Related Research Articles

Neisseria is a large genus of bacteria that colonize the mucosal surfaces of many animals. Of the 11 species that colonize humans, only two are pathogens, N. meningitidis and N. gonorrhoeae.
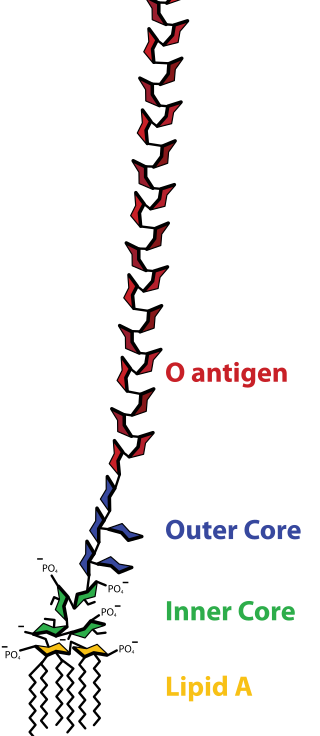
Lipopolysaccharides (LPS) are large molecules consisting of a lipid and a polysaccharide that are bacterial toxins. They are composed of an O-antigen, an outer core, and an inner core all joined by covalent bonds, and are found in the bacterial capsule, the outermost membrane of cell envelope of Gram-negative bacteria, such as E. coli and Salmonella. Today, the term endotoxin is often used synonymously with LPS, although there are a few endotoxins that are not related to LPS, such as the so-called delta endotoxin proteins produced by Bacillus thuringiensis.
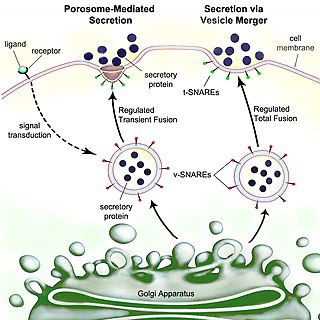
Secretion is the movement of material from one point to another, such as a secreted chemical substance from a cell or gland. In contrast, excretion is the removal of certain substances or waste products from a cell or organism. The classical mechanism of cell secretion is via secretory portals at the plasma membrane called porosomes. Porosomes are permanent cup-shaped lipoprotein structures embedded in the cell membrane, where secretory vesicles transiently dock and fuse to release intra-vesicular contents from the cell.

An enterotoxin is a protein exotoxin released by a microorganism that targets the intestines. They can be chromosomally or plasmid encoded. They are heat labile (>60⁰), of low molecular weight and water-soluble. Enterotoxins are frequently cytotoxic and kill cells by altering the apical membrane permeability of the mucosal (epithelial) cells of the intestinal wall. They are mostly pore-forming toxins, secreted by bacteria, that assemble to form pores in cell membranes. This causes the cells to die.
Adhesins are cell-surface components or appendages of bacteria that facilitate adhesion or adherence to other cells or to surfaces, usually in the host they are infecting or living in. Adhesins are a type of virulence factor.
Virulence factors are cellular structures, molecules and regulatory systems that enable microbial pathogens to achieve the following:
Diphtheria toxin is an exotoxin secreted mainly by Corynebacterium diphtheriae but also by Corynebacterium ulcerans and Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis, the pathogenic bacterium that causes diphtheria. The toxin gene is encoded by a prophage called corynephage β. The toxin causes the disease in humans by gaining entry into the cell cytoplasm and inhibiting protein synthesis.

CCAAT-enhancer-binding proteins is a family of transcription factors composed of six members, named from C/EBPα to C/EBPζ. They promote the expression of certain genes through interaction with their promoters. Once bound to DNA, C/EBPs can recruit so-called co-activators that in turn can open up chromatin structure or recruit basal transcription factors.
Adenylate cyclase toxin is a virulence factor produced by some members of the genus Bordetella. Together with the pertussis toxin it is the most important virulence factor of the causative agent of whooping cough, Bordetella pertussis. Bordetella bronchiseptica and Bordetella parapertussis, also able to cause pertussis-like symptoms, also produce adenylate cyclase toxin. It is a toxin secreted by the bacteria to influence the host immune system.
The AB5 toxins are six-component protein complexes secreted by certain pathogenic bacteria known to cause human diseases such as cholera, dysentery, and hemolytic–uremic syndrome. One component is known as the A subunit, and the remaining five components are B subunits. All of these toxins share a similar structure and mechanism for entering targeted host cells. The B subunit is responsible for binding to receptors to open up a pathway for the A subunit to enter the cell. The A subunit is then able to use its catalytic machinery to take over the host cell's regular functions.
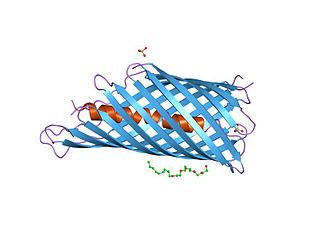
In molecular biology, an autotransporter domain is a structural domain found in some bacterial outer membrane proteins. The domain is always located at the C-terminal end of the protein and forms a beta-barrel structure. The barrel is oriented in the membrane such that the N-terminal portion of the protein, termed the passenger domain, is presented on the cell surface. These proteins are typically virulence factors, associated with infection or virulence in pathogenic bacteria.

Pathogenic bacteria are bacteria that can cause disease. This article focuses on the bacteria that are pathogenic to humans. Most species of bacteria are harmless and are often beneficial but others can cause infectious diseases. The number of these pathogenic species in humans is estimated to be fewer than a hundred. By contrast, several thousand species are part of the gut flora present in the digestive tract.
Clostridioides difficile toxin B (TcdB) is a cytotoxin produced by the bacteria Clostridioides difficile. It is one of two major kinds of toxins produced by C. difficile, the other being a related enterotoxin. Both are very potent and lethal.

The AB toxins are two-component protein complexes secreted by a number of pathogenic bacteria, though there is a pore-forming AB toxin found in the eggs of a snail. They can be classified as Type III toxins because they interfere with internal cell function. They are named AB toxins due to their components: the "A" component is usually the "active" portion, and the "B" component is usually the "binding" portion. The "A" subunit possesses enzyme activity, and is transferred to the host cell following a conformational change in the membrane-bound transport "B" subunit. These proteins consist of two independent polypeptides, which correspond to the A/B subunit moieties. The enzyme component (A) enters the cell through endosomes produced by the oligomeric binding/translocation protein (B), and prevents actin polymerisation through ADP-ribosylation of monomeric G-actin.
The RTX toxin superfamily is a group of cytolysins and cytotoxins produced by bacteria. There are over 1000 known members with a variety of functions. The RTX family is defined by two common features: characteristic repeats in the toxin protein sequences, and extracellular secretion by the type I secretion systems (T1SS). The name RTX refers to the glycine and aspartate-rich repeats located at the C-terminus of the toxin proteins, which facilitate export by a dedicated T1SS encoded within the rtx operon.

Streptococcal pyrogenic exotoxins also known as erythrogenic toxins, are exotoxins secreted by strains of the bacterial species Streptococcus pyogenes. SpeA and speC are superantigens, which induce inflammation by nonspecifically activating T cells and stimulating the production of inflammatory cytokines. SpeB, the most abundant streptococcal extracellular protein, is a cysteine protease. Pyrogenic exotoxins are implicated as the causative agent of scarlet fever and streptococcal toxic shock syndrome. There is no consensus on the exact number of pyrogenic exotoxins. Serotypes A-C are the most extensively studied and recognized by all sources, but others note up to thirteen distinct types, categorizing speF through speM as additional superantigens. Erythrogenic toxins are known to damage the plasma membranes of blood capillaries under the skin and produce a red skin rash. Past studies have shown that multiple variants of erythrogenic toxins may be produced, depending on the strain of S. pyogenes in question. Some strains may not produce a detectable toxin at all. Bacteriophage T12 infection of S. pyogenes enables the production of speA, and increases virulence.

In the field of molecular biology, enterotoxin type B, also known as Staphylococcal enterotoxin B (SEB), is an enterotoxin produced by the gram-positive bacteria Staphylococcus aureus. It is a common cause of food poisoning, with severe diarrhea, nausea and intestinal cramping often starting within a few hours of ingestion. Being quite stable, the toxin may remain active even after the contaminating bacteria are killed. It can withstand boiling at 100 °C for a few minutes. Gastroenteritis occurs because SEB is a superantigen, causing the immune system to release a large amount of cytokines that lead to significant inflammation.
Polymorphic toxins (PTs) are multi-domain proteins primarily involved in competition between bacteria but also involved in pathogenesis when injected in eukaryotic cells. They are found in all major bacterial clades.
Contact-dependent growth inhibition (CDI) is a phenomenon where a bacterial cell may deliver a polymorphic toxin molecule into neighbouring bacterial cells upon direct cell-cell contact, causing growth arrest or cell death.

Bacterial secretion systems are protein complexes present on the cell membranes of bacteria for secretion of substances. Specifically, they are the cellular devices used by pathogenic bacteria to secrete their virulence factors to invade the host cells. They can be classified into different types based on their specific structure, composition and activity. Generally, proteins can be secreted through two different processes. One process is a one-step mechanism in which proteins from the cytoplasm of bacteria are transported and delivered directly through the cell membrane into the host cell. Another involves a two-step activity in which the proteins are first transported out of the inner cell membrane, then deposited in the periplasm, and finally through the outer cell membrane into the host cell.
References
- ↑ Jamet, Anne; Jousset, Agnès B.; Euphrasie, Daniel; Mukorako, Paulette; Boucharlat, Alix; Ducousso, Alexia; Charbit, Alain; Nassif, Xavier (2015-01-01). "A new family of secreted toxins in pathogenic Neisseria species". PLOS Pathogens. 11 (1): e1004592. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1004592 . ISSN 1553-7374. PMC 4287609 . PMID 25569427.
- ↑ Arenas, Jesús; de Maat, Vincent; Catón, Laura; Krekorian, Massis; Herrero, Juan Cruz; Ferrara, Flavio; Tommassen, Jan (2015-08-05). "Fratricide activity of MafB protein of N. meningitidis strain B16B6". BMC Microbiology. 15: 156. doi: 10.1186/s12866-015-0493-6 . ISSN 1471-2180. PMC 4524018 . PMID 26242409.