sh.
Rusa I was a King of Urartu. He succeeded his father, king Sarduri II. His name is sometimes transliterated as Rusas or Rusha. He was known to Assyrians as Ursa and possibly Urzana. His birth name may have been Uedipri.

Muṣaṣir, in Urartian Ardini was an ancient city of Urartu, attested in Assyrian sources of the 9th and 8th centuries BC.

Erebuni Fortress is an Urartian fortified city, located in Yerevan, Armenia. It is 1,017 metres (3,337 ft) above sea level. It was one of several fortresses built along the northern Urartian border and was one of the most important political, economic and cultural centers of the vast kingdom. The name Yerevan itself is derived from Erebuni.
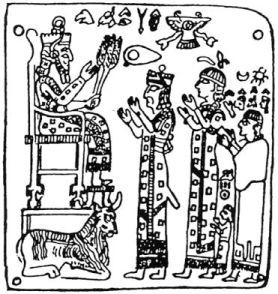
Ishpuini was king of Urartu. He succeeded his father, Sarduri I, who moved the capital to Tushpa (Van). Ishpuini conquered the Mannaean city of Musasir, which was then made the religious center of the empire. The main temple for the war god Haldi was in Musasir. Ishpuini's kingdom was then attacked by the forces of the Assyrian King Shamshi-Adad V. Ishpuini fought and defeated Shamshi-Adad. Ishpuini was so confident in his power that he began using names meaning everlasting glory, including, "King of the land of Nairi", "Glorious King", and "King of the Universe".
Sarduri I, also known as Sarduris, Sedur, and Asiduri, was a king of Urartu in Armenian Highlands. He was known as Ishtarduri to the Assyrians.

Argishti II was king of Urartu from 714 BC to 680 BC. He succeeded his father, King Rusa I. During the Urartu-Assyria War, Argishti was responsible for orchestrating major Urartian counter-offensives against the invading Assyrians. His forces drove the Assyrians back across the pre-war border and deep into the Assyrian heartlands, reconquering major towns and cities around Lake Urmia, including Mushashir, Ushnu, and Tepe, and conquering the territory as far south as the city of Nimrud on the Tigris River. These victories forced the Assyrians to accept a lengthy peace and cede large tracts of territory north of the Tigris. The remainder of Argishti's lengthy reign was characterized by a "Golden Age", a period of lengthy peace and economic prosperity, which carried into the reigns of Argishti's two successors, his son Rusa II and his grandson Sarduri III.

The Fortress of Van is a massive stone fortification built by the ancient kingdom of Urartu during the 9th to 7th centuries BC, and is the largest example of its kind. It overlooks the ruins of Tushpa, the ancient Urartian capital during the 9th century, which was centered upon the steep-sided bluff where the fortress now sits. A number of similar fortifications were built throughout the Urartian kingdom, usually cut into hillsides and outcrops in places where modern-day Armenia, Turkey and Iran meet. Successive groups such as the Medes, Achaemenids, Armenians, Parthians, Romans, Sassanid Persians, Byzantines, Arabs, Seljuks, Safavids, Afsharids, Ottomans and Russians each controlled the fortress at one time or another. The ancient fortress is located just west of Van and east of Lake Van in the Van Province of Turkey.

Tushpa was the 9th-century BC capital of Urartu, later becoming known as Van which is derived from Biainili, the native name of Urartu. The ancient ruins are located just west of Van and east of Lake Van in the Van Province of Turkey. In 2016 it was inscribed in the Tentative list of World Heritage Sites in Turkey.
Sarduri III was a king of Urartu between 639 BC and 635 BC.
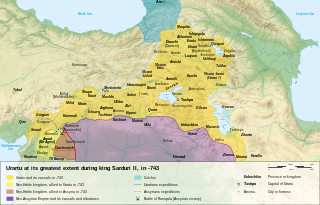
Sarduri II was a King of Urartu, succeeding his father Argishti I to the throne. The Urartian Kingdom was at its peak during his reign, campaigning successfully against several neighbouring powers, including Assyria.

Urartu was an Iron Age kingdom centered around Lake Van in the Armenian Highlands. It extended from the eastern bank of the upper Euphrates River to the western shores of Lake Urmia and from the mountains of northern Iraq to the Lesser Caucasus Mountains. Its kings left behind cuneiform inscriptions in the Urartian language, a member of the Hurro-Urartian language family. Since its re-discovery in the 19th century, Urartu, which is commonly believed to have been at least partially Armenian-speaking, has played a significant role in Armenian nationalism.

Sardurihinilli, also known as Haykaberd or Çavuştepe Kalesi, is an ancient Urartian fortified site located on a ridge on the northeastern edge of the village of Çavuştepe in the Gürpınar district of Van Province in eastern Turkey. It is located approximately 25 kilometers southeast of Van along the road leading to the city of Hakkâri, in a valley once known as Hayots Dzor in historic Armenia. It was founded by the Urartian king Sarduri II some time during his reign in the 8th century BC and is believed to be identical with the fortress of Sardurihurda mentioned in the same king's cuneiform inscriptions.
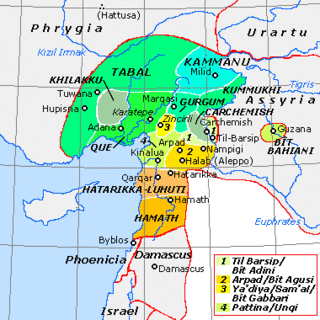
Kummuh was an Iron Age Neo-Hittite kingdom located on the west bank of the Upper Euphrates within the eastern loop of the river between Melid and Carchemish. Assyrian sources refer to both the land and its capital city by the same name. The city is identified with the classical-period Samosata, which has now been flooded under the waters of a newly built dam. Urartian sources refer to it as Kummaha. The name is also attested in at least one local royal inscription dating to the 8th century BCE. Other places that are mentioned in historical sources as lying within Kummuh are lands of Kištan and Halpi, and cities of Wita, Halpa, Parala, Sukiti and Sarita(?). Kummuh bordered the kingdoms of Melid to the north, Gurgum to the west and Carchemish to the south, while to the east it faced Assyria and later Urartu.

Argishtikhinili was a town in the ancient kingdom of Urartu, established during the expansion of the Urartians in the Transcaucasus under their king Argishti I, and named in his honour. It lasted between the 8th and 6th centuries BC. The ruins of the Argishtikhinili fortifications are 15 kilometres (9 mi) southwest of the present-day town of Armavir, Armenia, between the villages of Nor-Armavir and Armavir in the Armenian marz of Armavir. The town was founded on the left bank of the middle reaches of the Aras River. Over the centuries, the river channel has shifted to several kilometres south of the town.
Etiuni was the name of an early Iron Age tribal confederation in northern parts of Araxes River, roughly corresponding to the subsequent Ayrarat Province of the Kingdom of Armenia. Etiuni was frequently mentioned in the records of Urartian kings, who led numerous campaigns into Etiuni territory. It is very likely it was the "Etuna" or "Etina" which contributed to the fall of Urartu, according to Assyrian texts. Some scholars believe it had an Armenian-speaking population.

Erimena, according to tradition, was the twelfth king of Urartu and reigned from 625 to 605 BC. He was the successor of Sarduri III and father of Rusa III, who ruled Urartu from 610-590 B.C. Little is known about Erimena; his name was mentioned in an inscribed bronze shield found at Toprakkale by Hormuzd Rassam in 1880 that is now located in the British Museum. Erimena, according to a Babylonian chronicle, held an expedition in the mountainous region of Bit Hanounia, under the rule of Nabopolassar. He also suffered many attacks from the Babylonians which led to the decline of Urartu.














