Related Research Articles
Gnaeus Julius Agricola was a Roman Italo-Gallic general responsible for much of the Roman conquest of Britain. Written by his son-in-law Tacitus, the De vita et moribus Iulii Agricolae is the primary source for most of what is known about him, along with detailed archaeological evidence from northern Britain.
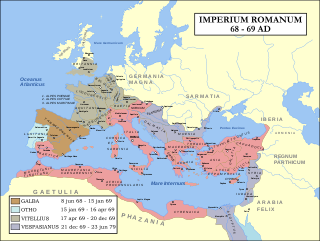
AD 69 (LXIX) was a common year starting on Sunday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Augustus and Rufinus. The denomination AD 69 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Gaius Suetonius Paulinus was a Roman general best known as the commander who defeated the rebellion of Boudica.

Aulus Plautius was a Roman politician and general of the mid-1st century. He began the Roman conquest of Britain in 43, and became the first governor of the new province, serving from 43 to 46.

Legio XX Valeria Victrix, in English Twentieth Victorious Valeria Legion was a legion of the Imperial Roman army.

The gens Julia was one of the most ancient patrician families in ancient Rome. Members of the gens attained the highest dignities of the state in the earliest times of the Republic. The first of the family to obtain the consulship was Gaius Julius Iulus in 489 BC. The gens is perhaps best known, however, for Gaius Julius Caesar, the dictator and grand uncle of the emperor Augustus, through whom the name was passed to the so-called Julio-Claudian dynasty of the first century AD. The nomen Julius became very common in imperial times, as the descendants of persons enrolled as citizens under the early emperors began to make their mark in history.
Quintus Petillius Cerialis Caesius Rufus, otherwise known as Quintus Petillius Cerialis, was a Roman general and administrator who served in Britain during Boudica's rebellion and went on to participate in the civil wars after the death of Nero. He later crushed the rebellion of Julius Civilis and returned to Britain as its governor.
Publius Petronius Turpilianus was a Roman senator who held a number of offices in the middle of the 1st century AD, most notably governor of Britain. He was an ordinary consul in the year 61 with Lucius Junius Caesennius Paetus as his colleague.
Marcus Trebellius Maximus was a Roman senator active during the reign of Nero. He was suffect consul for the nundinium of May to June 55 AD as the colleague of Seneca the Younger, replacing Publius Cornelius Dolabella.
Marcus Vettius Bolanus was a Roman senator and soldier. He was suffect consul for the nundinium of September-December 66 as the colleague of Marcus Arruntius Aquila.
Quintus Pompeius Falco was a Roman senator and general of the early 2nd century AD. He was governor of several provinces, most notably Roman Britain, where he hosted a visit to the province by the Emperor Hadrian in the last year. Falco achieved the rank of suffect consul for the nundinium of September to December 108 with Marcus Titius Lustricus Bruttianus as his colleague.
Gnaeus Julius Verus was Roman senator and general of the mid-2nd century AD. He was suffect consul, and governed several important imperial provinces: Germania Inferior, Britain, and Syria.

The gens Pompeia was a plebeian family at ancient Rome, first appearing in history during the second century BC, and frequently occupying the highest offices of the Roman state from then until imperial times. The first of the Pompeii to obtain the consulship was Quintus Pompeius in 141 BC, but by far the most illustrious of the gens was Gnaeus Pompeius, surnamed Magnus, a distinguished general under the dictator Sulla, who became a member of the First Triumvirate, together with Caesar and Crassus. After the death of Crassus, the rivalry between Caesar and Pompeius led to the Civil War, one of the defining events of the final years of the Roman Republic.
Titus Flavius T. f. T. n. Sabinus was a Roman politician and soldier. A native of Reate, he was the elder son of Titus Flavius Sabinus and Vespasia Polla, and brother of the Emperor Vespasian.
The gens Caelia was a plebeian family at ancient Rome. The nomen Caelius is frequently confounded with Coelius and Caecilius, with some individuals referred to as Caelius in manuscripts, while appearing as Coelius or Coilius on coins. Although the Caelii asserted their great antiquity, none of them attained any of the higher offices of the Roman state until the praetorship of Publius Caelius in 74 BC, and the first of this gens who obtained the consulship was Gaius Caelius Rufus in AD 17. The emperor Balbinus was a descendant of the Caelii.
Gaius Manlius Valens was a Roman senator of the late first century AD. He was selected as consul ordinarius in his ninetieth year, serving with Gaius Antistius Vetus in AD 96.
Gaius Curtius Justus was a Roman senator who held several posts in the emperor's service during the Antonine dynasty. He was suffect consul in 151 with Publius Julius Nauto as his colleague. Justus is known primarily through surviving inscriptions, although he could be identical with the Curtius Justus mentioned as a scriptor rei rusticae by Gargilius Martialis (2.1.4,7).
Lucius Roscius Aelianus Maecius Celer was a Roman senator of the second century. He was suffect consul in the nundinium of November-December AD 100 with Tiberius Claudius Sacerdos Julianus as his colleague. Celer is primarily known from inscriptions.
The gens Roscia, probably the same as Ruscia, was a plebeian family at ancient Rome. Members of this gens are mentioned as early as the fifth century BC, but after this time they vanish into obscurity until the final century of the Republic. A number of Roscii rose to prominence in imperial times, with some attaining the consulship from the first to the third centuries.
References
- ↑ Paul Gallivan, "The Fasti for A. D. 70-96", Classical Quarterly , 31 (1981), pp. 189, 215
- 1 2 Birley, The Fasti of Roman Britain, (Oxford: Clarendon Press, 1981) p. 232
- ↑ Tacitus, Histories 2.65
- ↑ Tacitus, Agricola 7
| Political offices | ||
|---|---|---|
| Preceded by Lucius Flavius Silva Nonius Bassus, and Lucius Asinius Pollio Verrucosus as suffect consuls | Suffect consul of the Roman Empire 81 with Gaius Julius Juvenalis | Succeeded by Lucius Julius Vettius Paullus, and Titus Junius Montanus as suffect consuls |