Related Research Articles

Magnesium sulfate or magnesium sulphate is a chemical compound, a salt with the formula MgSO4, consisting of magnesium cations Mg2+ (20.19% by mass) and sulfate anions SO2−4. It is a white crystalline solid, soluble in water but not in ethanol.

Lidocaine, also known as lignocaine and sold under the brand name Xylocaine among others, is a local anesthetic of the amino amide type. It is also used to treat ventricular tachycardia. When used for local anaesthesia or in nerve blocks, lidocaine typically begins working within several minutes and lasts for half an hour to three hours. Lidocaine mixtures may also be applied directly to the skin or mucous membranes to numb the area. It is often used mixed with a small amount of adrenaline (epinephrine) to prolong its local effects and to decrease bleeding.

Seborrhoeic dermatitis is a long-term skin disorder. Symptoms include flaky, scaly, greasy, and occasionally itchy and inflamed skin. Areas of the skin rich in oil-producing glands are often affected including the scalp, face, and chest. It can result in social or self-esteem problems. In babies, when the scalp is primarily involved, it is called cradle cap. Seborrhoeic dermatitis of the scalp may be described in lay terms as dandruff due to the dry, flaky character of the skin. However, as dandruff may refer to any dryness or scaling of the scalp, not all dandruff is seborrhoeic dermatitis. Seborrhoeic dermatitis is sometimes inaccurately referred to as seborrhoea.
Iontophoresis is a process of transdermal drug delivery by use of a voltage gradient on the skin. Molecules are transported across the stratum corneum by electrophoresis and electroosmosis and the electric field can also increase the permeability of the skin. These phenomena, directly and indirectly, constitute active transport of matter due to an applied electric current. The transport is measured in units of chemical flux, commonly μmol/(cm2×hour). Iontophoresis has experimental, therapeutic and diagnostic applications.

A transdermal patch is a medicated adhesive patch that is placed on the skin to deliver a specific dose of medication through the skin and into the bloodstream. An advantage of a transdermal drug delivery route over other types of medication delivery is that the patch provides a controlled release of the medication into the patient, usually through either a porous membrane covering a reservoir of medication or through body heat melting thin layers of medication embedded in the adhesive. The main disadvantage to transdermal delivery systems stems from the fact that the skin is a very effective barrier; as a result, only medications whose molecules are small enough to penetrate the skin can be delivered by this method. The first commercially available prescription patch was approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration in December 1979. These patches administered scopolamine for motion sickness.
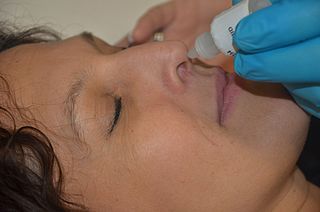
A topical medication is a medication that is applied to a particular place on or in the body. Most often topical medication means application to body surfaces such as the skin or mucous membranes to treat ailments via a large range of classes including creams, foams, gels, lotions, and ointments. Many topical medications are epicutaneous, meaning that they are applied directly to the skin. Topical medications may also be inhalational, such as asthma medications, or applied to the surface of tissues other than the skin, such as eye drops applied to the conjunctiva, or ear drops placed in the ear, or medications applied to the surface of a tooth. The word topical derives from Greek τοπικόςtopikos, "of a place".

A nicotine patch is a transdermal patch that releases nicotine into the body through the skin. It is used in nicotine replacement therapy (NRT), a process for smoking cessation. Endorsed and approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), it is considered one of the safer NRTs available for the treatment of tobacco use disorder.

Lotion is a low-viscosity topical preparation intended for application to the skin. By contrast, creams and gels have higher viscosity, typically due to lower water content. Lotions are applied to external skin with bare hands, a brush, a clean cloth, or cotton wool.

Calcium gluconate is the calcium salt of gluconic acid and is used as a mineral supplement and medication. As a medication it is used by injection into a vein to treat low blood calcium, high blood potassium, and magnesium toxicity. Supplementation is generally only required when there is not enough calcium in the diet. Supplementation may be done to treat or prevent osteoporosis or rickets. It can also be taken by mouth but is not recommended for injection into a muscle.

The human skin is the outer covering of the body and is the largest organ of the integumentary system. The skin has up to seven layers of ectodermal tissue guarding muscles, bones, ligaments and internal organs. Human skin is similar to most of the other mammals' skin, and it is very similar to pig skin. Though nearly all human skin is covered with hair follicles, it can appear hairless. There are two general types of skin: hairy and glabrous skin (hairless). The adjective cutaneous literally means "of the skin".
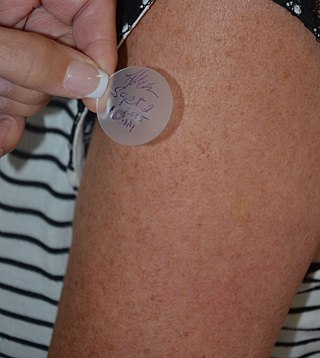
Transdermal is a route of administration wherein active ingredients are delivered across the skin for systemic distribution. Examples include transdermal patches used for medicine delivery. The drug is administered in the form of a patch or ointment that delivers the drug into the circulation for systemic effect.

Liquid paraffin, also known as paraffinum liquidum, paraffin oil, liquid paraffin oil or Russian mineral oil, is a very highly refined mineral oil used in cosmetics and medicine. Cosmetic or medicinal liquid paraffin should not be confused with the paraffin used as a fuel. The generic sense of paraffin meaning alkane led to regional differences for the meanings of both paraffin and paraffin oil. It is a transparent, colorless, nearly odorless, and oily liquid that is composed of saturated hydrocarbons derived from petroleum.

Samir Mitragotri is an Indian American professor at Harvard University, an inventor, an entrepreneur, and a researcher in the fields of drug delivery and biomaterials. He is currently the Hiller Professor of Bioengineering and Hansjörg Wyss Professor of Biologically Inspired Engineering at Harvard John A. Paulson School of Engineering and Applied Sciences and the Wyss Institute for Biologically Inspired Engineering. Prior to 2017, he was the Duncan and Suzanne Mellichamp Chair Professor at University of California, Santa Barbara.
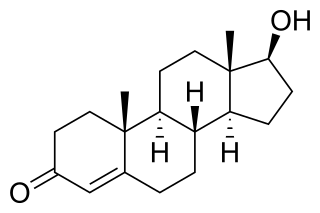
Testosterone (T) is a medication and naturally occurring steroid hormone. It is used to treat male hypogonadism, gender dysphoria, and certain types of breast cancer. It may also be used to increase athletic ability in the form of doping. It is unclear if the use of testosterone for low levels due to aging is beneficial or harmful. Testosterone can be used as a gel or patch that is applied to the skin, injection into a muscle, tablet that is placed in the cheek, or tablet that is taken by mouth.

Estradiol (E2) is a medication and naturally occurring steroid hormone. It is an estrogen and is used mainly in menopausal hormone therapy and to treat low sex hormone levels in women. It is also used in hormonal birth control for women, in feminizing hormone therapy for transgender women, and in the treatment of hormone-sensitive cancers like prostate cancer in men and breast cancer in women, among other uses. Estradiol can be taken by mouth, held and dissolved under the tongue, as a gel or patch that is applied to the skin, in through the vagina, by injection into muscle or fat, or through the use of an implant that is placed into fat, among other routes.

Magnesium sulfate as a medication is used to treat and prevent low blood magnesium and seizures in women with eclampsia. It is also used in the treatment of torsades de pointes, severe asthma exacerbations, constipation, and barium poisoning. It is given by injection into a vein or muscle as well as by mouth. As epsom salts, it is also used for mineral baths.

The pharmacology of estradiol, an estrogen medication and naturally occurring steroid hormone, concerns its pharmacodynamics, pharmacokinetics, and various routes of administration.

The pharmacokinetics of progesterone, concerns the pharmacodynamics, pharmacokinetics, and various routes of administration of progesterone.

The pharmacology of testosterone, an androgen and anabolic steroid (AAS) medication and naturally occurring steroid hormone, concerns its pharmacodynamics, pharmacokinetics, and various routes of administration.

Topical cream formulation is an emulsion semisolid dosage form that is used for skin external application. Most of the topical cream formulations contain more than 20 per cent of water and volatiles and/or less than 50 per cent of hydrocarbons, waxes, or polyethylene glycols as the vehicle for external skin application. In a topical cream formulation, ingredients are dissolved or dispersed in either a water-in-oil (W/O) emulsion or an oil-in-water (O/W) emulsion. The topical cream formulation has a higher content of oily substance than gel, but a lower content of oily ingredient than ointment. Therefore, the viscosity of topical cream formulation lies between gel and ointment. The pharmacological effect of the topical cream formulation is confined to the skin surface or within the skin. Topical cream formulation penetrates through the skin by transcellular route, intercellular route, or trans-appendageal route. Topical cream formulation is used for a wide range of diseases and conditions, including atopic dermatitis (eczema), psoriasis, skin infection, acne, and wart. Excipients found in a topical cream formulation include thickeners, emulsifying agents, preservatives, antioxidants, and buffer agents. Steps required to manufacture a topical cream formulation include excipient dissolution, phase mixing, introduction of active substances, and homogenization of the product mixture.
References
- ↑ Criscuolo, Giulia (October 2011). "Transdermal Magnesium". #76. The South African Journal of Natural Medicine. Archived from the original on January 15, 2015. Retrieved 22 January 2015.
- ↑ Werner, T.; Weidner, M.; Vormann, J. (2017). "Transdermal magnesium--myth or reality?". Journal of the Australian Traditional-Medicine Society. 23 (4). Retrieved 16 May 2022.
- ↑ Gröber U, Werner T, Vormann J, Kisters K (July 2017). "Myth or Reality-Transdermal Magnesium?". Nutrients. 9 (8): 813. doi: 10.3390/nu9080813 . PMC 5579607 . PMID 28788060.