
The terms anno Domini (AD) and before Christ (BC) are used when designating years in the Julian and Gregorian calendars. The term anno Domini is Medieval Latin and means "in the year of the Lord" but is often presented using "our Lord" instead of "the Lord", taken from the full original phrase "anno Domini nostri Jesu Christi", which translates to "in the year of our Lord Jesus Christ". The form "BC" is specific to English, and equivalent abbreviations are used in other languages: the Latin form, rarely used in English, is ante Christum natum (ACN) or ante Christum (AC).
Ælfheah, more commonly known today as Alphege, was an Anglo-Saxon Bishop of Winchester, later Archbishop of Canterbury. He became an anchorite before being elected abbot of Bath Abbey. His reputation for piety and sanctity led to his promotion to the episcopate and, eventually, to his becoming archbishop. Ælfheah furthered the cult of Dunstan and also encouraged learning. He was captured by Viking raiders in 1011 during the siege of Canterbury and killed by them the following year after refusing to allow himself to be ransomed. Ælfheah was canonised as a saint in 1078. Thomas Becket, a later Archbishop of Canterbury, prayed to Ælfheah just before his murder in Canterbury Cathedral in 1170.

Ab urbe condita, or anno urbis conditae, abbreviated as AUC or AVC, expresses a date in years since 753 BC, the traditional founding of Rome. It is an expression used in antiquity and by classical historians to refer to a given year in Ancient Rome. In reference to the traditional year of the foundation of Rome, the year 1 BC would be written AUC 753, whereas AD 1 would be AUC 754. The foundation of the Roman Empire in 27 BC would be AUC 727. The current year AD 2024 would be AUC 2777.

Classics or classical studies is the study of classical antiquity. In the Western world, classics traditionally refers to the study of Classical Greek and Roman literature and their related original languages, Ancient Greek and Latin. Classics also includes Greco-Roman philosophy, history, archaeology, anthropology, art, mythology and society as secondary subjects.

A calendar is a system of organizing days. This is done by giving names to periods of time, typically days, weeks, months and years. A date is the designation of a single and specific day within such a system. A calendar is also a physical record of such a system. A calendar can also mean a list of planned events, such as a court calendar, or a partly or fully chronological list of documents, such as a calendar of wills.
Mellitus was the first bishop of London in the Saxon period, the third Archbishop of Canterbury, and a member of the Gregorian mission sent to England to convert the Anglo-Saxons from their native paganism to Christianity. He arrived in 601 AD with a group of clergy sent to augment the mission, and was consecrated as Bishop of London in 604. Mellitus was the recipient of a famous letter from Pope Gregory I known as the Epistola ad Mellitum, preserved in a later work by the medieval chronicler Bede, which suggested the conversion of the Anglo-Saxons be undertaken gradually, integrating pagan rituals and customs. In 610, Mellitus returned to Italy to attend a council of bishops, and returned to England bearing papal letters to some of the missionaries.

Vitruvius was a Roman architect and engineer during the 1st century BC, known for his multi-volume work titled De architectura. As the only treatise on architecture to survive from antiquity, it has been regarded since the Renaissance as the first book on architectural theory, as well as a major source on the canon of classical architecture. It is not clear to what extent his contemporaries regarded his book as original or important.

In Greek mythology, sirens are humanlike beings with alluring voices; they appear in a scene in the Odyssey in which Odysseus saves his crew's lives. Roman poets place them on some small islands called Sirenum scopuli. In some later, rationalized traditions, the literal geography of the "flowery" island of Anthemoessa, or Anthemusa, is fixed: sometimes on Cape Pelorum and at others in the islands known as the Sirenuse, near Paestum, or in Capreae. All such locations were surrounded by cliffs and rocks.

Ancient Roman architecture adopted the external language of classical ancient Greek architecture for the purposes of the ancient Romans, but was different from Greek buildings, becoming a new architectural style. The two styles are often considered one body of classical architecture. Roman architecture flourished in the Roman Republic and to an even greater extent under the Empire, when the great majority of surviving buildings were constructed. It used new materials, particularly Roman concrete, and newer technologies such as the arch and the dome to make buildings that were typically strong and well engineered. Large numbers remain in some form across the former empire, sometimes complete and still in use today.
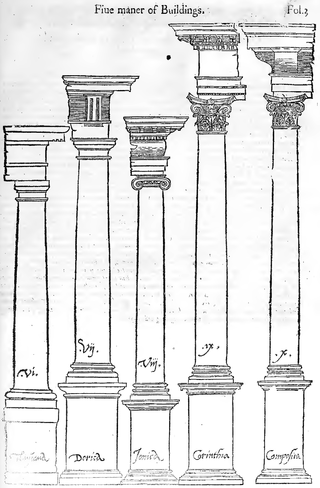
Classical architecture usually denotes architecture which is more or less consciously derived from the principles of Greek and Roman architecture of classical antiquity, or sometimes more specifically, from the works of the Roman architect Vitruvius. Different styles of classical architecture have arguably existed since the Carolingian Renaissance, and prominently since the Italian Renaissance. Although classical styles of architecture can vary greatly, they can in general all be said to draw on a common "vocabulary" of decorative and constructive elements. In much of the Western world, different classical architectural styles have dominated the history of architecture from the Renaissance until World War II. Classical architecture continues to inform many architects.

In Ancient Roman architecture, a basilica was a large public building with multiple functions that was typically built alongside the town's forum. The basilica was in the Latin West equivalent to a stoa in the Greek East. The building gave its name to the basilica architectural form.

Aulus Gellius was a Roman author and grammarian, who was probably born and certainly brought up in Rome. He was educated in Athens, after which he returned to Rome. He is famous for his Attic Nights, a commonplace book, or compilation of notes on grammar, philosophy, history, antiquarianism, and other subjects, preserving fragments of the works of many authors who might otherwise be unknown today.

Marcus Terentius Varro was a Roman polymath and a prolific author. He is regarded as ancient Rome's greatest scholar, and was described by Petrarch as "the third great light of Rome". He is sometimes called Varro Reatinus to distinguish him from his younger contemporary Varro Atacinus.
A barbarism is a nonstandard word, expression or pronunciation in a language, particularly one regarded as an error in morphology, while a solecism is an error in syntax. The label was originally applied to mixing Ancient Greek or Latin with other languages, but expanded to indicate any inappropriate words or expressions in classical studies and eventually to any language considered unpolished or rude. The term is used mainly for the written language.
In architecture, entasis is the application of a convex curve to a surface for aesthetic purposes, or increasing strength. Its best-known use is in certain orders of Classical columns that diminish in a very gentle curve, rather than in a straight line as they narrow going upward. The human eye would believe that the middle of the column was diminishing in a concave curve halfway up the column, and entasis corrects this.

Proportion is a central principle of architectural theory and an important connection between mathematics and art. It is the visual effect of the relationship of the various objects and spaces that make up a structure to one another and to the whole. These relationships are often governed by multiples of a standard unit of length known as a "module".

De architectura is a treatise on architecture written by the Roman architect and military engineer Marcus Vitruvius Pollio and dedicated to his patron, the emperor Caesar Augustus, as a guide for building projects. As the only treatise on architecture to survive from antiquity, it has been regarded since the Renaissance as the first known book on architectural theory, as well as a major source on the canon of classical architecture.

Domes were a characteristic element of the architecture of Ancient Rome and of its medieval continuation, the Byzantine Empire. They had widespread influence on contemporary and later styles, from Russian and Ottoman architecture to the Italian Renaissance and modern revivals. The domes were customarily hemispherical, although octagonal and segmented shapes are also known, and they developed in form, use, and structure over the centuries. Early examples rested directly on the rotunda walls of round rooms and featured a central oculus for ventilation and light. Pendentives became common in the Byzantine period, provided support for domes over square spaces.
Leofranc Holford-Strevens is an English classical scholar, an authority on the works of Aulus Gellius, and a former reader for the Oxford University Press.

Etruscan architecture was created between about 900 BC and 27 BC, when the expanding civilization of ancient Rome finally absorbed Etruscan civilization. The Etruscans were considerable builders in stone, wood and other materials of temples, houses, tombs and city walls, as well as bridges and roads. The only structures remaining in quantity in anything like their original condition are tombs and walls, but through archaeology and other sources we have a good deal of information on what once existed.















