Related Research Articles

Nuclear fusion is a reaction in which two or more atomic nuclei, combine to form one or more atomic nuclei and neutrons. The difference in mass between the reactants and products is manifested as either the release or absorption of energy. This difference in mass arises as a result of the difference in nuclear binding energy between the atomic nuclei before and after the fusion reaction. Nuclear fusion is the process that powers active or main-sequence stars and other high-magnitude stars, where large amounts of energy are released.

A fusor is a device that uses an electric field to heat ions to a temperature at which they undergo nuclear fusion. The machine induces a potential difference between two metal cages, inside a vacuum. Positive ions fall down this voltage drop, building up speed. If they collide in the center, they can fuse. This is one kind of an inertial electrostatic confinement device – a branch of fusion research.

A cyclotron is a type of particle accelerator invented by Ernest Lawrence in 1929–1930 at the University of California, Berkeley, and patented in 1932. A cyclotron accelerates charged particles outwards from the center of a flat cylindrical vacuum chamber along a spiral path. The particles are held to a spiral trajectory by a static magnetic field and accelerated by a rapidly varying electric field. Lawrence was awarded the 1939 Nobel Prize in Physics for this invention.
In particle physics, cyclotron radiation is electromagnetic radiation emitted by non-relativistic accelerating charged particles deflected by a magnetic field. The Lorentz force on the particles acts perpendicular to both the magnetic field lines and the particles' motion through them, creating an acceleration of charged particles that causes them to emit radiation as a result of the acceleration they undergo as they spiral around the lines of the magnetic field.

A linear particle accelerator is a type of particle accelerator that accelerates charged subatomic particles or ions to a high speed by subjecting them to a series of oscillating electric potentials along a linear beamline. The principles for such machines were proposed by Gustav Ising in 1924, while the first machine that worked was constructed by Rolf Widerøe in 1928 at the RWTH Aachen University. Linacs have many applications: they generate X-rays and high energy electrons for medicinal purposes in radiation therapy, serve as particle injectors for higher-energy accelerators, and are used directly to achieve the highest kinetic energy for light particles for particle physics.

Inertial electrostatic confinement, or IEC, is a class of fusion power devices that use electric fields to confine the plasma rather than the more common approach using magnetic fields found in magnetic confinement fusion (MCF) designs. Most IEC devices directly accelerate their fuel to fusion conditions, thereby avoiding energy losses seen during the longer heating stages of MCF devices. In theory, this makes them more suitable for using alternative aneutronic fusion fuels, which offer a number of major practical benefits and makes IEC devices one of the more widely studied approaches to fusion.

In nuclear physics and nuclear chemistry, a nuclear reaction is a process in which two nuclei, or a nucleus and an external subatomic particle, collide to produce one or more new nuclides. Thus, a nuclear reaction must cause a transformation of at least one nuclide to another. If a nucleus interacts with another nucleus or particle, they then separate without changing the nature of any nuclide, the process is simply referred to as a type of nuclear scattering, rather than a nuclear reaction.

Neutron generators are neutron source devices which contain compact linear particle accelerators and that produce neutrons by fusing isotopes of hydrogen together. The fusion reactions take place in these devices by accelerating either deuterium, tritium, or a mixture of these two isotopes into a metal hydride target which also contains deuterium, tritium or a mixture of these isotopes. Fusion of deuterium atoms results in the formation of a helium-3 ion and a neutron with a kinetic energy of approximately 2.5 MeV. Fusion of a deuterium and a tritium atom results in the formation of a helium-4 ion and a neutron with a kinetic energy of approximately 14.1 MeV. Neutron generators have applications in medicine, security, and materials analysis.

The Z Pulsed Power Facility, informally known as the Z machine or simply Z, is the largest high frequency electromagnetic wave generator in the world, operated by Sandia National Laboratories in Albuquerque, New Mexico.

Aneutronic fusion is any form of fusion power in which very little of the energy released is carried by neutrons. While the lowest-threshold nuclear fusion reactions release up to 80% of their energy in the form of neutrons, aneutronic reactions release energy in the form of charged particles, typically protons or alpha particles. Successful aneutronic fusion would greatly reduce problems associated with neutron radiation such as damaging ionizing radiation, neutron activation, reactor maintenance, and requirements for biological shielding, remote handling and safety.
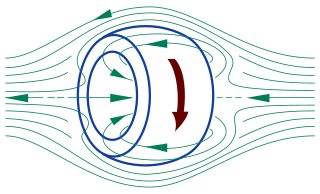
A field-reversed configuration (FRC) is a type of plasma device studied as a means of producing nuclear fusion. It confines a plasma on closed magnetic field lines without a central penetration. In an FRC, the plasma has the form of a self-stable torus, similar to a smoke ring.

The International Fusion Materials Irradiation Facility, also known as IFMIF, is a projected material testing facility in which candidate materials for the use in an energy producing fusion reactor can be fully qualified. IFMIF will be an accelerator-driven neutron source producing a high intensity fast neutron flux with a spectrum similar to that expected at the first wall of a fusion reactor using a deuterium-lithium nuclear reaction. The IFMIF project was started in 1994 as an international scientific research program, carried out by Japan, the European Union, the United States, and Russia, and managed by the International Energy Agency. Since 2007, it has been pursued by Japan and the European Union under the Broader Approach Agreement in the field of fusion energy research, through the IFMIF/EVEDA project, which conducts engineering validation and engineering design activities for IFMIF. The construction of IFMIF is recommended in the European Roadmap for Research Infrastructures Report, which was published by the European Strategy Forum on Research Infrastructures (ESFRI).
Neutral-beam injection (NBI) is one method used to heat plasma inside a fusion device consisting in a beam of high-energy neutral particles that can enter the magnetic confinement field. When these neutral particles are ionized by collision with the plasma particles, they are kept in the plasma by the confining magnetic field and can transfer most of their energy by further collisions with the plasma. By tangential injection in the torus, neutral beams also provide momentum to the plasma and current drive, one essential feature for long pulses of burning plasmas. Neutral-beam injection is a flexible and reliable technique, which has been the main heating system on a large variety of fusion devices. To date, all NBI systems were based on positive precursor ion beams. In the 1990s there has been impressive progress in negative ion sources and accelerators with the construction of multi-megawatt negative-ion-based NBI systems at LHD (H0, 180 keV) and JT-60U (D0, 500 keV). The NBI designed for ITER is a substantial challenge (D0, 1 MeV, 40 A) and a prototype is being constructed to optimize its performance in view of the ITER future operations. Other ways to heat plasma for nuclear fusion include RF heating, electron cyclotron resonance heating (ECRH), ion cyclotron resonance heating (ICRH), and lower hybrid resonance heating (LH).
Migma, sometimes migmatron or migmacell, was a proposed colliding beam fusion reactor designed by Bogdan Maglich in 1969. Migma uses self-intersecting beams of ions from small particle accelerators to force the ions to fuse. Similar systems using larger collections of particles, up to microscopic dust sized, were referred to as "macrons". Migma was an area of some research in the 1970s and early 1980s, but lack of funding precluded further development.
The polywell is a proposed design for a fusion reactor using an electric and magnetic field to heat ions to fusion conditions.

Solar energetic particles (SEP), formerly known as solar cosmic rays, are high-energy, charged particles originating in the solar atmosphere and solar wind. They consist of protons, electrons and heavy ions with energies ranging from a few tens of keV to many GeV. The exact processes involved in transferring energy to SEPs is a subject of ongoing study.
The Valkyrie is a theoretical spacecraft designed by Charles Pellegrino and Jim Powell. The Valkyrie is theoretically able to accelerate to 92% the speed of light and decelerate afterward, carrying a small human crew to another star system.

A particle accelerator is a machine that uses electromagnetic fields to propel charged particles to very high speeds and energies to contain them in well-defined beams. Small accelerators are used for fundamental research in particle physics. Accelerators are also used as synchrotron light sources for the study of condensed matter physics. Smaller particle accelerators are used in a wide variety of applications, including particle therapy for oncological purposes, radioisotope production for medical diagnostics, ion implanters for the manufacturing of semiconductors, and accelerator mass spectrometers for measurements of rare isotopes such as radiocarbon.
Colliding beam fusion (CBF), or colliding beam fusion reactor (CBFR), is a class of fusion power concepts that are based on two or more intersecting beams of fusion fuel ions that are independently accelerated to fusion energies using a variety of particle accelerator designs or other means. One of the beams may be replaced by a static target, in which case the approach is termed accelerator based fusion or beam-target fusion, but the physics is the same as colliding beams.
Heavy ion fusion is a fusion energy concept that uses a stream of high-energy ions from a particle accelerator to rapidly heat and compress a small pellet of fusion fuel. It is a subclass of the larger inertial confinement fusion (ICF) approach, replacing the more typical laser systems with an accelerator.
References
- ↑ Kirtley, David; Slough, John (2010). "Macron formed liner as a practical method for enabling magneto-inertial fusion". Journal of Fusion Energy. 29 (6): 561–566. Bibcode:2010JFuE...29..561K. doi:10.1007/s10894-010-9314-y. S2CID 20260462. Archived from the original on 12 July 2012. Retrieved 19 May 2012.