The M551 "Sheridan" AR/AAV was a light tank developed by the United States and named after General Philip Sheridan, of American Civil War fame. It was designed to be landed by parachute and to swim across rivers. It was armed with the technically advanced but troublesome M81/M81 Modified/M81E1 152 mm gun/launcher, which fired both conventional ammunition and the MGM-51 Shillelagh guided anti-tank missile.

The M2 machine gun or Browning .50 caliber machine gun is a heavy machine gun that was designed near the end of World War I by John Browning. While similar to Browning's M1919 Browning machine gun, which was chambered for the .30-06 cartridge, the M2 uses Browning's larger and more powerful .50 BMG cartridge. The design has had many designations; the official U.S. military designation for the infantry type is Browning Machine Gun, Cal. .50, M2, HB, Flexible. It has been used against infantry, light armored vehicles, watercraft, light fortifications, and low-flying aircraft.

The .50 BMG, also known as 12.7×99mm NATO, and designated as the 50 Browning by the C.I.P., is a .50 in (12.7 mm) caliber cartridge developed for the M2 Browning heavy machine gun in the late 1910s, entering official service in 1921. Under STANAG 4383, it is a standard service cartridge for NATO forces. The cartridge itself has been made in many variants: multiple generations of regular ball, tracer, armor-piercing (AP), incendiary, and saboted sub-caliber penetrator rounds. The rounds intended for machine guns are made into a continuous ammunition belt using metallic links.

The MBT-70 was an American–West German joint project to develop a new main battle tank during the 1960s.

The M60 is an American second-generation main battle tank (MBT). It was officially standardized as the Tank, Combat, Full Tracked: 105-mm Gun, M60 in March 1959. Although developed from the M48 Patton, the M60 tank series was never officially christened as a Patton tank. It has been called a "product-improved descendant" of the Patton tank's design. The design similarities are evident comparing the original version of the M60 and the M48A2. The United States fully committed to the MBT doctrine in 1963, when the Marine Corps retired the last (M103) heavy tank battalion. The M60 tank series became America's primary main battle tank during the Cold War, reaching a production total of 15,000 M60s. Hull production ended in 1983, but 5,400 older models were converted to the M60A3 variant ending in 1990.

The M60, officially the Machine Gun, Caliber 7.62 mm, M60, is a family of American general-purpose machine guns firing 7.62×51mm NATO cartridges from a disintegrating belt of M13 links. There are several types of ammunition approved for use in the M60, including ball, tracer, and armor-piercing rounds.

The M240 machine gun, officially the Machine Gun, 7.62 mm, M240, is the U.S. military designation for the FN MAG, a family of belt-fed, gas-operated medium machine guns that chamber the 7.62×51mm NATO cartridge.

The 75 mm gun, models M2 to M6, was the standard American medium caliber gun fitted to mobile platforms during World War II. They were primarily mounted on tanks, such as the M3 Lee and M4 Sherman, but one variant was also used as an air-to-ground gun on the B-25 Mitchell medium bomber aircraft. There were five main variants used during the war: M2, M3, M4, M5 and M6.

The 37 mm gun M3 is the first dedicated anti-tank gun fielded by United States forces in numbers. Introduced in 1940, it became the standard anti-tank gun of the U.S. infantry with its size enabling it to be pulled by a jeep. However, the continuing improvement of German tanks quickly rendered the 37 mm ineffective and, by 1943, it was being gradually replaced in the European and Mediterranean theaters by the more powerful British-developed 57 mm gun M1. In the Pacific, where the Japanese tank threat was less significant, the M3 remained in service until the end of the war, but some 57mm guns were issued.
Tank development both evolved considerably from World War II and played a key role during the Cold War (1947–1991). The period pitted the nations of the Eastern Bloc and the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) against each other.
The General Dynamics Land Systems (GDLS) M60-2000 or 120S was an upgrade of the M60 tank. The development of the M60-2000 was initiated primarily due to the large number of M60 main battle tanks in service with many Middle Eastern nations unable to afford a sufficient force of more modern main battle tanks. The upgrade was marketed at those M60 users with the industrial capability to convert the tanks themselves. The M60-2000/120S was a GDLS supplied conversion kit that married the turret of the M1A1 variant of the M1 Abrams to the M60A1 hull of the M60, offering many features of the M1A1 Abrams to existing M60 users at a reduced cost.

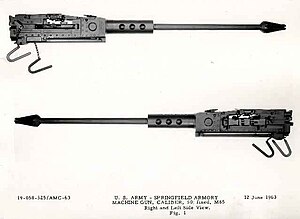
The M73 and M219 are 7.62 mm NATO caliber machine guns designed for tank use. It is no longer in use by NATO countries. They were used on the M48 Patton and M60 Patton MBT series, as well as the MBT-70 prototype vehicles, and on the M551 Sheridan Armored Reconnaissance/Airborne Assault Vehicle (AR/AAV). They were also used in a twin mount in the turret of the V-100 Commando (M706) light armored car during the Vietnam War.

The T92 Light Tank, or 76-mm Gun Tank, T92, was an American light tank developed in the 1950s by Aircraft Armaments. It was designed as an airborne/airdropped replacement for the heavier M41 Walker Bulldog while retaining the mobility, protection level, and firepower of the latter. The unveiling of the Soviet PT-76 amphibious light tank pointed out that the future US light tank should be able to swim as well. Making the T92 amphibious was deemed impractical and the light gun tank program was cancelled in June 1958.

The United States has produced tanks since their inception in World War I, up until the present day. While there were several American experiments in tank design, the first American tanks to see service were copies of French light tanks and a joint heavy tank design with the United Kingdom.

This article deals with the history and development of American tanks from the end of World War II and during the Cold War.

The M3 Bradley Cavalry Fighting Vehicle (CFV) is an American tracked armored reconnaissance vehicle manufactured by BAE Systems Platforms & Services. A member of the Bradley Fighting Vehicle family, the M3 CFV is used by heavy armored cavalry units in the United States Army.

The M2 Bradley, or Bradley IFV, is an American infantry fighting vehicle that is a member of the Bradley Fighting Vehicle family. It is manufactured by BAE Systems Land & Armaments and entered service in 1981, with fielding beginning in 1983.

The M1919 Browning is a .30 caliber medium machine gun that was widely used during the 20th century, especially during World War II, the Korean War, and the Vietnam War. The M1919 saw service as a light infantry, coaxial, mounted, aircraft, and anti-aircraft machine gun by the U.S and many other countries.

The M68 is an American 105 mm tank gun. It uses British-designed L7 gun tube and cartridges with an American-designed mount, breech assembly and recoil mechanism.