
Technology is the application of conceptual knowledge to achieve practical goals, especially in a reproducible way. The word technology can also mean the products resulting from such efforts, including both tangible tools such as utensils or machines, and intangible ones such as software. Technology plays a critical role in science, engineering, and everyday life.

Transhumanism is a philosophical and intellectual movement that advocates the enhancement of the human condition by developing and making widely available new and future technologies that can greatly enhance longevity, cognition, and well-being.

Automation describes a wide range of technologies that reduce human intervention in processes, mainly by predetermining decision criteria, subprocess relationships, and related actions, as well as embodying those predeterminations in machines. Automation has been achieved by various means including mechanical, hydraulic, pneumatic, electrical, electronic devices, and computers, usually in combination. Complicated systems, such as modern factories, airplanes, and ships typically use combinations of all of these techniques. The benefit of automation includes labor savings, reducing waste, savings in electricity costs, savings in material costs, and improvements to quality, accuracy, and precision.
The term superhuman refers to humans, humanoids or other beings with qualities and abilities that exceed those naturally found in humans. These qualities may be acquired through natural ability, self-actualization or technological aids. The related concept of a super race refers to an entire category of beings with the same or varying superhuman characteristics, created from present-day human beings by deploying various means such as eugenics, euthenics, genetic engineering, nanotechnology, and/or brain–computer interfacing to accelerate the process of human evolution.

Post-scarcity is a theoretical economic situation in which most goods can be produced in great abundance with minimal human labor needed, so that they become available to all very cheaply or even freely.
Post-capitalism is in part a hypothetical state in which the economic systems of the world can no longer be described as forms of capitalism. Various individuals and political ideologies have speculated on what would define such a world. According to classical Marxist and social evolutionary theories, post-capitalist societies may come about as a result of spontaneous evolution as capitalism becomes obsolete. Others propose models to intentionally replace capitalism, most notably socialism, communism, anarchism, nationalism and degrowth.

Humanitarianism in raelian literature is a collection of economic ideas which, according to its creator Raël, is designed to complement Geniocracy.
Many of the tropes of science fiction can be viewed as similar to the goals of transhumanism. Science fiction literature contains many positive depictions of technologically enhanced human life, occasionally set in utopian societies. However, science fiction's depictions of technologically enhanced humans or other posthuman beings frequently come with a cautionary twist. The more pessimistic scenarios include many dystopian tales of human bioengineering gone wrong.
Emerging technologies are technologies whose development, practical applications, or both are still largely unrealized. These technologies are generally new but also include old technologies finding new applications. Emerging technologies are often perceived as capable of changing the status quo.

Giulio Prisco is an Italian information technology and virtual reality consultant; as well as a writer, futurist, transhumanist, and cosmist. He is an advocate of cryonics and contributes to the science and technology online magazine Tendencias21. He produced teleXLR8, an online talk program using virtual reality and video conferencing, and focused on highly imaginative science and technology. He writes and speaks on a wide range of topics, including science, information technology, emerging technologies, virtual worlds, space exploration and futurology.
"The Triple Revolution" was an open memorandum sent to U.S. President Lyndon B. Johnson and other government figures on March 22, 1964. It concerned three megatrends of the time: increasing use of automation, the nuclear arms race, and advancements in human rights. Drafted under the auspices of the Center for the Study of Democratic Institutions, it was signed by an array of noted social activists, professors, and technologists who identified themselves as the Ad Hoc Committee on the Triple Revolution. The chief initiator of the proposal was W. H. "Ping" Ferry, at that time a vice-president of CSDI, basing it in large part on the ideas of the futurist Robert Theobald.
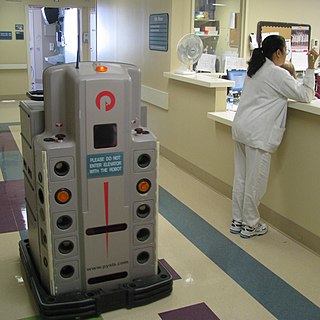
Technological unemployment is the loss of jobs caused by technological change. It is a key type of structural unemployment. Technological change typically includes the introduction of labour-saving "mechanical-muscle" machines or more efficient "mechanical-mind" processes (automation), and humans' role in these processes are minimized. Just as horses were gradually made obsolete as transport by the automobile and as labourer by the tractor, humans' jobs have also been affected throughout modern history. Historical examples include artisan weavers reduced to poverty after the introduction of mechanized looms. Thousands of man-years of work was performed in a matter of hours by the bombe codebreaking machine during World War II. A contemporary example of technological unemployment is the displacement of retail cashiers by self-service tills and cashierless stores.

"Fourth Industrial Revolution", "4IR", or "Industry 4.0" is a neologism describing rapid technological advancement in the 21st century. It follows the Third Industrial Revolution. The term was popularised in 2016 by Klaus Schwab, the World Economic Forum founder and executive chairman, who asserts that these developments represent a significant shift in industrial capitalism.

Martin Ford is an American futurist and author focusing on artificial intelligence and robotics, and the impact of these technologies on the job market, economy and society.
Robotic process automation (RPA) is a form of business process automation that is based on software robots (bots) or artificial intelligence (AI) agents. RPA should not be confused with artificial intelligence as it is based on automotive technology following a predefined workflow. It is sometimes referred to as software robotics.
In futurology, political science, and science fiction, a post-work society is a society in which the nature of work has been radically transformed and traditional employment has largely become obsolete due to technological progress.

The War on Normal People: The Truth About America's Disappearing Jobs and Why Universal Basic Income Is Our Future is a 2018 book written by Andrew Yang, an American entrepreneur and Venture for America founder, who would later run as a 2020 Democratic presidential candidate on policy strategies discussed in the book. It was published by Hachette Books in the United States on April 3, 2018. A paperback edition was released on April 2, 2019. Yang narrated an audiobook version released on YouTube in September 2018.

Work or labor is the intentional activity people perform to support the needs and desires of themselves, other people, or organizations. In the context of economics, work can be viewed as the human activity that contributes towards the goods and services within an economy.










