
The poverty threshold, poverty limit, poverty line, or breadline is the minimum level of income deemed adequate in a particular country. The poverty line is usually calculated by estimating the total cost of one year's worth of necessities for the average adult. The cost of housing, such as the rent for an apartment, usually makes up the largest proportion of this estimate, so economists track the real estate market and other housing cost indicators as a major influence on the poverty line. Individual factors are often used to account for various circumstances, such as whether one is a parent, elderly, a child, married, etc. The poverty threshold may be adjusted annually. In practice, like the definition of poverty, the official or common understanding of the poverty line is significantly higher in developed countries than in developing countries.

The Kerala model refers to the practices adopted by the Indian state of Kerala to further human development. It is characterised by results showing strong social indicators when compared to the rest of the country such as high literacy and life expectancy rates, highly improved access to healthcare, and low infant mortality and birth rates. Despite having a lower per capita income, the state is sometimes compared to developed countries. These achievements along with the factors responsible for such achievements have been considered characteristic results of the Kerala model. Academic literature discusses the primary factors underlying the success of the Kerala model as its decentralization efforts, the political mobilization of the poor, and the active involvement of civil society organizations in the planning and implementation of development policies.

Meru County is one of the 47 counties of Kenya. It borders Isiolo County to the north, Tharaka-Nithi County to the South, Nyeri County to the southwest and Laikipia County to the west. The home of the Meru people, Meru County has a population of 1.35 million people.

Isiolo is a town in Isiolo County, of which it is the capital. It is located in the upper eastern region of Kenya and is geographically considered the center of the country Kenya. It lies 285 kilometers north of the capital Nairobi. The town grew around the local military camps. Much of the population consists of Somali, Borana and Ameru community. The town has an estimated population of 78,250, most of them living around the outskirts of the town. Like most African cities, there has been a steady increase in the urban population in recent years, especially moving from as far as Moyale, Marsabit and Mandera. Isiolo town is also becoming a centre of interest because of its newly acquired status as a resort city cashing in on the popular Samburu and Shaba Game reserves, which have become preferred destinations after the famed Maasai Mara. Isiolo lies along the long A2 Road, leading towards Marsabit and Moyale much further north.

Education in El Salvador is regulated by the country's Ministry of Education. El Salvador consists of the following levels of education:
Racial steering refers to the practice in which real estate brokers guide prospective home buyers towards or away from certain neighborhoods based on their race. The term is used in the context of de facto residential segregation in the United States, and is often divided into two broad classes of conduct:
- Advising customers to purchase homes in particular neighborhoods on the basis of race.
- Failing, on the basis of race, to show, or to inform buyers of homes that meet their specifications.

The educational attainment of the U.S. population refers to the highest level of education completed. The educational attainment of the U.S. population is similar to that of many other industrialized countries with the vast majority of the population having completed secondary education and a rising number of college graduates that outnumber high school dropouts. As a whole, the population of the United States is spending more years in formal educational programs. As with income, levels differ by race, age, household configuration, and geography.
The education system of the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan includes basic, secondary, and higher education and has dramatically evolved since the establishment of the state in the early 1900s. The role played by a good education system has been significant in the development of Jordan from a predominantly agrarian to an industrialized nation over time.
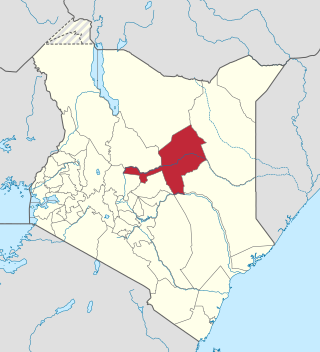
Isiolo County is a county in the former Eastern Province of Kenya. Its population is 268,002 and its capital and largest city is Isiolo. Isiolo County is to be the first county to be developed as part of the Kenya Vision 2030 program. Other upcoming urban centres are: Garbatulla, Modogashe, Kinna, Merti and Oldonyiro.The county is home to Sakuye and Borana tribes but also has a significant number of people from Turkana, Samburu, Gabra, Garre and Meru communities.

Garissa County is an administrative county in Kenya. It is located in Eastern Kenya bordering Somalia to the East, Wajir County and Isiolo County to the North, Tana River County to the West and Lamu County to the South. Its capital and largest urban area is Garissa.

Lewa Airport is an airport in Kenya.

Socioeconomic status (SES) is an economic and sociological combined total measure of a person's work experience and of an individual's or family's access to economic resources and social position in relation to others. When analyzing a family's SES, the household income and the education and occupations of its members are examined, whereas for an individual's SES only their own attributes are assessed. Recently, research has revealed a lesser-recognized attribute of SES as perceived financial stress, as it defines the "balance between income and necessary expenses". Perceived financial stress can be tested by deciphering whether a person at the end of each month has more than enough, just enough, or not enough money or resources. However, SES is more commonly used to depict an economic difference in society as a whole.

Malaysia is classified by The World Bank as upper middle income country and is attempting to achieve high-income status by 2020 and to move further up the value-added production chain by attracting investments in high technology, knowledge-based industries and services. Malaysia's HDI value for 2015 was recorded at 0.789 and HDI rank no 59 out of 188 countries and territories on the United Nations Development Programme's Human Development Index. In 2016, the population of Malaysia is 31 million; Total expenditure on health per capita is 1040; Total expenditure on health as % of GDP (2014) was 4.2 Gross national income (GNI) per capita was recorded at 24,620
Somali Canadians are Canadians of Somali origin or are dual Somali and Canadian nationality.

Education in St. Lucia is primarily based on the British education system and is provided in public and private schools.

In the United States, poverty has both social and political implications. In 2020, there were 37.2 million people in poverty. Some of the many causes include income inequality, inflation, unemployment, debt traps and poor education. The majority of adults living in poverty are employed and have at least a high school education. Although the US is a relatively wealthy country by international standards, it has a persistently high poverty rate compared to other developed countries due in part to a less generous welfare system.
In the New Zealand education system, decile was a key measure of socioeconomic status used to target funding and support schools. In academic contexts the full term "socioeconomic decile" or "socioeconomic decile band" was used.
Isiolo Airport, also Isiolo International Airport is an airport located in Isiolo, Isiolo County, and Meru County, Kenya.
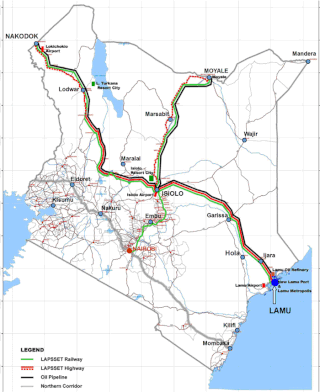
Lamu Port-South Sudan-Ethiopia-Transport (LAPSSET) Corridor project, also known as Lamu corridor is a transport and infrastructure project in Kenya that, when complete, will be the country's second transport corridor. Kenya's other transport corridor is the Northern Corridor, which links Mombasa to Uganda, passing through Nairobi and much of the Northern Rift. Some basic LAPSSET infrastructure has been built. The construction of LAPSSET's main components is currently ongoing with construction of the first berth at Lamu Port completed in October 2019.. Although the project is not formally stalled, its short to medium term success looks increasingly unlikely. Insecurity and political instability in Kenya are mostly to blame for this, as are more commercially viable alternative pipeline options through Tanzania or Ethiopia. The low oil prices since 2015 also affect LAPSSET's commercial prospects.

Taxes in Spain are levied by national (central), regional and local governments. Tax revenue in Spain stood at 36.3% of GDP in 2013. A wide range of taxes are levied on different sources, the most important ones being income tax, social security contributions, corporate tax, value added tax; some of them are applied at national level and others at national and regional levels. Most national and regional taxes are collected by the Agencia Estatal de Administración Tributaria which is the bureau responsible for collecting taxes at the national level. Other minor taxes like property transfer tax (regional), real estate property tax (local), road tax (local) are collected directly by regional or local administrations. Four historical territories or foral provinces collect all national and regional taxes themselves and subsequently transfer the portion due to the central Government after two negotiations called Concierto and the Convenio. The tax year in Spain follows the calendar year. The tax collection method depends on the tax; some of them are collected by self-assessment, but others follow a system of pay-as-you-earn tax with monthly withholdings that follow a self-assessment at the end of the term.















