This article needs additional citations for verification .(May 2015) |
The Malta Standards Authority (MSA) is Malta's national standards body.
This article needs additional citations for verification .(May 2015) |
The Malta Standards Authority (MSA) is Malta's national standards body.
The MSA is a government agency under the Office of the Prime Minister. The MSA consists of two divisions. The Legal Metrology Division is responsible for inspection and verification. The National Metrology Institute (MSA-NMS) is responsible for maintaining measurement standards for Malta. [1]
MSA-NMS is located at the Kordin Business Incubation Centre near Paola. As a national metrology institute, MSA-NMS is a member of EURAMET. [2]
MSA-NMS has three goals. [3]
MSA-NMS maintains standards and is able to perform calibrations in the following measurement disciplines:

The International Bureau of Weights and Measures is an intergovernmental organisation, through which its 59 member-states act on measurement standards in four areas: chemistry, ionising radiation, physical metrology, as well as Coordinated Universal Time. It is based in Saint-Cloud, near Paris, France. The organisation has been referred to as IBWM in older literature.
The General Conference on Weights and Measures is the supreme authority of the International Bureau of Weights and Measures (BIPM), the intergovernmental organization established in 1875 under the terms of the Metre Convention through which member states act together on matters related to measurement science and measurement standards. The CGPM is made up of delegates of the governments of the member states and observers from the Associates of the CGPM. It elects the International Committee for Weights and Measures as the supervisory board of the BIPM to direct and supervise it.
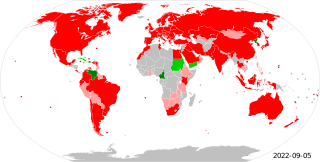
The Metre Convention, also known as the Treaty of the Metre, is an international treaty that was signed in Paris on 20 May 1875 by representatives of 17 nations: Argentina, Austria-Hungary, Belgium, Brazil, Denmark, France, Germany, Italy, Peru, Portugal, Russia, Spain, Sweden and Norway, Switzerland, Ottoman Empire, United States of America, and Venezuela.
In measurement technology and metrology, calibration is the comparison of measurement values delivered by a device under test with those of a calibration standard of known accuracy. Such a standard could be another measurement device of known accuracy, a device generating the quantity to be measured such as a voltage, a sound tone, or a physical artifact, such as a meter ruler.

Metrology is the scientific study of measurement. It establishes a common understanding of units, crucial in linking human activities. Modern metrology has its roots in the French Revolution's political motivation to standardise units in France when a length standard taken from a natural source was proposed. This led to the creation of the decimal-based metric system in 1795, establishing a set of standards for other types of measurements. Several other countries adopted the metric system between 1795 and 1875; to ensure conformity between the countries, the Bureau International des Poids et Mesures (BIPM) was established by the Metre Convention. This has evolved into the International System of Units (SI) as a result of a resolution at the 11th General Conference on Weights and Measures (CGPM) in 1960.
Traceability is the capability to trace something. In some cases, it is interpreted as the ability to verify the history, location, or application of an item by means of documented recorded identification.

The Physikalisch-Technische Bundesanstalt (PTB) is the national metrology institute of the Federal Republic of Germany, with scientific and technical service tasks. It is a higher federal authority and a public-law institution directly under federal government control, without legal capacity, under the auspices of the Federal Ministry for Economic Affairs and Energy.
AFMETCAL, located in Heath, Ohio is the primary manager of metrology services for the U.S. Air Force. It retains engineering authority for all calibrations performed in the PMEL labs throughout the Air Force, and oversees the contractor managed and operated Air Force Primary Standards Lab (AFPSL). It currently operates as a direct reporting unit of the Air Force Life Cycle Management Center for Wright-Patterson AFB, Wright-Patterson, OH.

The International Organization of Legal Metrology, is an intergovernmental organisation that was created in 1955 to promote the global harmonisation of the legal metrology procedures that underpin and facilitate international trade.
A Precision Measurement Equipment Laboratory (PMEL) is a United States Air Force (USAF) facility in which the calibration and repair of test equipment takes place. This practice is also known as metrology: the science of measurement. Metrology is defined as the science of weights & measures, while a PMEL is the place where technicians perform all of the metrology for the U.S. Air Force. Air personnel in this career field are primarily responsible for the repair, calibration, and modification of test, measurement, and diagnostic equipment (TMDE), including precision measurement equipment laboratory standards and automatic test equipment. They also supervise the process and use of TMDE to perform voltage, current, power, impedance, frequency, microwave, temperature, physical-dimensional, and optical measurements. They perform these functions in a strictly controlled laboratory environment where the temperature and humidity are constantly monitored. The Air Force Specialty Code (AFSC) of air personnel trained to work in the PMEL is 2P0X1 replacing 324X0 where "X" represents a variable number which denotes the level of expertise of the individual. There are also defense contractors and government civilians who perform this job. The Air Force's PMELs are governed by AFMETCAL
EURAMET is a collaborative alliance of national metrological organizations from member states of the European Union (EU) and of the European Free Trade Association (EFTA) whose purpose is to achieve higher efficiency by co-ordinating and sharing metrological activities and services.
The National Measurement and Regulation Office (NMRO) was an executive agency of the UK Government's Department for Business, Innovation and Skills (BIS). Its function were to provide a measurement infrastructure which supports innovation, facilitates fair competition, promotes international trade and protects consumers and the environment.

Nanometrology is a subfield of metrology, concerned with the science of measurement at the nanoscale level. Nanometrology has a crucial role in order to produce nanomaterials and devices with a high degree of accuracy and reliability in nanomanufacturing.

NCSL International (NCSLI) is a global, non-profit organization whose membership is open to any organization with an interest in metrology and its application in research, development, education, and commerce.

The National Institute of Metrology, Standardization and Industrial Quality (INMETRO) is a Brazilian federal autarchy, linked to MDIC, the Ministry of Development, Industry and Foreign Trade.

In metrology, a standard is an object, system, or experiment that bears a defined relationship to a unit of measurement of a physical quantity. Standards are the fundamental reference for a system of weights and measures, against which all other measuring devices are compared. Historical standards for length, volume, and mass were defined by many different authorities, which resulted in confusion and inaccuracy of measurements. Modern measurements are defined in relationship to internationally standardized reference objects, which are used under carefully controlled laboratory conditions to define the units of length, mass, electrical potential, and other physical quantities.
The National Measurement Institute (NMI) is Australia's peak measurement body responsible for biological, chemical, legal and physical measurement and is currently administered within the Australian Government's Department of Industry, Innovation and Science.

From the beginning of 2015, the Centre for Metrology (MIKES) (Finnish: Mittatekniikan keskus; Swedish: Mätteknikcentralen) formerly the Centre for Metrology and Accreditation has been part of VTT Technical Research Centre of Finland Ltd. As the National Metrology Institute of Finland, MIKES is responsible for the implementation and development of the national measurement standards system and realisation of the SI units in Finland. MIKES designates other National Standards Laboratories in Finland. Moreover, MIKES performs research in metrology, i.e., in measurement science. MIKES’s customers include both Finnish and international companies as well as the public sector. Other national metrology institutes are for example PTB (Germany), NPL (UK), NMIJ (Japan), NIST (USA), and Główny Urząd Miar (Poland). As a part of VTT MIKES operates under the administrative domain of the Ministry of Employment and the Economy.

The Korea Research Institute of Standards and Science (KRISS) is the national measurement standards laboratory for the Republic of Korea. It is a government-funded institute responsible for providing national measurement standards and advancing measurement technologies. KRISS is also an active member of the General Conference on Weights and Measures (CGPM).
The National Quality Management Commission, formerly the State Administration of Quality Management of the Democratic People's Republic of Korea (SAQM) is the North Korean standards organization. It oversees standards and metrology, including application of both the metric system and traditional Korean units, in accordance with the 1993 Law on Metrology. It is located at 1 Inhung-Dong in Moranbong District, Pyongyang.