Manganese chloride may refer to:
- Manganese(II) chloride (manganous chloride, manganese dichloride), MnCl2, stable pink solid
- Manganese(III) chloride (manganic chloride, manganese trichloride), MnCl3, hypothetical chemical compound
Manganese chloride may refer to:

Chlorine is a chemical element with the symbol Cl and atomic number 17. The second-lightest of the halogens, it appears between fluorine and bromine in the periodic table and its properties are mostly intermediate between them. Chlorine is a yellow-green gas at room temperature. It is an extremely reactive element and a strong oxidising agent: among the elements, it has the highest electron affinity and the third-highest electronegativity on the revised Pauling scale, behind only oxygen and fluorine.

Manganese dioxide is the inorganic compound with the formula MnO
2. This blackish or brown solid occurs naturally as the mineral pyrolusite, which is the main ore of manganese and a component of manganese nodules. The principal use for MnO
2 is for dry-cell batteries, such as the alkaline battery and the zinc–carbon battery. MnO
2 is also used as a pigment and as a precursor to other manganese compounds, such as KMnO
4. It is used as a reagent in organic synthesis, for example, for the oxidation of allylic alcohols. MnO
2 is α polymorph that can incorporate a variety of atoms in the "tunnels" or "channels" between the manganese oxide octahedra. There is considerable interest in α-MnO
2 as a possible cathode for lithium-ion batteries.
In chemistry, water(s) of crystallization or water(s) of hydration are water molecules that are present inside crystals. Water is often incorporated in the formation of crystals from aqueous solutions. In some contexts, water of crystallization is the total mass of water in a substance at a given temperature and is mostly present in a definite (stoichiometric) ratio. Classically, "water of crystallization" refers to water that is found in the crystalline framework of a metal complex or a salt, which is not directly bonded to the metal cation.
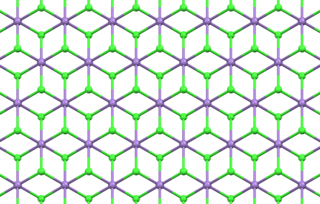
Manganese(II) chloride is the dichloride salt of manganese, MnCl2. This inorganic chemical exists in the anhydrous form, as well as the dihydrate (MnCl2·2H2O) and tetrahydrate (MnCl2·4H2O), with the tetrahydrate being the most common form. Like many Mn(II) species, these salts are pink, with the paleness of the color being characteristic of transition metal complexes with high spin d5 configurations.

Iron(II) chloride, also known as ferrous chloride, is the chemical compound of formula FeCl2. It is a paramagnetic solid with a high melting point. The compound is white, but typical samples are often off-white. FeCl2 crystallizes from water as the greenish tetrahydrate, which is the form that is most commonly encountered in commerce and the laboratory. There is also a dihydrate. The compound is highly soluble in water, giving pale green solutions.

A permanganate is a chemical compound containing the manganate(VII) ion, MnO−
4, the conjugate base of permanganic acid. Because the manganese atom is in the +7 oxidation state, the permanganate(VII) ion is a strong oxidizing agent. The ion is a transition metal oxo complex with tetrahedral geometry. Permanganate solutions are purple in color and are stable in neutral or slightly alkaline media. The exact chemical reaction is dependent upon the organic contaminants present and the oxidant utilized. For example, trichloroethane (C2H3Cl3) is oxidized by permanganate ions to form carbon dioxide (CO2), manganese dioxide (MnO2), hydrogen ions (H+), and chloride ions (Cl−).
Comproportionation or synproportionation is a chemical reaction where two reactants containing the same element but with different oxidation numbers, form a compound having an intermediate oxidation number. It is the opposite of disproportionation.

A zinc–carbon battery (or carbon zinc battery in U.S. English) is a dry cell primary battery that provides direct electric current from the electrochemical reaction between zinc and manganese dioxide (MnO2) in the presence of an electrolyte. It produces a voltage of about 1.5 volts between the zinc anode, which is typically constructed as a cylindrical container for the battery cell, and a carbon rod surrounded by a compound with a higher Standard electrode potential (positive polarity), known as the cathode, that collects the current from the manganese dioxide electrode. The name "zinc-carbon" is slightly misleading as it implies that carbon is acting as the oxidizing agent rather than the manganese dioxide.

The Leclanché cell is a battery invented and patented by the French scientist Georges Leclanché in 1866. The battery contained a conducting solution (electrolyte) of ammonium chloride, a cathode of carbon, a depolarizer of manganese dioxide (oxidizer), and an anode of zinc (reductant). The chemistry of this cell was later successfully adapted to manufacture a dry cell.

Manganese(II) sulfide is a chemical compound of manganese and sulfur. It occurs in nature as the mineral alabandite (isometric), rambergite (hexagonal), and recently found browneite.

Ammonium permanganate is the chemical compound NH4MnO4, or NH3·HMnO4. It is a water soluble, violet-brown or dark purple salt.
Organomanganese chemistry is the chemistry of organometallic compounds containing a carbon to manganese chemical bond. In a 2009 review, Cahiez et al. argued that as manganese is cheap and benign, organomanganese compounds have potential as chemical reagents, although currently they are not widely used as such despite extensive research.
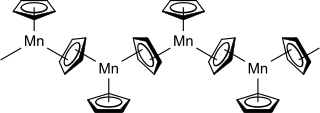
Manganocene or bis(cyclopentadienyl)manganese(II) is an organomanganese compound with the formula [Mn(C5H5)2]n. It is a thermochromic solid that degrades rapidly in air. Although the compound is of little utility, it is often discussed as an example of a metallocene with ionic character.

Manganese(II) iodide is the chemical compound composed of manganese and iodide with the formula MnI2. The anhydrous compound adopts the cadmium iodide crystal structure. The pink tetrahydrate is known. Unlike MnX2(H2O)4, which are cis for X = Cl, Br, the iodides are trans in MnI2(H2O)4.

Barium manganate is an inorganic compound with the formula BaMnO4. It is used as an oxidant in organic chemistry. It belongs to a class of compounds known as manganates in which the manganese resides in a +6 oxidation state. Manganate should not to be confused with permanganate which contains manganese(VII). Barium manganate is a powerful oxidant, popular in organic synthesis and can be used in a wide variety of oxidation reactions.
Manganese oxalate is a chemical compound, a salt of manganese and oxalic acid with the chemical formula MnC
2O
4. The compound creates light pink crystals, does not dissolve in water, and forms crystalline hydrates. It occurs naturally as the mineral Lindbergite.

Chromium(II) sulfide is an inorganic compound of chromium and sulfur with the chemical formula CrS. The compound forms black hexagonal crystals, insoluble in water.

In chemistry, a transition metal ether complex is a coordination complex consisting of a transition metal bonded to one or more ether ligand. The inventory of complexes is extensive. Common ether ligands are diethyl ether and tetrahydrofuran. Common chelating ether ligands include the glymes, dimethoxyethane (dme) and diglyme, and the crown ethers. Being lipophilic, metal-ether complexes often exhibit solubility in organic solvents, a property of interest in synthetic chemistry. In contrast, the di-ether 1,4-dioxane is generally a bridging ligand.
Manganese(III) chloride is the hypothetical inorganic compound with the formula MnCl3.

Bis(triphenylphosphineoxide) manganese(III) chloride is a coordination complex of manganese(III) chloride. Unlike most compounds containing "Mn(III)Cl3", [MnCl3(OPPh3)2] can be stored under normal laboratory conditions. It is a blue, paramagnetic solid.