The Single UNIX Specification (SUS) is a standard for computer operating systems, compliance with which is required to qualify for using the "UNIX" trademark. The standard specifies programming interfaces for the C language, a command-line shell, and user commands. The core specifications of the SUS known as Base Specifications are developed and maintained by the Austin Group, which is a joint working group of IEEE, ISO/IEC JTC 1/SC 22/WG 15 and The Open Group. If an operating system is submitted to The Open Group for certification, and passes conformance tests, then it is deemed to be compliant with a UNIX standard such as UNIX 98 or UNIX 03.
troff, short for "typesetter roff", is the major component of a document processing system developed by Bell Labs for the Unix operating system. troff and the related nroff were both developed from the original roff.
In computing, traceroute and tracert are computer network diagnostic commands for displaying possible routes (paths) and measuring transit delays of packets across an Internet Protocol (IP) network. The history of the route is recorded as the round-trip times of the packets received from each successive host in the route (path); the sum of the mean times in each hop is a measure of the total time spent to establish the connection. Traceroute proceeds unless all sent packets are lost more than twice; then the connection is lost and the route cannot be evaluated. Ping, on the other hand, only computes the final round-trip times from the destination point.

A man page is a form of software documentation usually found on a Unix or Unix-like operating system. Topics covered include computer programs, formal standards and conventions, and even abstract concepts. A user may invoke a man page by issuing the man command.

In Unix-like and some other operating systems, the pwd command writes the full pathname of the current working directory to the standard output.
In computing, touch is a command used to update the access date and/or modification date of a computer file or directory. It is included in Unix and Unix-like operating systems, TSC's FLEX, Digital Research/Novell DR DOS, the AROS shell, the Microware OS-9 shell, and ReactOS. The command is also available for FreeDOS and Microsoft Windows.
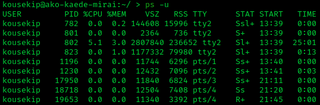
In most Unix and Unix-like operating systems, the ps program displays the currently-running processes. A related Unix utility named top provides a real-time view of the running processes.
In computing, echo is a command that outputs the strings that are passed to it as arguments. It is a command available in various operating system shells and typically used in shell scripts and batch files to output status text to the screen or a computer file, or as a source part of a pipeline.

cksum is a command in Unix and Unix-like operating systems that generates a checksum value for a file or stream of data. The cksum command reads each file given in its arguments, or standard input if no arguments are provided, and outputs the file's 32-bit cyclic redundancy check (CRC) checksum and byte count. The CRC output by cksum is different from the CRC-32 used in zip, PNG and zlib.

In computing, cmp is a command-line utility on Unix and Unix-like operating systems that compares two files of any type and writes the results to the standard output. By default, cmp is silent if the files are the same; if they differ, the byte and line number at which the first difference occurred is reported. The command is also available in the OS-9 shell.
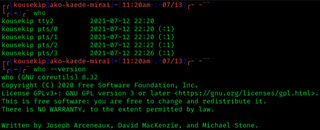
The standard Unix command who displays a list of users who are currently logged into the computer.

rm is a basic command on Unix and Unix-like operating systems used to remove objects such as computer files, directories and symbolic links from file systems and also special files such as device nodes, pipes and sockets, similar to the del command in MS-DOS, OS/2, and Microsoft Windows. The command is also available in the EFI shell.

In computing, exit is a command used in many operating system command-line shells and scripting languages.
In computing, tee is a command in command-line interpreters (shells) using standard streams which reads standard input and writes it to both standard output and one or more files, effectively duplicating its input. It is primarily used in conjunction with pipes and filters. The command is named after the T-splitter used in plumbing.
In computing, sleep is a command in Unix, Unix-like and other operating systems that suspends program execution for a specified time.
AppleSingle Format and AppleDouble Format are file formats developed by Apple Computer to store Mac OS "dual-forked" files on the Unix filesystem being used in A/UX, the Macintosh platform's first Unix-like operating system. AppleSingle combined both file forks and the related Finder meta-file information into a single file, whereas AppleDouble stored them as two separate files. Support for the formats was later added to Unix software such as NFS and MAE, but they saw little use outside this small market.

Unix is a family of multitasking, multi-user computer operating systems that derive from the original AT&T Unix, whose development started in 1969 at the Bell Labs research center by Ken Thompson, Dennis Ritchie, and others.
mandoc is a utility used for formatting man pages in BSD Operating Systems, specifically those written in the mdoc and man macro languages. Unlike the groff and older troff and nroff tools that are predominantly used for this purpose by tools such as man, mandoc focuses specifically on manuals and is not suitable for general-purpose type-setting.

cat is a standard Unix utility that reads files sequentially, writing them to standard output. The name is derived from its function to (con)catenate files. It has been ported to a number of operating systems.











