External links
- Object Management Group (OMG) website
- Object Management Group, MOF Model to Text Transformation Language (MOFM2T), 1.0 - Specification
MOF Model to Text Transformation Language (Mof2Text or MOFM2T) is an Object Management Group (OMG) specification for a model transformation language. Specifically, it can be used to express transformations which transform a model into text (M2T), for example a platform-specific model into source code or documentation. MOFM2T is one part of OMG's Model-driven architecture (MDA) and reuses many concepts of MOF, OMG's metamodeling architecture. Whereas MOFM2T is used for expressing M2T transformations, OMG's QVT is used for expressing M2M transformations.

The Unified Modeling Language (UML) is a general-purpose, developmental, modeling language in the field of software engineering that is intended to provide a standard way to visualize the design of a system.
The XML Metadata Interchange (XMI) is an Object Management Group (OMG) standard for exchanging metadata information via Extensible Markup Language (XML).

The Meta-Object Facility (MOF) is an Object Management Group (OMG) standard for model-driven engineering. Its purpose is to provide a type system for entities in the CORBA architecture and a set of interfaces through which those types can be created and manipulated. The official reference page may be found at OMG's website.
A platform-specific model is a model of a software or business system that is linked to a specific technological platform. Platform-specific models are indispensable for the actual implementation of a system.
Model Driven Architecture (MDA) is a software design approach for the development of software systems. It provides a set of guidelines for the structuring of specifications, which are expressed as models. Model Driven Architecture is a kind of domain engineering, and supports model-driven engineering of software systems. It was launched by the Object Management Group (OMG) in 2001.
The Object Constraint Language (OCL) is a declarative language describing rules applying to Unified Modeling Language (UML) models developed at IBM and is now part of the UML standard. Initially, OCL was merely a formal specification language extension for UML. OCL may now be used with any Meta-Object Facility (MOF) Object Management Group (OMG) meta-model, including UML. The Object Constraint Language is a precise text language that provides constraint and object query expressions on any MOF model or meta-model that cannot otherwise be expressed by diagrammatic notation. OCL is a key component of the new OMG standard recommendation for transforming models, the Queries/Views/Transformations (QVT) specification.
Given that metadata is a set of descriptive, structural and administrative data about a group of computer data, Java Metadata Interface is a platform-neutral specification that defines the creation, storage, access, lookup and exchange of metadata in the Java programming language.
The common warehouse metamodel (CWM) defines a specification for modeling metadata for relational, non-relational, multi-dimensional, and most other objects found in a data warehousing environment. The specification is released and owned by the Object Management Group, which also claims a trademark in the use of "CWM".
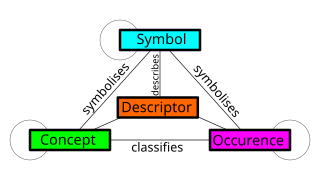
A metamodel or surrogate model is a model of a model, and metamodeling is the process of generating such metamodels. Thus metamodeling or meta-modeling is the analysis, construction and development of the frames, rules, constraints, models and theories applicable and useful for modeling a predefined class of problems. As its name implies, this concept applies the notions of meta- and modeling in software engineering and systems engineering. Metamodels are of many types and have diverse applications.
Model-driven engineering (MDE) is a software development methodology that focuses on creating and exploiting domain models, which are conceptual models of all the topics related to a specific problem. Hence, it highlights and aims at abstract representations of the knowledge and activities that govern a particular application domain, rather than the computing concepts.

ATL is a model transformation language and toolkit developed and maintained by OBEO and AtlanMod. It was initiated by the AtlanMod team. In the field of Model-Driven Engineering (MDE), ATL provides ways to produce a set of target models from a set of source models.
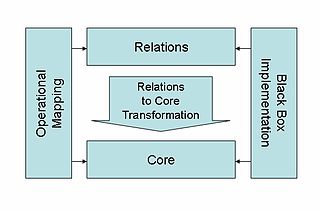
QVT (Query/View/Transformation) is a standard set of languages for model transformation defined by the Object Management Group.
A model transformation language in systems and software engineering is a language intended specifically for model transformation.
KM3 or Kernel Meta Meta Model is a neutral computer language to write metamodels and to define Domain Specific Languages. KM3 has been defined at INRIA and is available under the Eclipse platform.
The UML profile for Enterprise Distributed Object Computing (EDOC) is a standard of the Object Management Group in support of open distributed computing using model-driven architecture and service-oriented architecture. Its aim is to simplify the development of component based (EDOC) systems by providing a UML-based modeling framework conforming to the MDA of the OMG.
Tefkat is a Model Transformation Language and a model transformation engine. The language is based on F-logic and the theory of stratified logic programs. The engine is an Eclipse plug-in for the Eclipse Modeling Framework (EMF).
Knowledge Discovery Metamodel (KDM) is a publicly available specification from the Object Management Group (OMG). KDM is a common intermediate representation for existing software systems and their operating environments, that defines common metadata required for deep semantic integration of Application Lifecycle Management tools. KDM was designed as the OMG's foundation for software modernization, IT portfolio management and software assurance. KDM uses OMG's Meta-Object Facility to define an XMI interchange format between tools that work with existing software as well as an abstract interface (API) for the next-generation assurance and modernization tools. KDM standardizes existing approaches to knowledge discovery in software engineering artifacts, also known as software mining.
Architecture-driven modernization in computing and computer science, is the name of the initiative of the Object Management Group related to building and promoting standards that can be applied to modernize legacy systems. The objective of this initiative is to provide standard representations of views of existing systems, in order to enable common modernization activities, such as code analysis and comprehension, and software transformation.
The Semantics of Business Vocabulary and Business Rules (SBVR) is an adopted standard of the Object Management Group (OMG) intended to be the basis for formal and detailed natural language declarative description of a complex entity, such as a business. SBVR is intended to formalize complex compliance rules, such as operational rules for an enterprise, security policy, standard compliance, or regulatory compliance rules. Such formal vocabularies and rules can be interpreted and used by computer systems. SBVR is an integral part of the OMG's model-driven architecture (MDA).
The first version of the Enterprise Collaboration Architecture (ECA) has been published by the Object Management Group (OMG) in 2001. The vision of the (ECA) is to simplify the development of component based and services oriented systems by providing a modeling framework aligned with the model-driven architecture (MDA) of the Object Management Group (OMG).