
Singer Corporation is an American manufacturer of consumer sewing machines, first established as I. M. Singer & Co. in 1851 by Isaac M. Singer with New York lawyer Edward C. Clark. Best known for its sewing machines, it was renamed Singer Manufacturing Company in 1865, then the Singer Company in 1963. The global headquarters are based in Nashville, Tennessee. Its first large factory for mass production was built in 1863 in Elizabeth, New Jersey.

A centrifuge is a device that uses centrifugal force to subject a specimen to a specified constant force - for example, to separate various components of a fluid. This is achieved by spinning the fluid at high speed within a container, thereby separating fluids of different densities or liquids from solids. It works by causing denser substances and particles to move outward in the radial direction. At the same time, objects that are less dense are displaced and moved to the centre. In a laboratory centrifuge that uses sample tubes, the radial acceleration causes denser particles to settle to the bottom of the tube, while low-density substances rise to the top. A centrifuge can be a very effective filter that separates contaminants from the main body of fluid.
Rank Xerox Limited was formed in 1956 as a joint venture between the Xerox Corporation of United States and The Rank Organisation of the United Kingdom, to manufacture and market Xerox equipment initially in Europe and later in Africa and Asia. A further joint venture between Rank Xerox and Modi Group in India formed Modi Xerox to manufacture and sell Xerox equipment in the Indian subcontinent.

Agilent Technologies, Inc. is an American global company headquartered in Santa Clara, California, that provides instruments, software, services, and consumables for laboratories. Agilent was established in 1999 as a spin-off from Hewlett-Packard. The resulting IPO of Agilent stock was the largest in the history of Silicon Valley at the time. From 1999 to 2014, the company produced optics, semiconductors, EDA software and test and measurement equipment for electronics; that division was spun off to form Keysight. Since then, the company has continued to expand into pharmaceutical, diagnostics & clinical, and academia & government (research) markets.

A laboratory is a facility that provides controlled conditions in which scientific or technological research, experiments, and measurement may be performed. Laboratories are found in a variety of settings such as schools, universities, privately owned research institutions, corporate research and testing facilities, government regulatory and forensic investigation centers, physicians' offices, clinics, hospitals, regional and national referral centers, and even occasionally personal residences.

Sanyo Electric Co., Ltd. was a Japanese electronics manufacturer founded in 1947 by Toshio Iue, the brother-in-law of Kōnosuke Matsushita, the founder of Matsushita Electric Industrial, now known as Panasonic. Iue left Matsushita Electric to start his own business, acquiring some of its equipment to produce bicycle generator lamps. In 1950, the company was established. Sanyo began to diversify in the 1960s, having launched Japan's first spray-type washing machine in 1953. In the 2000s, it was known as one of the 3S along with Sony and Sharp. Sanyo also focused on solar cell and lithium battery businesses. In 1992, it developed the world's first hybrid solar cell, and in 2002, it had a 41% share of the global lithium-ion battery market. In its heyday in 2003, Sanyo had sales of about ¥2.5 trillion. However, it fell into a financial crisis as a result of its huge investment in the semiconductor business. In 2009, Sanyo was acquired by Panasonic, and in 2011, it was fully consolidated into Panasonic and its brand disappeared. The company still exists as a legal entity for the purpose of winding up its affairs.

The Škoda Works was one of the largest European industrial conglomerates of the 20th century. In 1859, Czech engineer Emil Škoda bought a foundry and machine factory in Plzeň, Bohemia, Austria-Hungary that had been established ten years previously, founding Škoda Works. By World War I, Škoda Works had become the largest arms manufacturer in Austria-Hungary, supplying the Austro-Hungarian army with mountain guns, mortars and machine guns, including the Škoda M1909, and the ships of the Austro-Hungarian navy with heavy guns. After the end of the war and the creation of the First Czechoslovak Republic, the company, previously focused on manufacturing of armaments, diversified and became a major manufacturer of locomotives, aircraft, ships, machine tools, steam turbines, equipment for power utilities, among other industrial products.

Bendix Corporation is an American manufacturing and engineering company which, during various times in its existence, made automotive brake shoes and systems, vacuum tubes, aircraft brakes, aeronautical hydraulics and electric power systems, avionics, aircraft and automobile fuel control systems, radios, televisions and computers.

Pye Ltd was an electronics company founded in 1896 in Cambridge, England, as a manufacturer of scientific instruments. The company merged with EKCO in 1960. Philips of the Netherlands acquired a majority shareholding in 1967, and later gained full ownership.

The Argent Centre is a Grade II* listed building on the corner of Frederick Street and Legge Road in the Jewellery Quarter of Birmingham, England.
Eppendorf, a company with its registered office in Germany, develops, produces and sells products and services for laboratories around the world.

Panasonic Electric Works Co., Ltd. is a Japanese company specializing in the production of industrial devices. It can trace its beginnings to a firm that was founded in 1918 by Konosuke Matsushita. Matsushita began making the flashlight components for bicycles, then progressed to making lighting fixtures.
Fisons plc was a British multinational pharmaceutical, scientific instruments and horticultural chemicals company headquartered in Ipswich, United Kingdom. It was listed on the London Stock Exchange and was once a constituent of the FTSE 100 Index. It was acquired by Rhone-Poulenc in 1995.
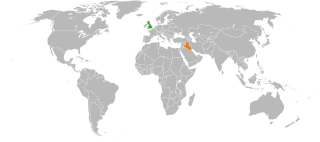
The United Kingdom supported Ba'athist Iraq as early as 1981 during the Iran–Iraq War by covertly providing military equipment and arms. Although officially neutral in the conflict, the United Kingdom made direct sales to both Iraq and Iran. With an embargo in effect various companies also supplied Iraq and Iran by shipping materials through third-party countries and from those countries to the belligerents. While some of this exporting was legal, permitted or tolerated by parliament, Iraqi clandestine procurement operations were especially active in Britain.
DRDC Toronto is a major military research station located at the former site of CFB Downsview in Toronto, Ontario, Canada. It is one of several centres making up Defence Research and Development Canada (DRDC).

Megger Group Limited is a British manufacturing company that manufactures electronic test equipment and measuring instruments for electrical power applications.

Norbar Torque Tools Ltd specialises in the manufacture and worldwide distribution of torque tools for torque tightening, measurement and calibration. The primary office and factory location is in Banbury, United Kingdom and there are also Norbar sales, service and calibration facilities in Australia, United States, New Zealand, Singapore, China and India.
ELGA LabWater is the laboratory water brand name of Veolia Water Solutions & Technologies. ELGA manufactures, supplies and services water purification systems for use in general, R&D, healthcare and clinical laboratories. Its offices and distributors are located in more than 60 countries.

Poulenc Frères was a French chemical, pharmaceutical and photographic supplies company that had its origins in a Paris pharmacy founded in 1827. From 1852 it began to manufacture photographic chemicals. It took the name Poulenc Frères in 1881, and by 1900 had a range of high-quality products. That year it went public as the Établissements Poulenc Frères. It began production of synthetic medicines, and continued to grow during World War I (1914–18). In 1928 it merged with the Société des usines chimiques du Rhône to form Rhône-Poulenc.














