
Maduropeptin consists of a 1:1 complex of a carrier protein (MdpA) and a chromophore isolated from Actinomadura madurae . [1] The chromophore has an enediyne structure and is an antibiotic with anticancer activity.[ citation needed ]

Maduropeptin consists of a 1:1 complex of a carrier protein (MdpA) and a chromophore isolated from Actinomadura madurae . [1] The chromophore has an enediyne structure and is an antibiotic with anticancer activity.[ citation needed ]
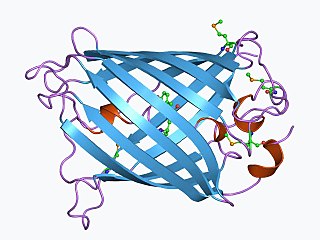
The green fluorescent protein (GFP) is a protein that exhibits bright green fluorescence when exposed to light in the blue to ultraviolet range. The label GFP traditionally refers to the protein first isolated from the jellyfish Aequorea victoria and is sometimes called avGFP. However, GFPs have been found in other organisms including corals, sea anemones, zoanithids, copepods and lancelets.
In organic chemistry, polyenes are poly-unsaturated, organic compounds that contain at least three alternating double and single carbon–carbon bonds. These carbon–carbon double bonds interact in a process known as conjugation, resulting in some unusual optical properties. Related to polyenes are dienes, where there are only two alternating double and single bonds.

A chromophore is the part of a molecule responsible for its color. The color that is seen by our eyes is the one not absorbed by the reflecting object within a certain wavelength spectrum of visible light. The chromophore is a region in the molecule where the energy difference between two separate molecular orbitals falls within the range of the visible spectrum. Visible light that hits the chromophore can thus be absorbed by exciting an electron from its ground state into an excited state. In biological molecules that serve to capture or detect light energy, the chromophore is the moiety that causes a conformational change in the molecule when hit by light.

The Masamune-Bergman cyclization or Masamune-Bergman reaction or Masamune-Bergman cycloaromatization is an organic reaction and more specifically a rearrangement reaction taking place when an enediyne is heated in presence of a suitable hydrogen donor. It is the most famous and well-studied member of the general class of cycloaromatization reactions. It is named for Japanese-American chemist Satoru Masamune and American chemist Robert G. Bergman. The reaction product is a derivative of benzene.

Neocarzinostatin (NCS) is a macromolecular chromoprotein enediyne antitumor antibiotic secreted by Streptomyces macromomyceticus.

The calicheamicins are a class of enediyne antitumor antibiotics derived from the bacterium Micromonospora echinospora, with calicheamicin γ1 being the most notable. It was isolated originally in the mid-1980s from the chalky soil, or "caliche pits", located in Kerrville, Texas. The sample was collected by a scientist working for Lederle Labs. It is extremely toxic to all cells and, in 2000, a CD33 antigen-targeted immunoconjugate N-acetyl dimethyl hydrazide calicheamicin was developed and marketed as targeted therapy against the non-solid tumor cancer acute myeloid leukemia (AML). A second calicheamicin-linked monoclonal antibody, inotuzumab ozogamicin an anti-CD22-directed antibody-drug conjugate, was approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration on August 17, 2017, for use in the treatment of adults with relapsed or refractory B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Calicheamicin γ1 and the related enediyne esperamicin are the two of the most potent antitumor agents known.

The esperamicins are chromoprotein enediyne antitumor antibiotics of bacterial origin. Esperamicin A1 is the most well studied compound in this class. Esperamcin A1 and the related enediyne calicheamicin are the two most potent antitumor agents known. The esperamicins are extremely toxic DNA splicing compounds.

In organic chemistry, enediynes are organic compounds containing two triple bonds and one double bond.
Micromonospora echinospora is a species of bacteria that is known for producing the enediyne antibiotic calicheamicins.

Echinomycin is a peptide antibiotic. It is a dimer of two peptides creating a cyclic structure. It contains a bicyclic aromatic chromophore that is attached to the dimerized cyclic peptide core and a thioacetal bridge. It intercalates into DNA at two specific sites, thereby blocking the binding of hypoxia inducible factor 1 alpha (HIF1alpha).

Dynemicin A is an anti-cancer enediyne drug. It displays properties which illustrate promise for cancer treatments, but still requires further research.
2-Amino-4-deoxychorismate dehydrogenase is an enzyme with systematic name (2S)-2-amino-4-deoxychorismate:FMN oxidoreductase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
2-amino-4-deoxychorismate synthase is an enzyme with systematic name (2S)-2-amino-4-deoxychorismate:2-oxoglutarate aminotransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Free radical damage to DNA can occur as a result of exposure to ionizing radiation or to radiomimetic compounds. Damage to DNA as a result of free radical attack is called indirect DNA damage because the radicals formed can diffuse throughout the body and affect other organs. Malignant melanoma can be caused by indirect DNA damage because it is found in parts of the body not exposed to sunlight. DNA is vulnerable to radical attack because of the very labile hydrogens that can be abstracted and the prevalence of double bonds in the DNA bases that free radicals can easily add to.

Kedarcidin is a chromoprotein antitumor antibiotic first isolated from an Actinomycete in 1992, comprising an ansa-bridged enediyne chromophore (shown) as well as an apoprotein that serves to stabilize the toxin in the Actinomycete. Like other members of the enediyne class of drugs—so named for the nine-or-ten-membered core structure bearing an alkene directly attached to two alkynyl appendages—kedarcidin was likely evolved to kill bacteria that compete with the producing organism. Because it achieves this by causing DNA damage, however, kedarcidin is capable of harming tumor cells, as well. Kedarcidin is thus the subject of scientific research, both for its structural complexity as well as its anticancer properties.

Pluramycin A is an antibiotic/anticancer compound that inhibits nucleic acid biosynthesis. The pluramycin family of natural products are an important group of complex C-aryl glycoside antibiotics that possess the tetracyclic 4H-anthra[1,2-b]pyran-4,7,12-trione moiety A–D as an aromatic core. The D-ring is adorned with two deoxyaminosugars that are appended by C-aryl glycosidic linkages. The E-ring sugar is angolosamine, a carbohydrate that is also found in the antibiotic angolamycin. The F-ring sugar is the N,N-dimethyl derivative of vancosamine, which is the sugar found in the glycopeptide antibiotic vancomycin.
Horst Prinzbach was a German chemist and professor emeritus.

First described in 1965, the moenomycins are a family of phosphoglycolipid antibiotics, metabolites of the bacterial genus Streptomyces. Moenomycin A is the founding member of the antibiotic family with the majority discovered by the end of the late 1970s.

C-1027 or Lidamycin is an antitumor antibiotic consisting of a complex of an enediyne chromophore and an apoprotein. It shows antibiotic activity against most Gram-positive bacteria. It is one of the most potent cytotoxic molecules known, due to its induction of a higher ratio of DNA double-strand breaks than single-strand breaks.
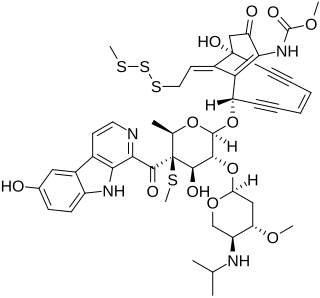
Shishijimicin A is an enediyne antibiotic isolated from Didemnum proliferum. Isolated in 2003 it is part of the family of 10 member ringed enediyne antitumor antibiotic agents, which includes: namenamicin, esperamicin and, calicheamicin. Due to its high potency from cytotoxicity, Shishjimicin A is currently undergoing testing as a possible Antibody-antibiotic Conjugate (ADCs) cancer treatment. Laboratory tests indicate it to be “more than 1,000 times as toxic to cancer cells as the anticancer drug taxol”, also known as Paclitaxel, a prevalent chemotherapy medication. As such, theoretically, only an administration of a minuscule dose of the molecule would be necessary per each treatment. As shishjimicin A supply is scarce and the full extent of its side effects is not yet established, there is still a need for further biological and clinical studies.