The Wisconsin Range is a major mountain range of the Horlick Mountains in Antarctica, comprising the Wisconsin Plateau and numerous glaciers, ridges and peaks bounded by the Reedy Glacier, Shimizu Ice Stream, Horlick Ice Stream and the interior ice plateau.
The Amundsen Glacier is a major Antarctic glacier, about 7 to 11 km wide and 150 km (80 nmi) long. It originates on the Antarctic Plateau where it drains the area to the south and west of Nilsen Plateau, then descends through the Queen Maud Mountains to enter the Ross Ice Shelf just west of the MacDonald Nunataks.

The Prince Charles Mountains are a major group of mountains in Mac. Robertson Land in Antarctica, including the Athos Range, the Porthos Range, and the Aramis Range. The highest peak is Mount Menzies, with a height of 3,228 m (10,591 ft). Other prominent peaks are Mount Izabelle and Mount Stinear. These mountains, together with other scattered peaks, form an arc about 420 km (260 mi) long, extending from the vicinity of Mount Starlight in the north to Goodspeed Nunataks in the south.
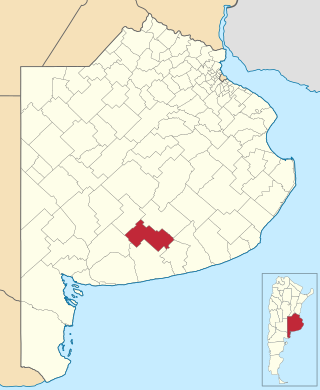
Adolfo Gonzales Chaves is a partido of Buenos Aires Province in Argentina, it is located at coordinates 38°02′S60°05′W.
Athos Range is the northernmost range in the Prince Charles Mountains of Mac. Robertson Land, Antarctica. The range consists of many individual mountains and nunataks that trend east–west for 40 miles (64 km) along the north side of Scylla Glacier.

Joaíma is a Brazilian municipality located in the northeast of the state of Minas Gerais.

Liv Glacier is a steep valley glacier, 40 nautical miles long, emerging from the Antarctic Plateau just southeast of Barnum Peak and draining north through the Queen Maud Mountains to enter Ross Ice Shelf between Mayer Crags and Duncan Mountains. It was discovered in 1911 by Roald Amundsen, who named it for the daughter of Fridtjof Nansen.
The Mariner Glacier is a major glacier over 60 nautical miles long, descending southeast from the plateau of Victoria Land, Antarctica, between Mountaineer Range and Malta Plateau, and terminating at Lady Newnes Bay, Ross Sea, where it forms the floating Mariner Glacier Tongue.
The Gothic Mountains is a group of mountains, 20 nautical miles long, in the Queen Maud Mountains of Antarctica, located west of Watson Escarpment and bounded by Scott Glacier, Albanus Glacier, and Griffith Glacier.

Potaka Inlet is a narrow ice-filled inlet about 8 nautical miles (15 km) long, indenting the north side of Thurston Island immediately east of Starr Peninsula. It was first delineated from air photos taken by U.S. Navy Operation Highjump in December 1946. It was named by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names for Dr. Louis H. Potaka, a medical officer with the Byrd Antarctic Expedition, 1933–35.
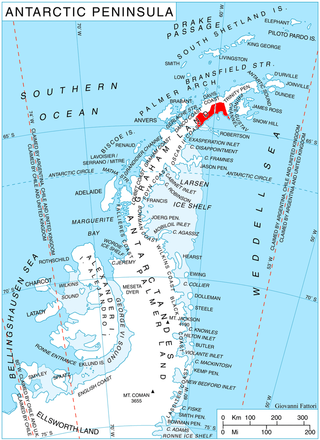
Edgeworth Glacier is a glacier 12 nautical miles (22 km) long, flowing south-southwestwards from the edge of Detroit Plateau below Wolseley Buttress and Paramun Buttress between Trave Peak and Chipev Nunatak into Mundraga Bay west of Sobral Peninsula, on the Nordenskjöld Coast of Graham Land. It was mapped from surveys by the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey (1960–61), and was named by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee for Richard Lovell Edgeworth, the British inventor of the "portable railway," the first track-laying vehicle, in 1770.
Gambacorta Peak is a peak 1,840 metres (6,040 ft) high, standing 4 nautical miles east of Mount Kaschak in the southern Neptune Range, Pensacola Mountains, Antarctica.

Mount Gardner is a mountain, 4,587 metres (15,050 ft) high, standing 1.5 nautical miles (3 km) west of Mount Tyree in the west-central part of the Sentinel Range, in the Ellsworth Mountains of Antarctica. It surmounts Patton Glacier to the northeast.

Tait Glacier is a glacier about 4 nautical miles (7 km) long on the southwest coast of James Ross Island, flowing southwest into Carlsson Bay. Probably first seen by Dr. Otto Nordenskjold in 1903. Surveyed by Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey (FIDS) in 1945. Named by United Kingdom Antarctic Place-Names Committee (UK-APC) for Murdo F. Tait, FIDS meteorological observer at Hope Bay in 1952 and 1953.
The Mackin Table is an ice-topped, wedge-shaped plateau, about 20 nautical miles long, standing just north of Patuxent Ice Stream in the Patuxent Range of the Pensacola Mountains, Antarctica.

Rush Glacier is a glacier in Antarctica. Situated in southern Brabant Island, it is 4 nautical miles (7 km) long, draining the northwest slopes of Solvay Mountains and flowing west between Mount Aciar and Mount Sarnegor into the Buragara Cove of Dallmann Bay in the Palmer Archipelago. It was shown on an Argentine government chart in 1953, but not named. It was photographed by Hunting Aerosurveys Ltd in 1956–57, and mapped from these photos in 1959. The glacier was named by the United Kingdom Antarctic Place-Names Committee (UK-APC) for Benjamin Rush (1745–1813), a noted American physician and philanthropist, and a signatory of the Declaration of Independence.

Luke Glacier is a glacier at least 15 nautical miles (28 km) long, flowing northwest into the head of Leroux Bay on the west coast of Graham Land, Antarctica. It is surmounted by Mount Chevreux on the south, Mount Perchot on the southwest and Mount Radotina on the northeast. The glacier was first sighted and roughly surveyed in 1909 by the Fourth French Antarctic Expedition. It was resurveyed in 1935–36 by the British Graham Land Expedition and later named for George Lawson Johnston, 1st Baron Luke of Pavenham, Chairman of Bovril Ltd, who contributed toward the cost of the expedition.

Rennell Glacier is a glacier, 10 nautical miles long, in the Pioneer Heights, Heritage Range. It drains northwest, to the east of Inferno Ridge, to join Splettstoesser Glacier. Named by the University of Minnesota Geological Party to these mountains, 1963–64, for K.P. Rennell, biologist with the party.











