
Casablanca, located in the central-western part of Morocco and bordering the Atlantic Ocean, is the largest city in Morocco. It is also the largest city in the Maghreb region, as well as one of the largest and most important cities in Africa, both economically and demographically.
History of human habitation in Morocco spans since Lower Paleolithic, with the earliest known being Jebel Irhoud. Much later Morocco was part of Iberomaurusian culture, including Taforalt. It dates from the establishment of Mauretania and other ancient Berber kingdoms, to the establishment of the Moroccan state by the Idrisid dynasty followed by other Islamic dynasties, through to the colonial and independence periods.

Moroccan cuisine is influenced by Morocco's interactions and exchanges with other cultures and nations over the centuries. Moroccan cuisine is typically a mix of Berber, Arabic, Andalusian, and Mediterranean cuisines with slight European and sub-Saharan influences.

Marrakesh is a major city of the Kingdom of Morocco. It is the fourth largest city in the country, after Casablanca, Fez and Tangier. It is the capital city of the mid-southwestern region of Marrakesh-Safi. Located to the north of the foothills of the snow-capped Atlas Mountains, Marrakesh is situated 580 km (360 mi) southwest of Tangier, 327 km (203 mi) southwest of the Moroccan capital of Rabat, 239 km (149 mi) south of Casablanca, and 246 km (153 mi) northeast of Agadir.

Western Sahara is a disputed territory on the northwest coast and in the Maghreb region of North and West Africa, partially controlled by the self-proclaimed Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic and partially occupied by neighboring Morocco. Its surface area amounts to 266,000 square kilometres (103,000 sq mi). It is one of the most sparsely populated territories in the world, mainly consisting of desert flatlands. The population is estimated at just over 500,000, of which nearly 40% live in Laayoune, the largest city in Western Sahara.

Rabat is the capital city of Morocco and the country's seventh largest city with an urban population of approximately 580,000 (2014) and a metropolitan population of over 1.2 million. It is also the capital city of the Rabat-Salé-Kénitra administrative region.

Mohammed VI is the King of Morocco. He is a member of the Alaouite dynasty and ascended to the throne on 23 July 1999 upon the death of his father, King Hassan II.

King Hassan II was King of Morocco from 1961 until his death in 1999. He is descended from the Alaouite tribe. He was the eldest son of Mohammed V, Sultan, then King of Morocco (1909–1961), and his second wife, Lalla Abla bint Tahar (1909–1992). Hassan was known to be one of the most severe rulers of Morocco.

The Alaouite dynasty, or Alawite dynasty, is the current Moroccan royal family. The name Alaouite comes from the ‘Alī of ‘Alī ibn Abī Ṭālib, Muhammad's son-in-law and cousin, whose descendant Sharif ibn Ali became Prince of Tafilalt in 1631. His son Mulay Al-Rashid (1664–1672) was able to unite and pacify the country. The Alaouite family claim descent from the Islamic prophet Muhammad, through his daughter Fāṭimah az-Zahrah and her husband ‘Alī ibn Abī Ṭālib.

Spanish Sahara, officially the Overseas Province of the Spanish Sahara, was the name used for the modern territory of Western Sahara when it was occupied and ruled by Spain between 1884 and 1975. It had been one of the most recent acquisitions of the Spanish Empire as well as one of its last remaining holdings, which had once extended from the Americas to the Philippines and East Asia.

The French protectorate in Morocco, also known as French Morocco, was a territory established by the Treaty of Fez. It existed from 1912, when the protectorate was formally established, until independence and dissolution in 1956. It shared territory variously with the Spanish protectorate, established and dissolved the same years; its borders consisted of the area of Morocco between the "Corridor of Taza" and the Draa River, including sparse tribal lands, and the official capital was Rabat.

The Morocco national football team, nicknamed "Atlas Lions", is the national team of Morocco. It is managed by Hervé Renard.

The Spanish protectorate in Morocco was established on 27 November 1912 by a treaty between France and Spain that converted the Spanish sphere of influence in Morocco into a formal protectorate.

The Ifni War, sometimes called the Forgotten War in Spain, was a series of armed incursions into Spanish West Africa by Moroccan insurgents that began in October 1957 and culminated with the abortive siege of Sidi Ifni.

The Tangier American Legation is a building in the medina of Tangier, Morocco. The first American public property outside the United States, it commemorates the historic cultural and diplomatic relations between the United States and the Kingdom of Morocco. It is now officially called the Tangier American Legation Institute for Moroccan Studies, and is a cultural center, museum, and a research library, concentrating on Arabic language studies.

The Western Sahara conflict is an ongoing conflict between the Polisario Front and the Kingdom of Morocco. The conflict originated from an insurgency by the Polisario Front against Spanish colonial forces from 1973 to 1975 and the subsequent Western Sahara War against Morocco between 1975 and 1991. Today the conflict is dominated by unarmed civil campaigns of the Polisario Front and their self-proclaimed SADR state to gain fully recognized independence for Western Sahara.
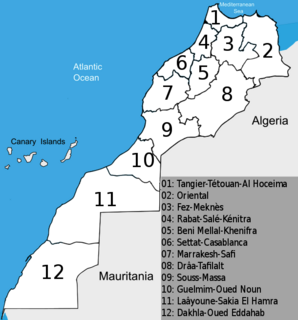
Regions are currently the highest administrative divisions in Morocco. Since 2015, Morocco officially administers 12 regions, including one that lies completely within the disputed territory of Western Sahara and two that lie partially within it. The regions are subdivided into a total of 75 second-order administrative divisions, which are prefectures and provinces.

The French conquest of Morocco took place in 1911 in the aftermath of the Agadir Crisis, when Moroccan forces besieged the French-occupied city of Fez. On 30 March 1912, Sultan Abdelhafid signed the Treaty of Fez, formally ceding Moroccan sovereignty to France, transforming Morocco into a protectorate of France. However, many regions remained in revolt until 1934, when Morocco was declared pacified, but, in several regions, French authority was maintained by cooperation with local chiefs and not by military strength.

The Sahrawi Republic, officially the Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic, is a partially recognized state that claims the non-self-governing territory of Western Sahara, but controls only the easternmost one-fifth of that territory. Until 1976, Western Sahara was known as Spanish Sahara, a Spanish colony.

















