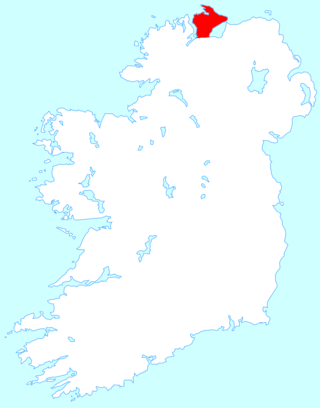
Inishowen is a peninsula in the north of County Donegal in Ireland. Inishowen is the largest peninsula on the island of Ireland.

Shornemead Fort is a now-disused artillery fort that was built in the 1860s to guard the entrance to the Thames from seaborne attack. Constructed during a period of tension with France, it stands on the south bank of the river at a point where the Thames curves sharply north and west, giving the fort long views up and downriver in both directions. It was the third fort constructed on the site since the 18th century, but its location on marshy ground led to major problems with subsidence. The fort was equipped for a time with a variety of large-calibre artillery guns which were intended to support two other nearby Thamesside forts. However, the extent of the subsidence meant that it became unsafe for the guns to be fired and the fort was disarmed by the early 20th century.

Fort Dunree is a coastal defence fortification located on the west side of the Inishowen peninsula, County Donegal, Ireland.

Lenan Head Fort, Lough Swilly, Inishowen, County Donegal was built in 1895, initially with three 9.2 inch Breech Loading (BL) guns. Following recommendations of the Owen Committee in 1905, it was refitted in 1911 with two newer Mark X 9.2 inch models. Both guns were operational during the First World War.

Ned's Point Fort is one of several Napoleonic batteries built along the shores of Lough Swilly in county Donegal, to defend the north west of Ireland. It was part of a scheme to fortify Lough Swilly and Lough Foyle against French Invasion during the Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars. It is situated on Ned's Point, near the once important naval town of Buncrana, and its current form largely dates to works completed between 1812 and 1813. It comprised a rectangular blockhouse mounting two guns and a supporting battery mounting four guns. The fort is surrounded by a ditch.

Lough Swilly in Ireland is a glacial fjord or sea inlet lying between the western side of the Inishowen Peninsula and the Fanad Peninsula, in County Donegal. Along with Carlingford Lough and Killary Harbour it is one of three glacial fjords in Ireland.

Fort Paull was a gun battery situated on the north bank of the Humber, near the village of Paull, downstream from Hull in northern England.

Following the establishment of the Irish Free State, three deep water Treaty Ports at Berehaven, Spike Island, and Lough Swilly were retained by the United Kingdom in accordance with the Anglo-Irish Treaty of 6 December 1921.

The Royal Horse Artillery (RHA) was formed in 1793 as a distinct arm of the Royal Regiment of Artillery to provide horse artillery support to the cavalry units of the British Army. Although the cavalry link remained part of its defining character, as early as the Battle of Waterloo the RHA was sometimes deployed more along the lines of conventional field artillery, fighting from comparatively fixed positions.

The Palmerston Forts are a group of forts and associated structures around the coasts of the United Kingdom and Ireland.

Rathmullan is a seaside village and townland on the Fanad Peninsula in County Donegal, Ireland. It is situated on the western shore of Lough Swilly, 11 kilometres (7 mi) north-east of Ramelton and 12 km (7 mi) east of Milford. Rathmullan was the point of departure during the Flight of the Earls in 1607, a major turning point in Irish history.
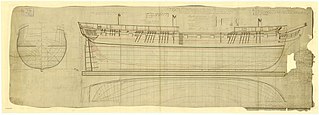
HMS Saldanha was a 36-gun fifth-rate Apollo-class frigate of the Royal Navy. She was commissioned in April 1810 and spent her entire career serving on the Irish Station, including capturing a fast-sailing French privateer on 11 October 1811. In the evening of 4 December that year Saldanha was serving off Lough Swilly when she was caught in a storm. Last seen sailing off Fanad Head, the ship was wrecked in a nearby bay with every person on board being killed and the only survivors being a parrot and a dog. The wreck was memorialised by Thomas Sheridan in his poem The Loss of the Saldanha.

The BL 6-inch gun Mark VII was a British naval gun dating from 1899, which was mounted on a heavy travelling carriage in 1915 for British Army service to become one of the main heavy field guns in the First World War, and also served as one of the main coast defence guns throughout the British Empire until the 1950s.

Camden Fort Meagher is a coastal defence fortification close to Crosshaven, County Cork, Ireland. Together with similar structures at Fort Mitchell, Fort Davis (Whitegate), and Templebreedy Battery, the fort was built to defend the mouth of Cork Harbour. Though originally constructed in the 16th century, the current structures of the fort date to the 1860s. Originally named Fort Camden and operated by the British Armed Forces, the fort was handed-over to the Irish Defence Forces in 1938. Renamed Fort Meagher in honour of Thomas Francis Meagher, it remained an Irish military installation until 1989 when the Irish Army handed the fort over to Cork County Council. It remained largely overgrown until 2010 when a group of local volunteers began restoration and development of the fort for heritage and tourism purposes. The fort was renamed Camden Fort Meagher and is now open seasonally to visitors, with exhibits on the fort's Brennan torpedo installation.

Fort Davis, is a coastal defence fortification close to Whitegate, County Cork, Ireland. Together with similar structures at Fort Mitchel, Fort Camden (Crosshaven), and Templebreedy Battery, the fort was built to defend the mouth of Cork Harbour. Though used as a fortification from the early 17th century, the current structures of the 74-acre site date primarily from the 1860s. Originally named Fort Carlisle and operated by the British Armed Forces, the fort was handed-over to the Irish Defence Forces in 1938, and renamed Fort Davis. The facility is owned by the Department of Defence, and is used as a military training site with no public access.

Cove Fort is a small bastioned land battery to the east of Cobh in County Cork, Ireland. Built as a coastal defence fortification in 1743, on instruction of the then Vice-Admiral of the Coast, it replaced a number of temporary coastal artillery batteries which defended Cork Harbour.

Grey Point Fort is a battery located at Helen's Bay on the south side of Belfast Lough. It was part of the defences of Belfast.
The Antrim Artillery was a part-time reserve unit of Britain's Royal Artillery based in County Antrim, Northern Ireland, from 1853 to 1919. It numbered 1st on the order of precedence of the Militia Artillery. Volunteers from the unit served in the Second Boer War. During World War I it defended Belfast Lough and trained gunners for service overseas. Subsequent units continued the Antrim Artillery traditions.

Inch Fort, Lough Swilly, Inishowen, County Donegal was built between 1812 and 1813, during the Napoleonic Wars. It had positions for nine guns, six in an open battery and a further three in a blockhouse. Following the peace in 1815, the defences of Lough Swilly were neglected.

Knockalla Fort is one of several Napoleonic batteries built along the shores of Lough Swilly in county Donegal, to defend the north west of Ireland. It was part of a scheme to fortify Lough Swilly and Lough Foyle against French Invasion during the Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars and was completed between 1812 and 1813. On the other side of the Lough is Fort Dunree. The fort was built on the site of a temporary fortification first built in 1798.




















