Entre Rios or Entre Ríos may refer to:

Chusquea is a genus of evergreen bamboos in the grass family. Most of them are native to mountain habitats in Latin America, from Mexico to southern Chile and Argentina.

Companhia Energética de Minas Gerais S.A. is a Brazilian power company headquartered in Belo Horizonte, capital of the state of Minas Gerais. The company is one of the main electricity concessionaires in Brazil. It operates in the areas of generation, transmission, distribution and commercialization of electric energy and also in the distribution of natural gas. The company is responsible for 12% of the Brazil's distribution. It is the fourth-largest electricity company in Brazil by revenue after Eletrobras, Energisa and CPFL Energia.

The Maxakalían languages were first classified into the Jê languages. It was only in 1931 that Čestmír Loukotka separated them from the Jê family. Alfred Métraux and Curt Nimuendajú considered the Maxakalían family isolated from others. John Alden Mason suggests a connection with the Macro-Jê stock, confirmed by Aryon Rodrigues.

The Mantiqueira Mountains are a mountain range in Southeastern Brazil, with parts in the states of São Paulo, Minas Gerais and Rio de Janeiro. It rises abruptly from the northwestern bank of the Paraíba do Sul River and extends northeastward for approximately 320 km (200 mi), reaching a height of 2,798 m (9,180 ft) at Pedra da Mina. The mountains, which eventually merge with the Serra do Espinhaço, were originally forest-covered, except for the peaks that rise above the tree line. They provide charcoal and pasture for cattle; on the lower slopes there are several health and tourist resorts, such as Campos do Jordão, Brazil's highest city. The name Mantiqueira derives from a Tupi word meaning "mountains that cry", denoting the large number of springs and streams found there.

Purian is a pair of extinct languages of eastern Brazil:

BR-262 is an east-west highway connecting the Brazilian states of Espírito Santo, Minas Gerais, São Paulo and Mato Grosso do Sul.
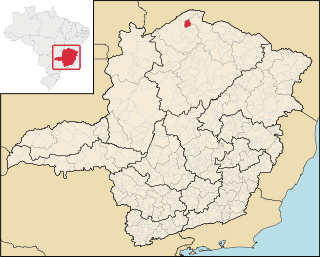
Miravânia is a municipality in the north of the state of Minas Gerais in Brazil. As of 2020 the population was 4,914 in an area of 603 km². It is located on the left bank of the São Francisco River. It is connected by dirt road to São João das Missões by paved BR-135. The distance is 112 km. Neighboring municipalities are: Montalvânia, Manga, Cônego Marinho, and São João das Missões.
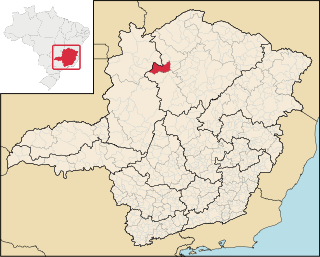
São Romão is a Brazilian municipality located in the north of the state of Minas Gerais. In 2020 the population was 12,529 in a total area of 2,432 km². It became a municipality in 1943.
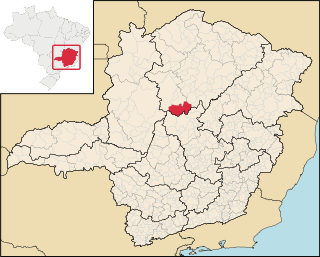
Lassance is a Brazilian municipality located in the north of the state of Minas Gerais. In 2020 the population was 6,503 in a total area of 3,213 km². It became a municipality in 1953.

The Paraopeba River is a river in the state of Minas Gerais, Brazil. In the Tupi language "Para" means "great river or sea," and "peba" means "flat," together meaning "flat river".

The Manso River is a river of Rio Negro Province of Argentina and Los Lagos Region of Chile, both part of Patagonia. The Manso River is located in the Andes. It follows a winding route through snow-capped mountains and connects many glacial lakes. The Manso flows generally southward until its confluence with the Puelo River in Chile. The river while in Argentina flows through the Nahuel Huapi National Park. Most of the southern part of Nahuel Huapi is in the drainage basin of the Manso River.
There are several rivers named Manso River.
Rio Manso is a municipality in the state of Minas Gerais in the Southeast region of Brazil.
MMX is the mining company of the EBX Group founded in 2005. It is engaged in the extraction, beneficiation and sale of iron ore and minerals in Brazil and Chile. The company was filed for bankruptcy in 2016, and it is part of the current investigation of fraud and money laundering linked to its owner Eike Batista.
Mata dos Ausentes Ecological Station is a state-administered ecological station in Minas Gerais, Brazil.

The Immediate Geographic Region of Oliveira is one of the 6 immediate geographic regions in the Intermediate Geographic Region of Divinópolis, one of the 70 immediate geographic regions in the Brazilian state of Minas Gerais and one of the 509 of Brazil, created by the National Institute of Geography and Statistics (IBGE) in 2017.












