Related Research Articles

The First Punic War was the first of three wars fought between Rome and Carthage, the two main powers of the western Mediterranean in the early 3rd century BC. For 23 years, in the longest continuous conflict and greatest naval war of antiquity, the two powers struggled for supremacy. The war was fought primarily on the Mediterranean island of Sicily and its surrounding waters, and also in North Africa. After immense losses on both sides, the Carthaginians were defeated and Rome gained territory from Carthage.
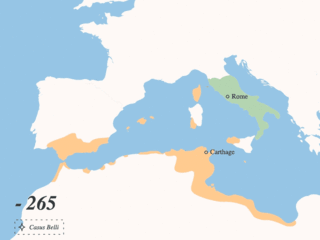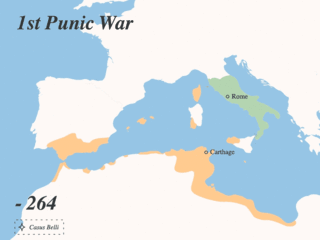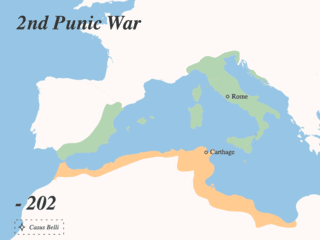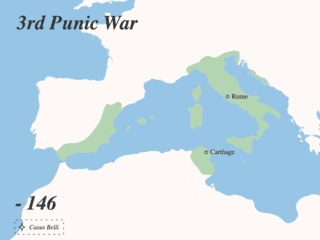
The Punic Wars were a series of wars between 264 and 146 BC fought between the Roman Republic and Ancient Carthage. Three wars took place, on both land and sea, across the western Mediterranean region and involved a total of forty-three years of warfare. The Punic Wars are also considered to include the four-year-long revolt against Carthage which started in 241 BC. Each war involved immense materiel and human losses on both sides.

The Second Punic War was the second of three wars fought between Carthage and Rome, the two main powers of the western Mediterranean in the 3rd century BC. For 17 years the two states struggled for supremacy, primarily in Italy and Iberia, but also on the islands of Sicily and Sardinia and, towards the end of the war, in North Africa. After immense materiel and human losses on both sides, the Carthaginians were once again defeated. Macedonia, Syracuse and several Numidian kingdoms were drawn into the fighting, and Iberian and Gallic forces fought on both sides. There were three main military theatres during the war: Italy, where Hannibal defeated the Roman legions repeatedly, with occasional subsidiary campaigns in Sicily, Sardinia and Greece; Iberia, where Hasdrubal, a younger brother of Hannibal, defended the Carthaginian colonial cities with mixed success before moving into Italy; and Africa, where Rome finally won the war.
This article concerns the period 269 BC – 260 BC.

The Third Punic War was the third and last of the Punic Wars fought between Carthage and Rome. The war was fought entirely within Carthaginian territory, in what is now northern Tunisia. When the Second Punic War ended in 201 BC one of the terms of the peace treaty prohibited Carthage from waging war without Rome's permission. Rome's ally, King Masinissa of Numidia, exploited this to repeatedly raid and seize Carthaginian territory with impunity. In 149 BC Carthage sent an army, under Hasdrubal, against Masinissa, the treaty notwithstanding. The campaign ended in disaster as the Battle of Oroscopa ended with a Carthaginian defeat and the surrender of the Carthaginian army. Anti-Carthaginian factions in Rome used the illicit military action as a pretext to prepare a punitive expedition.
Hamilcar Barca or Barcas was a Carthaginian general and statesman, leader of the Barcid family, and father of Hannibal, Hasdrubal and Mago. He was also father-in-law to Hasdrubal the Fair.

Hiero II, also called Hieron II, was the Greek tyrant of Syracuse, Greek Sicily, from 275 to 215 BC, and the illegitimate son of a Syracusan noble, Hierocles, who claimed descent from Gelon. He was a former general of Pyrrhus of Epirus and an important figure of the First Punic War. He figures in the story of famed thinker Archimedes shouting "Eureka".
Manius Valerius Maximus Messalla was consul in 263 BC with Manius Otacilius Crassus as his consular collegae. Messalla served as censor in 252 BC.

The siege of Carthage was the main engagement of the Third Punic War fought between Carthage and Rome. It consisted of the nearly-three-year siege of the Carthaginian capital, Carthage. In 149 BC, a large Roman army landed at Utica in North Africa. The Carthaginians hoped to appease the Romans, but despite the Carthaginians surrendering all of their weapons, the Romans pressed on to besiege the city of Carthage. The Roman campaign suffered repeated setbacks through 149 BC, only alleviated by Scipio Aemilianus, a middle-ranking officer, distinguishing himself several times. A new Roman commander took over in 148 BC, and fared equally badly. At the annual election of Roman magistrates in early 147 BC, the public support for Scipio was so great that the usual age restrictions were lifted to allow him to be appointed commander in Africa.

The Battle of Agrigentum was the first pitched battle of the First Punic War and the first large-scale military confrontation between Carthage and the Roman Republic. The battle was fought after a long siege which started in 262 BC and resulted both in a Roman victory and the beginning of Roman control of Sicily.

The Battle of the Lipari Islands or Battle of Lipara was a naval encounter fought in 260 BC during the First Punic War. A squadron of 20 Carthaginian ships commanded by Boödes surprised 17 Roman ships under the senior consul for the year Gnaeus Cornelius Scipio in Lipara Harbour. The inexperienced Romans made a poor showing, with all 17 of their ships captured, along with their commander.

The Battle of Mylae took place in 260 BC during the First Punic War and was the first real naval battle between Carthage and the Roman Republic. This battle was key in the Roman victory of Mylae as well as Sicily itself. It also marked Rome's first naval triumph and also the first use of the corvus in battle.

Sicilia was the first province acquired by the Roman Republic, encompassing the island of Sicily. The western part of the island was brought under Roman control in 241 BC at the conclusion of the First Punic War with Carthage. A praetor was regularly assigned to the island from c. 227 BC. The Kingdom of Syracuse under Hieron II remained an independent ally of Rome until its defeat in 212 BC during the Second Punic War. Thereafter the province included the whole of the island of Sicily, the island of Malta, and the smaller island groups.
The Treaty of Lutatius was the agreement between Carthage and Rome of 241 BC, that ended the First Punic War after 23 years of conflict. Most of the fighting during the war took place on, or in the waters around, the island of Sicily and in 241 BC a Carthaginian fleet was defeated by a Roman fleet commanded by Gaius Lutatius Catulus while attempting to lift the blockade of its last, beleaguered, strongholds there. Accepting defeat, the Carthaginian Senate ordered their army commander on Sicily, Hamilcar Barca, to negotiate a peace treaty with the Romans, on whatever terms he could negotiate. Hamilcar refused, claiming the surrender was unnecessary, and the negotiation of the peace terms was left to Gisco, the commander of Lilybaeum, as the next most senior Carthaginian on the island. A draft treaty was rapidly agreed upon, but when it was referred to Rome for ratification it was rejected.
The gens Otacilia, originally Octacilia, was a plebeian family at ancient Rome. The gens first rose to prominence during the First Punic War, but afterwards lapsed into obscurity. The first of the family to obtain the consulship was Manius Otacilius Crassus, in 263 BC.

The Battle of Messana in 264 BC was the first military clash between the Roman Republic and Carthage. It marked the start of the First Punic War. In that period, and after the recent successes in southern Italy, Sicily became of increasing strategic importance to Rome.
Lucius Valerius Flaccus was a Roman statesman and general during the middle era of the Roman Republic. He was one of the two consuls of 261 BCE, serving with Titus Otacilius Crassus. Together they fought in the ongoing First Punic War; they campaigned in Sicily. Before sailing to Sicily they strengthened the coastal defences of Italy against attacks by Hannibal Gisco, a Carthaginian admiral sent to raid the Tyrrhenian coast. The consuls besieged Mytistraton, but were eventually driven off by Hamilcar, the new commander of Carthage's Sicilian army, who inflicted a defeat on them at Thermae near Palermo. They returned to Italy were they started building a fleet. This fleet was the first Roman fleet of war ships ever and created after Carthaginian example. In 260, this fleet was ready.
Titus Otacilius Crassus was a Roman statesman and general during the middle era of the Roman Republic. He was one of the two consuls of 261 BCE, serving with Lucius Valerius Flaccus. During his consulship, he and his consular colleague Flaccus fought against the Carthaginians on Sicily as part of the ongoing First Punic War. Before sailing to Sicily they strengthened the coastal defences of Italy against attacks by Hannibal Gisco, a Carthaginian admiral sent to raid the Tyrrhenian coast. The consuls besieged Mytistraton, but were eventually driven off by Hamilcar, the new commander of Carthage's Sicilian army, who defeated them at Thermae near Palermo. They returned to Italy were they started building Rome's first warfleet, created after Carthaginian example. In 260, the fleet was ready and would be used by Gnaeus Cornelius Scipio Asina, one of the two consuls of that year.
Gnaeus Cornelius Blasio was a Roman statesman and general during the middle era of the Roman Republic. He was one of the two consuls of 257 BCE, serving with Gaius Atilius Regelus. Blasio was considered a princeps of the Senate. He was consul during the First Punic War against Carthage. During his consulship he commanded the Republic's land forces on Sicily, while his fellow consul Regelus led the fleet. He did not achieve any stunning victories, but focused on consolidating Rome's power on the island.
Gnaeus Servilius Caepio was a Roman statesman and general during the middle era of the Roman Republic. He was one of the two consuls of 253 BCE, serving with Gaius Sempronius Blaesus. He was consul during the First Punic War against Carthage. During his consulship Servilius Caepio commanded Rome's land forces on Sicily, while his consular colleague led a fleet to Africa.
References
- ↑ Nigel Bagnall (2008). The Punic Wars: Rome, Carthage and the Struggle for the Mediterranean. Random House. pp. 53f. ISBN 978-1-4090-2253-4.
- ↑ Polybius, 1.16.
- ↑ Treaty: Polybius 1.16.3--17.1; Diodorus 23.4.1; Zonaras 8 fr. 9.