
Muhammad Ahmad was a Nubian Sufi religious leader of the Samaniyya order in Sudan who, as a youth, studied Sunni Islam. In 1881, he claimed to be the Mahdi, and led a successful war against Ottoman-Egyptian military rule in Sudan and achieved a remarkable victory over the British, in the siege of Khartoum. He created a vast Islamic state extending from the Red Sea to Central Africa, and founded a movement that remained influential in Sudan a century later.
The Battle of Umm Diwaykarat on 25 November 1899 marked the final defeat of the Mahdist State in Sudan, when Anglo-Egyptian forces under the command of Lord Kitchener defeated what was left of the Mahdist armies under the command of the Abdallahi ibn Muhammad, known as the Khalifa, after the equally disastrous Battle of Omdurman a year earlier.

Abdullah Ibn-Mohammed Al-Khalifa or Abdullah al-Khalifa or Abdallahi al-Khalifa, also known as "The Khalifa" was a Sudanese Ansar ruler who was one of the principal followers of Muhammad Ahmad. Ahmad claimed to be the Mahdi, building up a large following. After Ahmad's death, Abdullah Ibn-Mohammed took over the movement, adopting the title of Khalifat al-Mahdi. He attempted to create a kingdom, which led to widespread discontent, and his eventual defeat and death at the hands of the British and Egyptians.
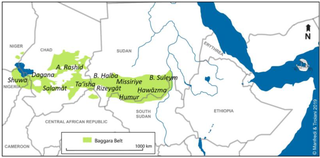
Ta'isha, or Ta'aisha, or Taaisha, one of a series of Arabic-speaking groups collectively called Baggara "cattle people", who live in Sudan, across southern Kordofan, Darfur, as well as Chad. The Ta'aisha tribal homeland is in the far southwest of Darfur, neighbouring to the east the Habbaniya, with whom they are closely related. The Ta'aisha rose to power when one of the members of their tribe, Abdallahi ibn Muhammad, later known as the Khalifa, became an early follower of Muhammad Ahmad, who would later become the Sudanese Mahdi. During the revolution, 'Abdallahi became the strongman of the movement and was designated as senior Khalifa by the Mahdi. Following the Mahdi's death in June 1885, the Khalifa 'Abdallahi ruled the Mahdist state until its destruction by an Anglo-Egyptian army. The Khalifa during his rule brought his tribe to Central Sudan and he went on to make extensive use of his relatives and other fellow Ta'a'isha as soldiers and administrators. Throughout the Mahdist period there was constant tension between the Ta'aisha leaders and the riverain Sudanese. Several Ta'aisha amirs who survived the Mahdiyya became prominent at the re-established Darfur Sultanate of Ali Dinar, one being Arabi Dafallah, who was appointed commander of the Equatorial province with its headquarters at Rejaf under the Khalifa's rule. Having been forced in 1897 to evacuate Equatoria by Belgians advancing from the Congo, he had made his way into southern Darfur where he faced Anglo-Egyptian forces and friendly tribes sent by Kitchener in pursuit of him. He then settled in the area of the present Central African Republic-Darfur border where he came into contact with encroaching French colonial power. After an unsuccessful attack on French outposts in the region he surrendered to Sultan 'Ali Dinar with his men and their arms in 1902, he subsequently lived in Al-Fashir and took part in many of the Sultan's military expeditions. Another one was 'Ali al-Sanusi, who was a Mahdist amir under Mahmud Ahmad in Atbara and fought at Karari after which he escaped to Darfur to be one of 'Ali Dinar's best generals. Under the British colonial rule, He was appointed Nazir of the Ta'aisha in Darfur and rendered valuable service to the new administration.

Mahdism in the Twelver branch of Shia Islam, derived from the belief in the reappearance of the Twelfth Shiite Imam, Muhammad al-Mahdi as the savior of the apocalypse for the salvation of human beings and the establishment of peace and justice. Mahdism is a kind of messianism. From this perspective, it is believed that Jesus Christ and Khidr are still alive and will emerge with Muhammad al-Mahdi in order to fulfil their mission of bringing peace and justice to the world.

The Mahdist State, also known as Mahdist Sudan or the Sudanese Mahdiyya, was a state based on a religious and political movement launched in 1881 by Muhammad Ahmad bin Abdullah against the Khedivate of Egypt, which had ruled the Sudan since 1821. After four years of struggle, the Mahdist rebels overthrew the Ottoman-Egyptian administration and established their own "Islamic and national" government with its capital in Omdurman. Thus, from 1885 the Mahdist government maintained sovereignty and control over the Sudanese territories until its existence was terminated by the Anglo-Egyptian forces in 1898.

The dominant religion in Sudan is Islam practiced by around 90.7% of the nation's population. Christianity is the largest minority faith in country accounting for around 5.4% of the population. A substantial population of the adherents of traditional faiths is also present.

The siege of Khartoum occurred from 13 March 1884 to 26 January 1885. Sudanese Mahdist forces captured the city of Khartoum from its Egyptian garrison, thereby gaining control over the whole of Sudan.
Mahdi is the prophesied redeemer of Islam. Mehdi is a variant alternative transliteration.

The Mahdist War was a war between the Mahdist Sudanese of the religious leader Muhammad Ahmad bin Abd Allah, who had proclaimed himself the "Mahdi" of Islam, and the forces of the Khedivate of Egypt, initially, and later the forces of Britain. Eighteen years of war resulted in the nominally joint-rule state of the Anglo-Egyptian Sudan (1899–1956), a de jure condominium of the British Empire and the Kingdom of Egypt in which Britain had de facto control over the Sudan. The Sudanese launched several unsuccessful invasions of their neighbours, expanding the scale of the conflict to include not only Britain and Egypt but also the Italian Empire, the Congo Free State and the Ethiopian Empire.
The Mahdi is a messianic figure in Islamic eschatology who is believed to appear at the end of times to rid the world of evil and injustice. He is said to be a descendant of Muhammad who will appear shortly before the prophet ʿĪsā (Jesus) and lead Muslims to rule the world.

Aba Island is an island on the White Nile to the south of Khartoum, Sudan. It is the original home of the Mahdi in Sudan and the spiritual base of the Umma Party.

Sayyid Abd al-Rahman al-Mahdi, KBE was one of the leading religious and political figures during the colonial era in the Anglo-Egyptian Sudan (1898–1955), and continued to exert great authority as leader of the Neo-Mahdists after Sudan became independent. The British tried to exploit his influence over the Sudanese people while at the same time profoundly distrusting his motives. Throughout most of the colonial era of the Anglo-Egyptian Sudan the British saw Sayyid Abd al-Rahman al-Mahdi as important as a moderate leader of the Mahdists.
al-Shakaba is a community in Al Jazirah state, Sudan. It lies on the west shore of the Blue Nile near Barakat, to the south of Wad Madani. The village is within the Gezira scheme, which provides irrigation water for cotton cultivation.

The Ansar is a Sufi religious movement in the Sudan whose followers are disciples of Muhammad Ahmad, a Sudanese religious leader based on Aba Island who proclaimed himself Mahdi on 29 June 1881. His followers won a series of victories against the Egyptians culminating in the capture of Khartoum in January 1885.
The Battle of Aba, which took place on August 12, 1881, was the opening battle of the Mahdist War. The incident saw Mahdist rebels, led by Muhammad Ahmad, who had proclaimed himself the Mahdi, rout Egyptian troops who had landed on Aba Island.

The Mahdi's tomb or qubba is located in Omdurman, Sudan. It was the burial place of Muhammad Ahmad, the leader of an Islamic revolt against the Ottoman-Egyptian occupation of Sudan in the late 19th century.

The jibba or jibbah, originally referring to an outer garment, cloak or coat,) is a long coat worn by Muslim men. During the Mahdist State in Sudan at the end of the 19th century, it was the garment worn by the followers of the Mahdī. Muhammad Ahmad proclaimed himself al-Mahdī al-Muntaẓar, successor of the Prophet Muhammad, in 1881. He exhorted his followers to join a jihad against the Ottoman-Egyptian occupation of Sudan.

Carl Christian Giegler was a German-born telegraph engineer who acted as governor-general of the Egyptian province of Sudan from February to May 1882 around the start of the Mahdist War.













