
John Keats was an English poet of the second generation of Romantic poets, along with Lord Byron and Percy Bysshe Shelley. His poems had been in publication for less than four years when he died of tuberculosis at the age of 25. They were indifferently received in his lifetime, but his fame grew rapidly after his death. By the end of the century, he was placed in the canon of English literature, strongly influencing many writers of the Pre-Raphaelite Brotherhood; the Encyclopædia Britannica of 1888 called one ode "one of the final masterpieces".

William Hazlitt was an English essayist, drama and literary critic, painter, social commentator, and philosopher. He is now considered one of the greatest critics and essayists in the history of the English language, placed in the company of Samuel Johnson and George Orwell. He is also acknowledged as the finest art critic of his age. Despite his high standing among historians of literature and art, his work is currently little read and mostly out of print.
Hyperion, a Fragment is an abandoned epic poem by 19th-century English Romantic poet John Keats. It was published in Lamia, Isabella, The Eve of St. Agnes, and Other Poems (1820). It is based on the Titanomachia, and tells of the despair of the Titans after their fall to the Olympians. Keats wrote the poem from late 1818 until the spring of 1819. The poem stops abruptly in the middle of the third book, with close to 900 lines having been completed. He gave it up as having "too many Miltonic inversions." He was also nursing his younger brother Tom, who died on 1 December 1818 of tuberculosis.

James Henry Leigh Hunt, best known as Leigh Hunt, was an English critic, essayist and poet.

"To Autumn" is a poem by English Romantic poet John Keats. The work was composed on 19 September 1819 and published in 1820 in a volume of Keats's poetry that included Lamia and The Eve of St. Agnes. "To Autumn" is the final work in a group of poems known as Keats's "1819 odes". Although personal problems left him little time to devote to poetry in 1819, he composed "To Autumn" after a walk near Winchester one autumnal evening. The work marks the end of his poetic career, as he needed to earn money and could no longer devote himself to the lifestyle of a poet. A little over a year after the publication of "To Autumn", Keats died in Rome.

"Ode to a Nightingale" is a poem by John Keats written either in the garden of the Spaniards Inn, Hampstead, London or, according to Keats' friend Charles Armitage Brown, under a plum tree in the garden of Keats' house at Wentworth Place, also in Hampstead. According to Brown, a nightingale had built its nest near the house that he shared with Keats in the spring of 1819. Inspired by the bird's song, Keats composed the poem in one day. It soon became one of his 1819 odes and was first published in Annals of the Fine Arts the following July. The poem is one of the most frequently anthologized in the English language.
"Negative capability" is the capacity of artists to pursue ideals of beauty, perfection and sublimity even when it leads them into intellectual confusion and uncertainty, as opposed to a preference for philosophical certainty over artistic beauty. The term, first used by John Keats in 1817, has been subsequently used by poets, philosophers and literary theorists to describe the ability to perceive and recognize truths beyond the reach of what Keats called "consecutive reasoning".
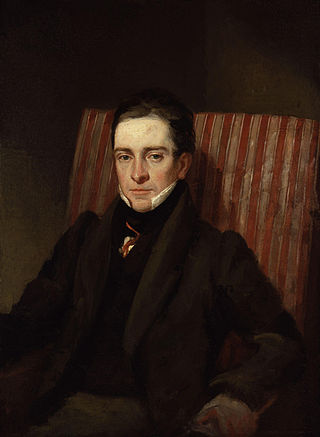
Thomas Hood was an English poet, author and humorist, best known for poems such as "The Bridge of Sighs" and "The Song of the Shirt". Hood wrote regularly for The London Magazine, Athenaeum, and Punch. He later published a magazine largely consisting of his own works. Hood, never robust, had lapsed into invalidism by the age of 41 and died at the age of 45. William Michael Rossetti in 1903 called him "the finest English poet" between the generations of Shelley and Tennyson. Hood was the father of the playwright and humorist Tom Hood (1835–1874) and the children's writer Frances Freeling Broderip (1830–1878).

The "Ode on Indolence" is one of five odes composed by English poet John Keats in the spring of 1819. The others were "Ode on a Grecian Urn", "Ode on Melancholy", "Ode to a Nightingale" and "Ode to Psyche". The poem describes the state of indolence, a word which is synonymous with "avoidance" or "laziness". The work was written during a time when Keats was presumably more than usually occupied with his material prospects. After finishing the spring poems, Keats wrote in June 1819 that its composition brought him more pleasure than anything else he had written that year. Unlike the other odes he wrote that year, "Ode on Indolence" was not published until 1848, 27 years after his death.
"When I Have Fears" is an Elizabethan sonnet by the English Romantic poet John Keats. The 14-line poem is written in iambic pentameter and consists of three quatrains and a couplet. Keats wrote the poem between 22 and 31 January 1818. It was published (posthumously) in 1848 in Life, Letters, and Literary Remains, of John Keats by Richard Monckton Milnes.

Adonais: An Elegy on the Death of John Keats, Author of Endymion, Hyperion, etc. is a pastoral elegy written by Percy Bysshe Shelley for John Keats in 1821, and widely regarded as one of Shelley's best and best-known works. The poem, which is in 495 lines in 55 Spenserian stanzas, was composed in the spring of 1821 immediately after 11 April, when Shelley heard of Keats' death. It is a pastoral elegy, in the English tradition of John Milton's Lycidas. Shelley had studied and translated classical elegies. The title of the poem is modelled on ancient works, such as Achilleis, an epic poem by the 1st-century AD Roman poet Statius, and refers to the untimely death of the Greek Adonis, a god of fertility. Some critics suggest that Shelley used Virgil's tenth Eclogue, in praise of Cornelius Gallus, as a model.

Keats House is a writer's house museum in what was once the home of the Romantic poet John Keats. It is in Keats Grove, Hampstead, toward the edge of inner north London. Maps before about 1915 show the road with one of its earlier names, John Street; the road has also been known as Albion Grove. The building was originally a pair of semi-detached houses known as "Wentworth Place". John Keats lodged in one of them with his friend Charles Brown from December 1818 to May 1820, and then in the other half of the house with the Brawne family from August to September 1820. These were perhaps Keats's most productive years. According to Brown, "Ode to a Nightingale" was written under a plum tree in the garden.

Endymion is a poem by John Keats first published in 1818 by Taylor and Hessey of Fleet Street in London. John Keats dedicated this poem to the late poet Thomas Chatterton. The poem begins with the line "A thing of beauty is a joy for ever". Endymion is written in rhyming couplets in iambic pentameter. Keats based the poem on the Greek myth of Endymion, the shepherd beloved of the moon goddess Selene. The poem elaborates on the original story and renames Selene "Cynthia".

"Ode to Psyche" is a poem by John Keats written in spring 1819. The poem is the first of his 1819 odes, which include "Ode on a Grecian Urn" and "Ode to a Nightingale". "Ode to Psyche" is an experiment in the ode genre, and Keats's attempt at an expanded version of the sonnet format that describes a dramatic scene. The poem serves as an important departure from Keats's early poems, which frequently describe an escape into the pleasant realms of one's imagination. Keats uses the imagination to show the narrator's intent to resurrect Psyche and reincarnate himself into Eros (love). Keats attempts this by dedicating an "untrodden region" of his mind to the worship of the neglected goddess.
Ghost Trio is a television play, written in English by Samuel Beckett. It was written in 1975, taped in October 1976 and the first broadcast was on BBC2 on 17 April 1977 as part of The Lively Arts programme Beckett himself entitled Shades. Donald McWhinnie directed with Ronald Pickup and Billie Whitelaw. The play's original title was to be Tryst. "On Beckett’s notebook, the word was crossed out vigorously and the new title Ghost Trio written next to it. On the title page of the BBC script the same handwritten title change can be found, indicating that it must have been corrected at the very last minute."
John Hamilton Reynolds was an English poet, satirist, critic, and playwright. He was a close friend and correspondent of poet John Keats, whose letters to Reynolds constitute a significant body of Keats' poetic thought. Reynolds was also the brother-in-law of the writer and humorist Thomas Hood, who was married to his sister Jane.
This article lists the complete poetic bibliography of John Keats (1795–1821), which includes odes, sonnets and fragments not published within his lifetime, as well as two plays.

Characters of Shakespear's Plays is an 1817 book of criticism of Shakespeare's plays, written by early nineteenth century English essayist and literary critic William Hazlitt. Composed in reaction to the neoclassical approach to Shakespeare's plays typified by Samuel Johnson, it was among the first English-language studies of Shakespeare's plays to follow the manner of German critic August Wilhelm Schlegel, and, with the work of Samuel Taylor Coleridge, paved the way for the increased appreciation of Shakespeare's genius that was characteristic of later nineteenth-century criticism. It was also the first book to cover all of Shakespeare's plays, intended as a guide for the general reader.

Frances "Fanny" Brawne Lindon is best known as the fiancée and muse to English Romantic poet John Keats. As Fanny Brawne, she met Keats, who was her neighbour in Hampstead, at the beginning of his brief period of intense creative activity in 1818. Although his first written impressions of Brawne were quite critical, his imagination seems to have turned her into the goddess-figure he needed to worship, as expressed in Endymion, and scholars have acknowledged her as his muse.

The Golden Lion is a pub in Fulham, in the London Borough of Hammersmith and Fulham, London, England. It is located on Fulham High Street, to the east of Fulham Palace Gardens. Built in 1455 it is reported as the oldest pub in Fulham and was rebuilt by one of its Victorian owners. Notable patrons include the playwrights Shakespeare and Fletcher as well as Bishop Bonner.