
Suleiman I, commonly known as Suleiman the Magnificent in the Western world and as Suleiman the Lawgiver in his own realm, was the Ottoman sultan between 1520 and his death in 1566. Under his administration, the Ottoman Empire ruled over at least 25 million people.

The Treaty of Karlowitz, concluding the Great Turkish War of 1683–1697, in which the Ottoman Empire was defeated by the Holy League at the Battle of Zenta, was signed in Karlowitz, in the Military Frontier of the Habsburg Monarchy, on 26 January 1699. Also known as "The Austrian treaty that saved Europe", it marks the end of Ottoman control in much of Central Europe, with their first major territorial losses in Europe, beginning the reversal of four centuries of expansion (1299–1683). The treaty established the Habsburg monarchy as the dominant power of the region.

The administrative divisions of the Ottoman Empire were administrative divisions of the state organisation of the Ottoman Empire. Outside this system were various types of vassal and tributary states.
Murat Reis the Elder was an Ottoman privateer and admiral, who served in the Ottoman Navy. He is regarded as one of the most important Barbary corsairs.

Eyalets, also known as beylerbeyliks or pashaliks, were the primary administrative divisions of the Ottoman Empire.

A series of military conflicts between the Ottoman Empire and various European states took place from the Late Middle Ages up through the early 20th century. The earliest conflicts began during the Byzantine–Ottoman wars, waged in Anatolia in the late 13th century before entering Europe in the mid-14th century with the Bulgarian–Ottoman wars. The mid-15th century saw the Serbian–Ottoman wars and the Albanian-Ottoman wars. Much of this period was characterized by the Ottoman expansion into the Balkans. The Ottoman Empire made further inroads into Central Europe in the 15th and 16th centuries, culminating in the peak of Ottoman territorial claims in Europe.

The Great Siege of Malta occurred in 1565 when the Ottoman Empire attempted to conquer the island of Malta, then held by the Knights Hospitaller. The siege lasted nearly four months, from 18 May to 8 September 1565.

The Eyalet of Silistra or Silistria, later known as Özü Eyalet meaning Province of Ochakiv was an eyalet of the Ottoman Empire along the Black Sea littoral and south bank of the Danube River in southeastern Europe. The fortress of Akkerman was under the eyalet's jurisdiction. Its reported area in the 19th century was 71,140 square kilometres (27,469 sq mi).

The Battle of Djerba took place in May 1560 near the island of Djerba, Tunisia. The Ottomans under Piyale Pasha's command overwhelmed a large joint Christian alliance fleet, composed chiefly of Spanish, Papal, Genoese, Maltese, and Neapolitan forces. The allies lost 27 galleys and some smaller vessels as well as the fortified island of Djerba. This victory marked perhaps the high point of Ottoman power in the Mediterranean Sea.

The Order of Knights of the Hospital of Saint John of Jerusalem, commonly known as the Knights Hospitaller, is a Catholic military order. It was founded in the crusader Kingdom of Jerusalem in the 12th century and had headquarters there until 1291, thereafter being based in Kolossi Castle in Cyprus (1302–1310), the island of Rhodes (1310–1522), Malta (1530–1798), and Saint Petersburg (1799–1801).

The Kapudan Pasha, also known as the Kapudan-ı Derya was the Grand Admiral of the navy of the Ottoman Empire. Typically, he was based at Galata and Gallipoli during the winter and charged with annual sailings during the summer months. The title of Kapudan Pasha itself is only attested from 1567 onwards; earlier designations for the supreme commander of the fleet include Derya Bey and Re'is Kapudan.
Antonio Busca was an Italian nobleman and Lieutenant of the Sovereign Military Order of Malta from 1821 to 1834.

The Eyalet of Bosnia, was an eyalet of the Ottoman Empire, mostly based on the territory of the present-day state of Bosnia and Herzegovina. Prior to the Great Turkish War, it had also included most of Slavonia, Lika, and Dalmatia in present-day Croatia. Its reported area in 1853 was 52,530 square kilometres (20,281 sq mi).
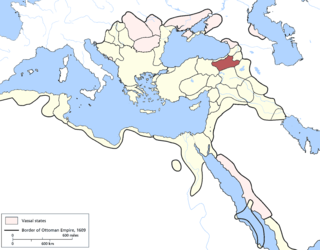
The Erzurum Eyalet was an eyalet of the Ottoman Empire. It was established after the conquest of Western Armenia by the Ottoman Empire. Its reported area in the 19th century was 11,463 square miles (29,690 km2).

The Sanjak of Rodos or Rhodes was a second-level Ottoman province encompassing the Dodecanese or Southern Sporades islands, off the coast of Anatolia in the Eastern Mediterranean, with Rhodes as its centre.

Hospitaller Malta, known in Maltese history as the Knights' Period, was a de facto state which existed between 1530 and 1798 when the Mediterranean islands of Malta and Gozo were ruled by the Order of St. John of Jerusalem. It was formally a vassal state of the Kingdom of Sicily, and it came into being when Emperor Charles V granted the islands as well as the city of Tripoli in modern Libya to the Order, following the latter's loss of Rhodes in 1522. Hospitaller Tripoli was lost to the Ottoman Empire in 1551, but an Ottoman attempt to take Malta in 1565 failed.

The navy of the Order of Saint John, also known as the Maltese Navy after 1530, was the first navy of a chivalric order. It was established in the Middle Ages, around the late 12th century. The navy reached its peak in the 1680s, during the reign of Grand Master Gregorio Carafa. It was disbanded following the French invasion of Malta in 1798, and its ships were taken over by the French Navy.

Kör Yusuf Ziyaüddin Pasha, also known as Yusuf Ziya Pasha, was an Ottoman statesman of Georgian origin, who twice served as the Grand Vizier of the Ottoman Empire in 1798–1805 and 1809–1811. Before, between and after his terms as grand vizier, he served numerous posts as governor of various provinces and districts throughout the empire. As grand vizier, he commanded the Ottoman ground forces against the French Army in the Ottoman reconquest of Egypt and later served as a commander in the Ottoman wars with the Russian Empire.

Slavery was practiced in Malta from classical antiquity to the early modern period, as was the case in many countries around the Mediterranean Sea. Sources dating back to when the islands were under Arab rule during the Middle Ages attest to the presence of slavery but lack details regarding the slaves' ethnic and religious backgrounds. When the islands were part of the Kingdom of Sicily during the late medieval period, it is apparent that many black Africans were domestic slaves on the islands.

Tripoli, today the capital city of Libya, was ruled by the Knights Hospitaller between 1530 and 1551. The city had been under Spanish rule for two decades before it was granted as a fief to the Hospitallers in 1530 along with the islands of Malta and Gozo. The Hospitallers found it difficult to control both the city and the islands, and at times they proposed to either move their headquarters to Tripoli or to abandon and raze the city. Hospitaller rule over Tripoli ended in 1551 when the city was captured by the Ottoman Empire following a siege.
















