
Chad is one of the 47 landlocked countries in the world and is located in North Central Africa, measuring 1,284,000 square kilometers (495,755 sq mi), nearly twice the size of France and slightly more than three times the size of California. Most of its ethnically and linguistically diverse population lives in the south, with densities ranging from 54 persons per square kilometer in the Logone River basin to 0.1 persons in the northern B.E.T. (Borkou-Ennedi-Tibesti) desert region, which itself is larger than France. The capital city of N'Djaména, situated at the confluence of the Chari and Logone Rivers, is cosmopolitan in nature, with a current population in excess of 700,000 people.

Lake Chad is an endorheic freshwater lake located at the junction of boundaries of Nigeria, Niger, Chad, and Cameroon in western and central Africa respectively. It is also an important wetland ecosystem in West Africa. The catchment area of Lake Chad is 1 million square kilometres (390,000 sq mi). In the 19th century, Lake Chad was substantially larger with an area of 28,000 square kilometres (11,000 sq mi). However, due to climate change and human water diversion, Lake Chad has been greatly reduced since the mid-1970s, and its area has fluctuated between 2,000 and 5,000 square kilometres.

Lake Nyos is a crater lake in the Northwest Region of Cameroon, located about 315 km (196 mi) northwest of Yaoundé, the capital. Nyos is a deep lake high on the flank of an inactive volcano in the Oku volcanic plain along the Cameroon line of volcanic activity. A volcanic dam impounds the lake waters.

The Logon or Logone River is a major tributary of the Chari River. The Logone's sources are located in the western Central African Republic, northern Cameroon, and southern Chad. It has two major tributaries: the Pendé River in the prefecture Ouham-Pendé in the Central African Republic and the Mbéré River at the east of Cameroon. Many swamps and wetlands surround the river.

Hartbeespoort Dam is an arch type dam situated in the North West Province of South Africa. It lies in a valley to the south of the Magaliesberg mountain range and north of the Witwatersberg mountain range, about 35 kilometres north west of Johannesburg and 20 kilometres west of Pretoria. The name of the dam means "dam at the gorge of the hartebeest" in Afrikaans. This "poort" in the Magaliesberg was a popular spot for hunters, where they cornered and shot the hartebeest. The dam was originally designed for irrigation, which is currently its primary use, as well as for domestic and industrial use. The dam has suffered from a hypertrophic state since the early 1970s. Mismanagement of waste water treatment from urban zones within the Hartbeespoort Dam catchment area is largely to blame, having distorted the food web with over 280 tons of phosphate and nitrate deposits.
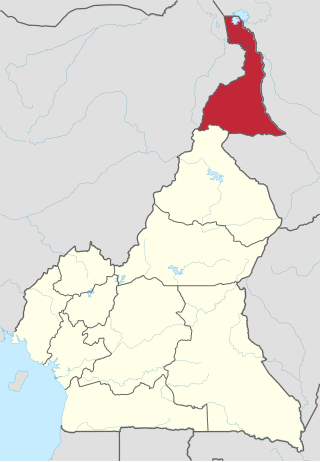
The Far North Region, also known as the Extreme North Region, is the northernmost and most populous constituent province of the Republic of Cameroon. It borders the North Region to the south, Chad to the east, and Nigeria to the west. The capital is Maroua.

A reservoir is an enlarged lake behind a dam. Such a dam may be either artificial, usually built to store fresh water, or it may be a natural formation.

Waza National Park is a national park in the Department of Logone-et-Chari, in Far North Region, Cameroon. It was founded in 1934 as a hunting reserve, and covers a total of 1,700 km2 (660 sq mi). Waza achieved national park status in 1968, and became a UNESCO biosphere reserve in 1979.

Thippagondanahalli Reservoir, also known as T G Halli Dam or Chamarajasagara, is located at the confluence of the Arkavathy and Kumudavathi rivers, 35 kilometres (22 mi) west of Bangalore, India. It is used by the Bangalore Water Supply and Sewerage Board as a major source of drinking water for western Bangalore. The lake is a man-made reservoir, created by the building of a dam which was inaugurated in 1933. M. Visvesvaraya supervised the construction work.

A volcanic dam is a type of natural dam produced directly or indirectly by volcanism, which holds or temporarily restricts the flow of surface water in existing streams, like a man-made dam. There are two main types of volcanic dams, those created by the flow of molten lava, and those created by the primary or secondary deposition of pyroclastic material and debris. This classification generally excludes other, often larger and longer lived dam-type geologic features, separately termed crater lakes, although these volcanic centers may be associated with the source of material for volcanic dams, and the lowest portion of its confining rim may be considered as such a dam, especially if the lake level within the crater is relatively high.
Perseverance Creek Dam is a reservoir in Crows Nest, Toowoomba Region, Queensland, Australia. It creates Lake Perseverance which is the second largest and the second oldest reservoir of Toowoomba city's three water supply dams. The other two storages used for Toowoomba are Cooby Dam and Cressbrook Dam which is located downstream of Perseverance.

Tims Ford Lake is a reservoir run by the Tennessee Valley Authority (TVA) in southern middle Tennessee. The lake encompasses 10,700 acres and approximately 250 miles of shoreline.

The Tiga Dam is located in southern part of Kano State in the Northwest of Nigeria, constructed in 1971–1974. It is a major reservoir on the Kano River, the main tributary of the Hadejia River. The dam was built during the administration of Governor Audu Bako in an attempt to improve food security through irrigation projects.

The Challawa Gorge Dam is in Karaye Local Government Area of Kano State in the Northwest of Nigeria, about 90 km southwest of Kano city. It is a major reservoir on the Challawa River, a tributary of the Kano River, which is the main tributary of the Hadejia River.

The Crocodile River is a river in South Africa. At its confluence with the Marico River, the Limpopo River is formed.
The Lake Chad replenishment project is a proposed major water diversion scheme to divert water from the Congo River basin to Lake Chad to prevent it drying up. Various versions have been proposed. Most would involve damming some of the right tributaries of the Congo River and channeling some of the water to Lake Chad via a canal to the Chari River basin.
Musgu is a cluster of closely related language varieties of the Biu–Mandara subgroup of the Chadic languages spoken in Cameroon and Chad. The endonym is Mulwi. Blench (2006) classifies the three varieties as separate languages. Speakers of the extinct related language Muskum have switched to one of these.
The Yaéré, from Fula yaayre, is the name of a vast annually-flooded grassland and savanna, part of the extensive floodplains around the shallow and variable Lake Chad in Central Africa. The Yaéré is part of the Lake Chad flooded savanna ecoregion.
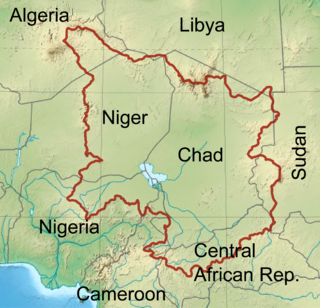
The Chad Basin is the largest endorheic basin in Africa, centered approximately on Lake Chad. It has no outlet to the sea and contains large areas of semi-arid desert and savanna. The drainage basin is approximately coterminous with the sedimentary basin of the same name, but extends further to the northeast and east.
Wixom Lake was a reservoir in the U.S. state of Michigan from 1925 to 2020. It was named after Frank Wixom, who was instrumental in building the Edenville Dam. Unusual for its size, Wixom Lake boasts a lighthouse on Musselman Island. From 2019 to 2020, an agreement to buy the dam and reservoir by the Four Lakes Task Force, a "county-delegated authority" under the State of Michigan, from Boyce Hydro L.L.C. was in place, However, in May 2020, the lake was destroyed when part of the earthen dam used to impound it collapsed. From 2018 to 2020, the impoundment was regulated by the Michigan Department of Environment, Great Lakes, and Energy (EGLE).
















