
William Nelson Joy is an American computer engineer and venture capitalist. He co-founded Sun Microsystems in 1982 along with Scott McNealy, Vinod Khosla, and Andy Bechtolsheim, and served as Chief Scientist and CTO at the company until 2003. He played an integral role in the early development of BSD UNIX while being a graduate student at Berkeley, and he is the original author of the vi text editor. He also wrote the 2000 essay Why The Future Doesn't Need Us, in which he expressed deep concerns over the development of modern technologies.

Automation is the technology by which a process or procedure is performed with minimal human assistance. Automation or automatic control is the use of various control systems for operating equipment such as machinery, processes in factories, boilers and heat treating ovens, switching on telephone networks, steering and stabilization of ships, aircraft and other applications and vehicles with minimal or reduced human intervention.
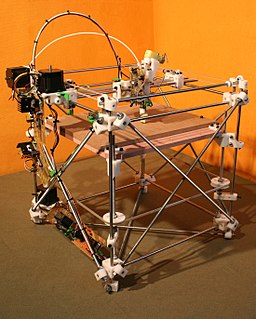
The open-design movement involves the development of physical products, machines and systems through use of publicly shared design information. This includes the making of both free and open-source software (FOSS) as well as open-source hardware. The process is generally facilitated by the Internet and often performed without monetary compensation. The goals and philosophy of the movement are identical to that of the open-source movement, but are implemented for the development of physical products rather than software. Open design is a form of co-creation, where the final product is designed by the users, rather than an external stakeholder such as a private company.

A fab lab is a small-scale workshop offering (personal) digital fabrication.

3D printing, or additive manufacturing, is the construction of a three-dimensional object from a CAD model or a digital 3D model. The term "3D printing" can refer to a variety of processes in which material is deposited, joined or solidified under computer control to create a three-dimensional object, with material being added together, typically layer by layer.

Chris Anderson is a British-American author and entrepreneur. He was with The Economist for seven years before joining WIRED magazine in 2001, where he was the editor-in-chief until 2012. He is known for his 2004 article entitled The Long Tail; which he later expanded into the 2006 book, The Long Tail: Why the Future of Business Is Selling Less of More. He is the cofounder and current CEO of 3D Robotics, a drone manufacturing company.

A hackerspace is a community-operated, often "not for profit", workspace where people with common interests, such as computers, machining, technology, science, digital art, or electronic art, can meet, socialize, and collaborate. Hackerspaces are comparable to other community-operated spaces with similar aims and mechanisms such as Fab Lab, men's sheds, and commercial "for-profit" companies.

Bre Pettis is an American entrepreneur, video blogger and creative artist. Pettis is best known as the co-founder and former CEO of MakerBot Industries, a 3D printer company now owned by Stratasys.

Open-source robotics (OSR) is where the physical artifacts of the subject are offered by the open design movement. This branch of robotics makes use of open-source hardware and free and open-source software providing blueprints, schematics, and source code. The term usually means that information about the hardware is easily discerned so that others can make it from standard commodity components and tools—coupling it closely to the maker movement and open science.

MakerBot Industries, LLC is an American desktop 3D printer manufacturer company headquartered in New York City. It was founded in January 2009 by Bre Pettis, Adam Mayer, and Zach "Hoeken" Smith to build on the early progress of the RepRap Project. It was acquired by Stratasys in June 2013. As of April 2016, MakerBot has sold over 100,000 desktop 3D printers worldwide. Since 2009, the company has released 6 generations of 3D printers, with the latest being the Replicator+ and Replicator Mini+. It was the leader of the desktop market with an important presence in the media but its market share is in decline. MakerBot also founded and operates Thingiverse, the largest online 3D printing community and file repository.

The maker culture is a contemporary subculture representing a technology-based extension of DIY culture that intersects with hacker culture and revels in the creation of new devices as well as tinkering with existing ones. The maker culture in general supports open-source hardware. Typical interests enjoyed by the maker culture include engineering-oriented pursuits such as electronics, robotics, 3-D printing, and the use of Computer Numeric Control tools, as well as more traditional activities such as metalworking, woodworking, and, mainly, its predecessor, traditional arts and crafts. The subculture stresses a cut-and-paste approach to standardized hobbyist technologies, and encourages cookbook re-use of designs published on websites and maker-oriented publications. There is a strong focus on using and learning practical skills and applying them to reference designs. There is also growing work on equity and the maker culture.

Ayah Bdeir is an entrepreneur, inventor, and interactive artist. She is the founder and CEO of littleBits.
The new manufacturing economy (NME) describes the role of advanced manufacturing in the rise of the New Economy. The term describes manufacturing enabled by digital technologies, advanced systems and processes and a highly trained and knowledgeable workforce. The new manufacturing economy integrates networks, 3D printers and other proficiencies into business strategies to further develop manufacturing practices.
Democratization of technology refers to the process by which access to technology rapidly continues to become more accessible to more people. New technologies and improved user experiences have empowered those outside of the technical industry to access and use technological products and services. At an increasing scale, consumers have greater access to use and purchase technologically sophisticated products, as well as to participate meaningfully in the development of these products. Industry innovation and user demand have been associated with more affordable, user-friendly products. This is an ongoing process, beginning with the development of mass production and increasing dramatically as digitization became commonplace.
Distributed manufacturing also known as distributed production, cloud producing and local manufacturing is a form of decentralized manufacturing practiced by enterprises using a network of geographically dispersed manufacturing facilities that are coordinated using information technology. It can also refer to local manufacture via the historic cottage industry model, or manufacturing that takes place in the homes of consumers.

Formlabs is a 3D printing technology developer and manufacturer. The Somerville, Massachusetts-based company was founded in September 2011 by three MIT Media Lab students. The company develops and manufactures 3D printers and related software and consumables. It is most known for raising nearly $3 million in a Kickstarter campaign and creating the Form 1, Form 1+, Form 2, Form Cell, Form 3, Form 3L, and Fuse 1 stereolithography and selective laser sintering 3D printers.

littleBits is a New York City-based startup that makes an open source library of modular electronics, which snap together with small magnets for prototyping and learning. The company's goal is to democratize hardware the way software and printing have been democratized. The littleBits mission is to "put the power of electronics in the hands of everyone, and to break down complex technologies so that anyone can build, prototype, and invent." littleBits units are available in more than 70 countries and used in more than 2,000 schools. The company was named to CNN's 10 Startups to Watch for 2013.
Avi Reichental is an Israeli-American businessperson in the 3D printing industry. He is the founder and executive chairman of XponentialWorks, a venture investment, advisory and product development company. Reichental serves as CEO, Chairman and Co-Founder of Nexa3D and Co-Founder and Executive Chairman of NXT Factory, Centaur Analytics and ParaMatters.
Maker education closely associated with STEM learning, is an approach to problem-based and project-based learning that relies upon hands-on, often collaborative, learning experiences as a method for solving authentic problems. People who participate in making often call themselves "makers" of the maker movement and develop their projects in makerspaces, or development studios which emphasize prototyping and the repurposing of found objects in service of creating new inventions or innovations. Culturally, makerspaces, both inside and outside of schools, are associated with collaboration and the free flow of ideas. In schools, maker education stresses the importance of learner-driven experience, interdisciplinary learning, peer-to-peer teaching, iteration, and the notion of "failing forward", or the idea that mistake-based learning is crucial to the learning process and eventual success of a project.
In recent years, 3D printing has developed significantly and can now perform crucial roles in many applications, with the most important being manufacturing, medicine, architecture, custom art and design.














