
Czech, historically also Bohemian, is a West Slavic language of the Czech–Slovak group. Spoken by over 10 million people, it serves as the official language of the Czech Republic. Czech is closely related to Slovak, to the point of mutual intelligibility to a very high degree. Like other Slavic languages, Czech is a fusional language with a rich system of morphology and relatively flexible word order. Its vocabulary has been extensively influenced by Latin and German.

The Ides of March was a day in the Roman calendar that corresponds to 15 March. It was marked by several religious observances and was notable for the Romans as a deadline for settling debts. In 44 BC, it became notorious as the date of the assassination of Julius Caesar which made the Ides of March a turning point in Roman history.
In traditional grammar, a part of speech' is a category of words which have similar grammatical properties. Words that are assigned to the same part of speech generally display similar behavior in terms of syntax—they play similar roles within the grammatical structure of sentences—and sometimes in terms of morphology, in that they undergo inflection for similar properties.

Tages was a founding prophet of Etruscan religion who is known from reports by Latin authors of the late Roman Republic and Roman Empire. He revealed a cosmic view of divinity and correct methods of ascertaining divine will concerning events of public interest. Divination was undertaken in Roman society by priestly officials called haruspices. Political officials also, such as the augures, were constituted with some responsibilities for divination. While the religion flourished, these priests accompanied public officials, including generals in the field, and were consulted on everything of interest to the senate and people of Rome.
In Etruscan mythology, Tarchon and his brother, Tyrrhenus, were culture heroes who founded the Etruscan League of twelve cities, the Dodecapoli. One author, Joannes Laurentius Lydus, distinguishes two legendary persons named Tarchon, the Younger and his father, the Elder. It was the Elder who received the Etrusca Disciplina from Tages, whom he identifies as a parable. The Younger fought with Aeneas after his arrival in Italy. The elder was a haruspex, who learned his art from Tyrrhenus, and was probably the founder of Tarquinia and the Etruscan League. Lydus does not state that, but the connection was being made at least as long ago as George Dennis. Lydus had the advantage in credibility, even though late, of stating that he read the part of the Etrusca Disciplina about Tages and that it was a dialogue with Tarchon's lines in "the ordinary language of the Italians" and Tages' lines in Etruscan, which was difficult for him to read. He relied on translations.
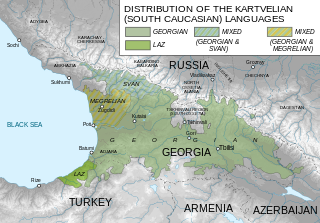
Georgian is a Kartvelian language spoken by Georgians. It is the official language of Georgia. Georgian is written in its own writing system, the Georgian script. Georgian is the literary language for all regional subgroups of Georgians, including those who speak other Kartvelian languages: Svans, Mingrelians and the Laz.
Apoplexy is bleeding within internal organs and the accompanying symptoms. For example, ovarian apoplexy is bleeding in the ovaries. The term formerly referred to what is now called a stroke; nowadays, health care professionals typically specify the type of apoplexy, such as cerebral, ovarian and pituitary apoplexy.

A powiat is the second-level unit of local government and administration in Poland, equivalent to a county, district or prefecture in other countries. The term "powiat" is most often translated into English as "county" or "district".

Kubaba is the only queen on the Sumerian King List, which states she reigned for 100 years – roughly in the Early Dynastic III period of Sumerian history. In later times, she was worshipped as a goddess.

Cytherean is an adjective meaning pertaining to Cythera, a small island now part of Greece, southeast of the Peloponnesus. It is also an adjective meaning pertaining to the planet Venus.
Priscian of Lydia, was one of the last of the Neoplatonists. Two works of his have survived.
Agapius was a Neoplatonist philosopher who lived in Athens. He was a notable philosopher in the Neoplatonist school in Athens when Marinus of Neapolis was scholarch after the death of Proclus. He was admired for his love of learning and for putting forward difficult problems.

Lida Castle was one of several citadels erected by Grand Duke Gediminas of Lithuania in the early 14th century to defend his lands against the expansion of the Teutonic Knights. Other links in this chain of defense included Hrodna, Navahrudak, Kreva, Medininkai, and Trakai. The modern town of Lida, Belarus grew up around this castle. Lida Castle is 141 metres (463 ft) above sea level.
Decanus means "chief of ten" in Late Latin. The term originated in the Roman army and became used thereafter for subaltern officials in the Byzantine Empire, as well as for various positions in the Church, whence derives the English title "dean".
The Ptoon Painter was an ancient Greek vase painter of black-figure style active in Athens in the middle third of the 6th century BC. His real name is unknown.
The Ptoon Painter predominantly painted ovoid neck amphorae, spherical '’hydriai’’ and Siana cups. His most distinguishing features are figural palmettes and striking black-and-red patterns on the wings of birds. Along with the Camtar Painter, he was one of the last painters to paint animal friezes. His work is considered of mediocre quality. He often used dotted rosettes for the backgrounds, a feature generally out of use at the time of his activity. The late date of his works is attested by certain details of his plant motifs and figures, which resemble the work of the Lydos Painter. His most famous work is the Hearst Hydria, on display in New York City.

Group E was a group of Attic vase painters of the black-figure style. They were active between 560 and 540 BC.
The BMN Painter was an Attic vase painter in the black-figure style, active during the third quarter of the 6th century BC.










