Related Research Articles

Cell biology is a branch of biology studying the structure and function of the cell, also known as the basic unit of life. Cell biology encompasses both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells and can be divided into many sub-topics which may include the study of cell metabolism, cell communication, cell cycle, biochemistry, and cell composition. The study of cells is performed using several techniques such as cell culture, various types of microscopy, and cell fractionation. These have allowed for and are currently being used for discoveries and research pertaining to how cells function, ultimately giving insight into understanding larger organisms. Knowing the components of cells and how cells work is fundamental to all biological sciences while also being essential for research in biomedical fields such as cancer, and other diseases. Research in cell biology is interconnected to other fields such as genetics, molecular genetics, biochemistry, molecular biology, medical microbiology, immunology, and cytochemistry.

Molecular biology is the branch of biology that concerns the molecular basis of biological activity in and between cells, including molecular synthesis, modification, mechanisms and interactions. The central dogma of molecular biology describes the process in which DNA is transcribed into RNA, then translated into protein.
Systems biology is the computational and mathematical analysis and modeling of complex biological systems. It is a biology-based interdisciplinary field of study that focuses on complex interactions within biological systems, using a holistic approach to biological research.
Louis "Lou" Siminovitch, is a Canadian molecular biologist. He was a pioneer in human genetics, researcher into the genetic basis of muscular dystrophy and cystic fibrosis, and helped establish Ontario programs exploring genetic roots of cancer.

Alphaherpesvirinae is a subfamily of viruses in the family Herpesviridae, primarily distinguished by reproducing more quickly than other subfamilies in the Herpesviridae. In animal virology the most important herpesviruses belong to the Alphaherpesvirinae. Pseudorabies virus is the causative agent of Aujeszky's disease in pigs and Bovine herpesvirus 1 is the causative agent of bovine infectious rhinotracheitis and pustular vulvovaginitis. Mammals serve as natural hosts. There are currently 42 species in this subfamily, divided among 5 genera with one species unassigned to a genus. Diseases associated with this subfamily include: HHV-1 and HHV-2: skin vesicles or mucosal ulcers, rarely encephalitis and meningitis, HHV-3: chickenpox (varicella) and shingles, GaHV-2: Marek's disease.

Israel Academy of Sciences and Humanities, based in Jerusalem, was established in 1961 by the State of Israel to foster contact between Israeli scholars in the sciences and humanities and create a think tank for advising the government on research projects of national importance. Its members include many of Israel's most distinguished scholars.

The Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai (ISMMS) is a private graduate medical school in Manhattan, New York City. Chartered by Mount Sinai Hospital in 1963, it is the academic teaching arm of the Mount Sinai Health System, which manages eight hospital campuses in the New York metropolitan area. Ranking 18th in the country for biomedical research, it leads the country in neuroscience research funding from the National Institutes of Health (#1), receiving $31.2 million in 2018. It attracted $348.5 million in total NIH funding in 2018.

James Edwin Darnell Jr. is an American biologist who made significant contributions to RNA processing and cytokine signaling and is author of the cell biology textbook Molecular Cell Biology.
Biology is the natural science that studies life and living organisms, including their physical structure, chemical processes, molecular interactions, physiological mechanisms, development and evolution. Despite the complexity of the science, certain unifying concepts consolidate it into a single, coherent field. Biology recognizes the cell as the basic unit of life, genes as the basic unit of heredity, and evolution as the engine that propels the creation and extinction of species. Living organisms are open systems that survive by transforming energy and decreasing their local entropy to maintain a stable and vital condition defined as homeostasis.
The Max Planck Institute of Molecular Plant Physiology is a German research institute for molecular plant physiology, based in the Golm district of Potsdam, Brandenburg. Founded on 1 January 1994, the MPIMP focuses on the study of the dynamics of plant metabolism and how that relates to the entire plant system. The institution is one of the 80 institutes in the Max Planck Society (Max-Planck-Gesellschaft).
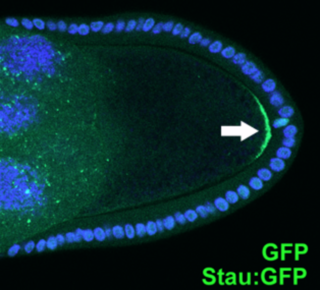
Cell polarity refers to spatial differences in shape, structure, and function within a cell. Almost all cell types exhibit some form of polarity, which enables them to carry out specialized functions. Classical examples of polarized cells are described below, including epithelial cells with apical-basal polarity, neurons in which signals propagate in one direction from dendrites to axons, and migrating cells. Furthermore, cell polarity is important during many types of asymmetric cell division to set up functional asymmetries between daughter cells.
Ihor R. Lemischka, Ph.D. was an internationally recognized stem cell biologist and stem cell research advocate and was both the Lillian and Henry M. Stratton Professor of Gene and Cell Medicine and Director of the Black Family Stem Cell Institute at Mount Sinai Medical Center in New York City.

Stuart A. Aaronson, M.D. is an American author and internationally recognized cancer biologist. He has authored more than 500 publications and holds over 50 patents, and was the Jane B. and Jack R. Aron Professor of Neoplastic Diseases and Chairman of Oncological Sciences at The Mount Sinai Hospital in New York City until March 2013, when he assumed the title of Founding Chair Emeritus of the Department of Oncological Sciences. The current Chairman of Oncological Sciences is Ramon E. Parsons.
Simon J. Hall, M.D., is the Associate Professor and Kyung Hyun Kim, M.D. Chair of Urology and Assistant Professor, Department of Gene and Cell Medicine at The Mount Sinai School of Medicine, as well as the Director of the Barbara and Maurice Deane Prostate Health and Research Center at The Mount Sinai Medical Center, both in New York City.
Ming-Ming Zhou, Ph.D., is an internationally recognized expert in structural and chemical biology, NMR spectroscopy of protein structure-function and rational small-molecule design. He is currently the Dr. Harold and Golden Lamport Professor and Chairman of the Department of Pharmacological Sciences and Co-Director of the Experimental Therapeutics Institute at the Mount Sinai School of Medicine and Mount Sinai Medical Center in New York City as well as Professor of Oncological Sciences.

Robert F. Margolskee is an American academic. He is the director of the Monell Chemical Senses Center and adjunct professor in the Department of Neuroscience at the Mount Sinai School of Medicine. Margolskee is also the a co-founder of Redpoint Bio. Margolskee has been a pioneer in the application of molecular biology and transgenic animal models to the study of taste transduction and chemosensation. He has made numerous seminal discoveries in the taste field, including the identification and molecular cloning of taste specific receptors, G proteins, channels and other taste signal transduction elements.

Eric Emil Schadt is an American mathematician and computational biologist. He is Dean for Precision Medicine at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai and Chief Executive Officer of Sema4, a spinout next generation health information company of the Mount Sinai Health System that provides advanced genomic testing and merges big data analytics with clinical diagnostics. He was previously founding director of the Icahn Institute for Genomics and Multiscale Biology and chair of the Department of Genetics and Genomics Sciences at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai. Schadt’s work combines supercomputing and advanced computational modeling with diverse biological data to understand the relationship between genes, gene products, other molecular features such as cells, organs, organisms, and communities and their impact on complex human traits such as disease. He is known for calling for a shift in molecular biology toward a network-oriented view of living systems to complement the reductionist, single-gene approaches that currently dominate biology to more accurately model the complexity of biological systems. Schadt has also worked to engage the public, encouraging people to participate in scientific research and helping them understand privacy concerns around DNA-based information.

Carlos Cordon-Cardo is a Spanish-born American physician and scientist known for his research in experimental pathology and molecular oncology. He holds the "Irene Heinz Given and John LaPorte Given" Chair in Pathology at Mount Sinai School of Medicine.

David Ron MD FRS FMedSci is a Professor of Cellular Pathophysiology and Clinical Biochemistry, Cambridge Institute for Medical Research and the Institute of Metabolic Science, University of Cambridge where he is also a Wellcome Trust Principal Research Fellow.
Howard J. Worman is an American physician and cell biologist. He is Professor of Medicine and Pathology and Cell Biology at Columbia University and Attending Physician at NewYork-Presbyterian Hospital.
References
- ↑ "Marek Mlodzik". Mt. Sinai Medical Center. Retrieved 25 January 2011.
| | This article about a biologist is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |