
Back injuries result from damage, wear, or trauma to the bones, muscles, or other tissues of the back. Common back injuries include sprains and strains, herniated discs, and fractured vertebrae. The lumbar spine is often the site of back pain. The area is susceptible because of its flexibility and the amount of body weight it regularly bears. It is estimated that low-back pain may affect as much as 80 to 90 percent of the general population in the United States.

A bone fracture is a medical condition in which there is a partial or complete break in the continuity of any bone in the body. In more severe cases, the bone may be broken into several fragments, known as a comminuted fracture. A bone fracture may be the result of high force impact or stress, or a minimal trauma injury as a result of certain medical conditions that weaken the bones, such as osteoporosis, osteopenia, bone cancer, or osteogenesis imperfecta, where the fracture is then properly termed a pathologic fracture.

A cervical fracture, commonly called a broken neck, is a fracture of any of the seven cervical vertebrae in the neck. Examples of common causes in humans are traffic collisions and diving into shallow water. Abnormal movement of neck bones or pieces of bone can cause a spinal cord injury, resulting in loss of sensation, paralysis, or usually death soon thereafter, primarily via compromising neurological supply to the respiratory muscles as well as innervation to the heart.
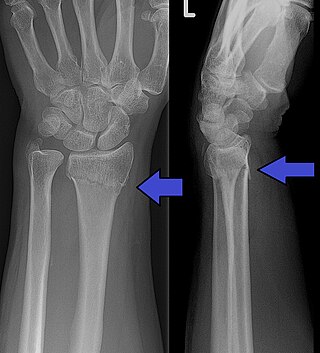
A distal radius fracture, also known as wrist fracture, is a break of the part of the radius bone which is close to the wrist. Symptoms include pain, bruising, and rapid-onset swelling. The ulna bone may also be broken.

A Jones fracture is a broken bone in a specific part of the fifth metatarsal of the foot between the base and middle part that is known for its high rate of delayed healing or nonunion. It results in pain near the midportion of the foot on the outside. There may also be bruising and difficulty walking. Onset is generally sudden.

A Smith's fracture, is a fracture of the distal radius.

External fixation is a surgical treatment wherein Kirschner pins and wires are inserted and affixed into bone and then exit the body to be attached to an external apparatus composed of rings and threaded rods — the Ilizarov apparatus, the Taylor Spatial Frame, and the Octopod External Fixator — which immobilises the damaged limb to facilitate healing. As an alternative to internal fixation, wherein bone-stabilising mechanical components are surgically emplaced in the body of the patient, external fixation is used to stabilize bone tissues and soft tissues at a distance from the site of the injury.

A hip dislocation is when the thighbone (femur) separates from the hip bone (pelvis). Specifically it is when the ball–shaped head of the femur separates from its cup–shaped socket in the hip bone, known as the acetabulum. The joint of the femur and pelvis is very stable, secured by both bony and soft-tissue constraints. With that, dislocation would require significant force which typically results from significant trauma such as from a motor vehicle collision or from a fall from elevation. Hip dislocations can also occur following a hip replacement or from a developmental abnormality known as hip dysplasia.
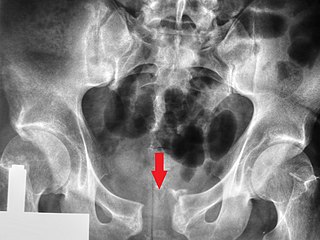
A pelvic fracture is a break of the bony structure of the pelvis. This includes any break of the sacrum, hip bones, or tailbone. Symptoms include pain, particularly with movement. Complications may include internal bleeding, injury to the bladder, or vaginal trauma.

Cataclasite is a cohesive granular fault rock. Comminution, also known as cataclasis, is an important process in forming cataclasites. They fall into the category of cataclastic rocks which are formed through faulting or fracturing in the upper crust. Cataclasites are distinguished from fault gouge, which is incohesive, and fault breccia, which contains coarser fragments.

A calcaneal fracture is a break of the calcaneus. Symptoms may include pain, bruising, trouble walking, and deformity of the heel. It may be associated with breaks of the hip or back.

An open fracture, also called a compound fracture, is a type of bone fracture that has an open wound in the skin near the fractured bone. The skin wound is usually caused by the bone breaking through the surface of the skin. Open fractures are emergencies and are often caused by high energy trauma such as road traffic accidents and are associated with a high degree of damage to the bone and nearby soft tissue. An open fracture can be life threatening or limb-threatening due to the risk of a deep infection and/or bleeding. Other complications including a risk of malunion of the bone or nonunion of the bone. The severity of open fractures can vary. For diagnosing and classifying open fractures, Gustilo-Anderson open fracture classification is the most commonly used method. It can also be used to guide treatment, and to predict clinical outcomes. Advanced trauma life support is the first line of action in dealing with open fractures and to rule out other life-threatening condition in cases of trauma. The person is also administered antibiotics for at least 24 hours to reduce the risk of an infection. Cephalosporins are generally the first line of antibiotics. Therapeutic irrigation, wound debridement, early wound closure and bone fixation are the main management of open fractures. All these actions aimed to reduce the risk of infections. The bone that is most commonly injured is the tibia and working-age young men are the group of people who are at highest risk of an open fracture. Older people with osteoporosis and soft-tissue problems are also at risk.

Joseph-François Malgaigne was a French surgeon and medical historian born in Charmes-sur-Moselle, Vosges.
The Gustilo open fracture classification system is the most commonly used classification system for open fractures. It was created by Ramón Gustilo and Anderson, and then further expanded by Gustilo, Mendoza, and Williams.
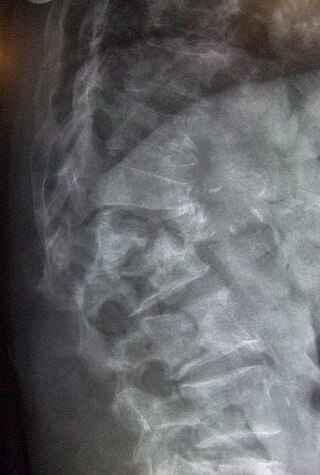
A spinal fracture, also called a vertebral fracture or a broken back, is a fracture affecting the vertebrae of the spinal column. Most types of spinal fracture confer a significant risk of spinal cord injury. After the immediate trauma, there is a risk of spinal cord injury if the fracture is unstable, that is, likely to change alignment without internal or external fixation.

Meteorite shock stage is a measure of the degree of fracturing of the matrix of a common chondrite meteorite. Impacts on the parent body of a meteoroid can produce very large pressures. These pressures heat, melt and deform the rocks. This is called shock metamorphism. Meteorites are often given a rating from 1 to 6 showing the level of shock metamorphism. However, the degree of shock can vary within a meteorite on the scale of centimeters.

Orthopedic surgery is the branch of surgery concerned with conditions involving the musculoskeletal system. Orthopedic surgeons use both surgical and nonsurgical means to treat musculoskeletal injuries, sports injuries, degenerative diseases, infections, bone tumours, and congenital limb deformities. Trauma surgery and traumatology is a sub-specialty dealing with the operative management of fractures, major trauma and the multiply-injured patient.
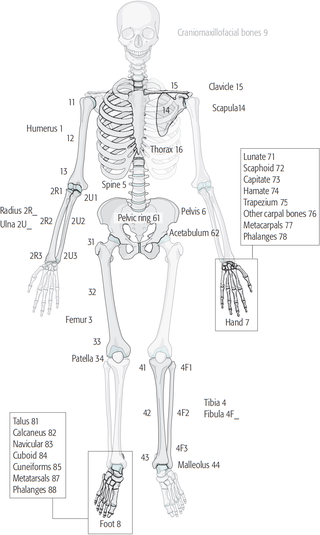
The Müller AO Classification of fractures is a system for classifying bone fractures initially published in 1987 by the AO Foundation as a method of categorizing injuries according to therognosis of the patient's anatomical and functional outcome. "AO" is an initialism for the German "Arbeitsgemeinschaft für Osteosynthesefragen", the predecessor of the AO Foundation.

A proximal humerus fracture is a break of the upper part of the bone of the arm (humerus). Symptoms include pain, swelling, and a decreased ability to move the shoulder. Complications may include axillary nerve or axillary artery injury.

















