Anuradhapura is a major city in Sri Lanka. It is the capital city of North Central Province, Sri Lanka and the capital of Anuradhapura District. Anuradhapura is one of the ancient capitals of Sri Lanka, famous for its well-preserved ruins of an ancient Sri Lankan civilization. It was the third capital of the kingdom of Rajarata, following the kingdoms of Tambapanni and Upatissa Nuwara.

The Kanheri Caves (Kānherī-guhāḥ) are a group of caves and rock-cut monuments cut into a massive basalt outcrop in the forests of the Sanjay Gandhi National Park, on the island of Salsette in the western outskirts of Mumbai, India. They contain Buddhist sculptures and relief carvings, paintings and inscriptions, dating from the 1st century BCE to the 10th century CE. Kanheri comes from the Sanskrit Krishnagiri, which means black mountain.

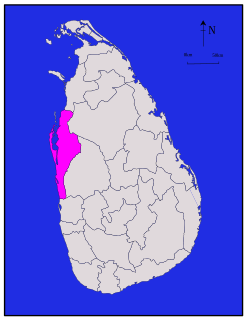
North Western Province is a province of Sri Lanka. The districts of Kurunegala and Puttalam formulate Wayamba. Its capital is Kurunegala, which has a population of 28,571. The province is known mainly for its numerous coconut plantations. Other main towns in this province are Chilaw (24,712) and Puttalam (45,661), which are both small fishing towns. The majority of the population of Wayamba province is of Sinhalese ethnicity. There is also a substantial Sri Lankan Moor minority around Puttalam and Sri Lankan Tamils in Udappu and Munneswaram. Fishing, prawn farming and rubber tree plantations are other prominent industries of the region. The province has an area of 7,888 km², and a population of 2,370,075.

Mihintale is a mountain peak near Anuradhapura in Sri Lanka. It is believed by Sri Lankans to be the site of a meeting between the Buddhist monk Mahinda and King Devanampiyatissa which inaugurated the presence of Buddhism in Sri Lanka. It is now a pilgrimage site, and the site of several religious monuments and abandoned structures.

Ramateertham is a village panchayat in Nellimarla mandal of Vizianagaram district in Andhra Pradesh in India.It is about 12 km from Vizianagaram city. It is a famous Pilgrimage and also Ancient Historical Site since 3rd Century BCE There is a post office at Ramateertham. The PIN code is 535 218.

Thuparamaya is the first Buddhist temple in Sri Lanka. Located in the sacred area of Mahamewna park, the Thuparamaya Stupa is the earliest Dagoba to be constructed in the island, dating back to the reign of King Devanampiya Tissa. The temple has been formally recognised by the Government as an archaeological site in Sri Lanka.
Atamasthana (අටමස්ථානය) or Eight sacred places are a series of locations in Sri Lanka where the Buddha had visited during his three visits to the country. The sacred places are known as Jaya Sri Maha Bodhiya, Ruwanwelisaya, Thuparamaya, Lovamahapaya, Abhayagiri Dagaba, Jetavanarama, Mirisaveti Stupa and Lankarama. They are situated in Anuradhapura, the capital of the ancient Anuradhapura Kingdom.

The architecture of ancient Sri Lanka displays a rich diversity, varying in form and architectural style from the Anuradhapura Kingdom through the Kingdom of Kandy (1469–1815). Sinhalese architecture also displays many ancient North Indian influences. Buddhism had a significant influence on Sri Lankan architecture after it was introduced to the island in the 3rd century BC, and ancient Sri Lankan architecture was mainly religious, with more than 25 styles of Buddhist monasteries. Significant buildings include the stupas of Jetavanaramaya and Ruwanvelisaya in the Anuradhapura kingdom and further in the Polonnaruwa Kingdom. The palace of Sigiriya is considered a masterpiece of ancient architecture and ingenuity, and the fortress in Yapahuwa and the Temple of the tooth in Kandy are also notable for their architectural qualities. Ancient Sri Lankan architecture is also significant to sustainability, notably Sigiriya which was designed as an environmentally friendly structure.

Stupas, also called dagobas and cetiyas, are considered an outstanding type of architectural creation of ancient Sri Lanka. Under the influence of Buddhism, there were several changes in the field of architecture in Sri Lanka. The stupa commands a prominent place among these changes. The Stupa is also known by synonymous names such as Chaithya, Dagaba, Thupa, Seya and Vehera. Stupas designed and constructed in Sri Lanka are the largest brick structures known to the pre-modern world.

The Miaoying Temple, also known as the "White Stupa Temple", is a Chinese Buddhist temple on the north side of Fuchengmennei Street in the Xicheng District of Beijing.

The Church of Saint Simeon Stylites is a building that can be traced back to the 5th century, located approximately 30 kilometres (19 mi) northwestern part of Aleppo, Syria. It is one of the oldest surviving church complexes. It was constructed on the site of the pillar of Saint Simeon Stylites, a renowned recluse monk. The church is popularly known as either Qalaat Semaan or Deir Semaan.

Bhamer, is a village with a historical fort in Sakri tehsil of Maharashtra state in India. It is situated at the foot of a great fortified hill lying 48.28 km (30.00 mi) north-west from Dhule city and 4.82 km (3.00 mi) south of Nijampur.
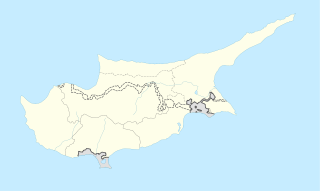
Steni is a village in the Paphos District of Cyprus, located 6 km southeast of Polis Chrysochous.

The Katskhi pillar is a natural limestone monolith located at the village of Katskhi in western Georgian region of Imereti, near the town of Chiatura. It is approximately 40 metres (130 ft) high, and overlooks the small river valley of Katskhura, a right affluent of the Q'virila.

Tulja Caves are located beyond the Shivneri hill, about 4km to the west of Junnar, India. Other caves surrounding the city of Junnar are: Manmodi caves, Shivneri caves and Lenyadri caves.

Ovagiriya is one of archaeological sites in Polwatta, Ampara District, Sri Lanka. It is situated on Ampara-Inginiyagala road, about 19 km (12 mi) away from Ampara town.

The Monastery of St. Simeon Stylites the Younger lies on a hill roughly 29 kilometres southwest of Antakya and six kilometres to the east of Samandağ, in the southernmost Turkish province of Hatay. The site is extensive but the monastery buildings are in ruins.

Panduwasnuwara is an ancient capital, situated in Kurunegala District, Sri Lanka. It is said to be the controlling centre known as Parakramapura of Dakkhinadesa in the 12th century, when it was ruled by Parakramabahu. The remaining ruins of the ancient kingdom still can be seen at Kotampitiya area which lies along Wariyapola-Chilaw main road about 19 km (12 mi) away from Wariyapola town.

Padiyadora Raja Maha Vihara is an ancient Buddhist temple in Padiyathalawa, Sri Lanka. The temple is located on Peradeniya – Chenkaladi - Badulla highway (A5) approximately 34 km (21 mi) distance from Mahiyangana town. The temple has been formally recognised by the Government as an archaeological site in Sri Lanka. The designation was declared on 10 October 2014 under the government Gazette number 1884.