Related Research Articles

A carcinogen is any substance, radionuclide, or radiation that promotes carcinogenesis, the formation of cancer. This may be due to the ability to damage the genome or to the disruption of cellular metabolic processes. Several radioactive substances are considered carcinogens, but their carcinogenic activity is attributed to the radiation, for example gamma rays and alpha particles, which they emit. Common examples of non-radioactive carcinogens are inhaled asbestos, certain dioxins, and tobacco smoke. Although the public generally associates carcinogenicity with synthetic chemicals, it is equally likely to arise in both natural and synthetic substances. Carcinogens are not necessarily immediately toxic; thus, their effect can be insidious.

Food additives are substances added to food to preserve flavor or enhance taste, appearance, or other sensory qualities. Some additives have been used for centuries as part of an effort to preserve food, for example vinegar (pickling), salt (salting), smoke (smoking), sugar (crystallization), etc. This allows for longer-lasting foods such as bacon, sweets or wines. With the advent of processed foods in the second half of the twentieth century, many additives have been introduced, of both natural and artificial origin. Food additives also include substances that may be introduced to food indirectly in the manufacturing process, through packaging, or during storage or transport.
Acrylamide (or acrylic amide) is an organic compound with the chemical formula CH2=CHC(O)NH2. It is a white odorless solid, soluble in water and several organic solvents. From the chemistry perspective, acrylamide is a vinyl-substituted primary amide (CONH2). It is produced industrially mainly as a precursor to polyacrylamides, which find many uses as water-soluble thickeners and flocculation agents. It is highly toxic, likely to be carcinogenic, but its main derivative polyacrylamide is nontoxic. The possibility that this innocuous bulk chemical contains traces of its hazardous precursor has long attracted attention.
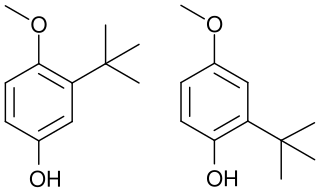
Butylated hydroxyanisole (BHA) is an antioxidant consisting of a mixture of two isomeric organic compounds, 2-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyanisole and 3-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyanisole. It is prepared from 4-methoxyphenol and isobutylene. It is a waxy solid used as a food additive with the E number E320. The primary use for BHA is as an antioxidant and preservative in food, food packaging, animal feed, cosmetics, rubber, and petroleum products. BHA also is commonly used in medicines, such as cholecalciferol, isotretinoin, lovastatin, and simvastatin, among others.

Glyphosate is a broad-spectrum systemic herbicide and crop desiccant. It is an organophosphorus compound, specifically a phosphonate, which acts by inhibiting the plant enzyme 5-enolpyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate synthase. It is used to kill weeds, especially annual broadleaf weeds and grasses that compete with crops. Its herbicidal effectiveness was discovered by Monsanto chemist John E. Franz in 1970. Monsanto brought it to market for agricultural use in 1974 under the trade name Roundup. Monsanto's last commercially relevant United States patent expired in 2000.

Piperonyl butoxide (PBO) is a pale yellow to light brown liquid organic compound used as a synergist component of pesticide formulations. That is, despite having no pesticidal activity of its own, it enhances the potency of certain pesticides such as carbamates, pyrethrins, pyrethroids, and rotenone. It is a semisynthetic derivative of safrole.
Furan is a heterocyclic organic compound, consisting of a five-membered aromatic ring with four carbon atoms and one oxygen atom. Chemical compounds containing such rings are also referred to as furans.
In genetics, genotoxicity describes the property of chemical agents that damages the genetic information within a cell causing mutations, which may lead to cancer. While genotoxicity is often confused with mutagenicity, all mutagens are genotoxic, whereas not all genotoxic substances are mutagenic. The alteration can have direct or indirect effects on the DNA: the induction of mutations, mistimed event activation, and direct DNA damage leading to mutations. The permanent, heritable changes can affect either somatic cells of the organism or germ cells to be passed on to future generations. Cells prevent expression of the genotoxic mutation by either DNA repair or apoptosis; however, the damage may not always be fixed leading to mutagenesis.

Diphenylamine is an organic compound with the formula (C6H5)2NH. The compound is a derivative of aniline, consisting of an amine bound to two phenyl groups. The compound is a colorless solid, but commercial samples are often yellow due to oxidized impurities. Diphenylamine dissolves well in many common organic solvents, and is moderately soluble in water. It is used mainly for its antioxidant properties. Diphenylamine is widely used as an industrial antioxidant, dye mordant and reagent and is also employed in agriculture as a fungicide and antihelmintic.
Patulin is an organic compound classified as a polyketide. It is a white powder soluble in acidic water and in organic solvents. It is a lactone that is heat-stable, so it is not destroyed by pasteurization or thermal denaturation. However, stability following fermentation is lessened. It is a mycotoxin produced by a variety of molds, in particular, Aspergillus and Penicillium and Byssochlamys. Most commonly found in rotting apples, the amount of patulin in apple products is generally viewed as a measure of the quality of the apples used in production. In addition, patulin has been found in other foods such as grains, fruits, and vegetables. Its presence is highly regulated.
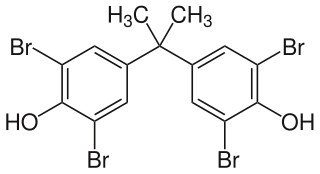
Tetrabromobisphenol A (TBBPA) is a brominated flame retardant. The compound is a white solid, although commercial samples appear yellow. It is one of the most common fire retardants.

Dioxins and dioxin-like compounds (DLCs) are a group of chemical compounds that are persistent organic pollutants (POPs) in the environment. They are mostly by-products of burning or various industrial processes - or, in case of dioxin-like PCBs and PBBs, unwanted minor components of intentionally produced mixtures.
Chromium toxicity refers to any poisonous toxic effect in an organism or cell that results from exposure to specific forms of chromium—especially hexavalent chromium. Hexavalent chromium and its compounds are toxic when inhaled or ingested. Trivalent chromium is a trace mineral that is essential to human nutrition. There is a hypothetical risk of genotoxicity in humans if large amounts of trivalent chromium were somehow able to enter living cells, but normal metabolism and cell function prevent this.

PhIP (2-Amino-1-methyl-6-phenylimidazo[4,5-b]pyridine) is one of the most abundant heterocyclic amines (HCAs) in cooked meat. PhIP is formed at high temperatures from the reaction between creatine or creatinine, amino acids, and sugar. PhIP formation increases with the temperature and duration of cooking and also depends on the method of cooking and the variety of meat being cooked. The U.S. Department of Health and Human Services National Toxicology Program has declared PhIP as "reasonably anticipated to be a human carcinogen". International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC), part of World Health Organization, has classified PhIP as IARC Group 2B carcinogen. There is sufficient evidence in experimental animals, as well as in vitro models, for the carcinogenicity of PhIP.

4-Methylimidazole is a heterocyclic organic chemical compound with molecular formula H
3C–C
3H
3N
2 or C
4H
6N
2. It is formally derived from imidazole through replacement of the hydrogen in position 4 by a methyl group. It is a slightly yellowish solid.
Toxicodynamics, termed pharmacodynamics in pharmacology, describes the dynamic interactions of a toxicant with a biological target and its biological effects. A biological target, also known as the site of action, can be binding proteins, ion channels, DNA, or a variety of other receptors. When a toxicant enters an organism, it can interact with these receptors and produce structural or functional alterations. The mechanism of action of the toxicant, as determined by a toxicant’s chemical properties, will determine what receptors are targeted and the overall toxic effect at the cellular level and organismal level.
The discipline of evidence-based toxicology (EBT) strives to transparently, consistently, and objectively assess available scientific evidence in order to answer questions in toxicology, the study of the adverse effects of chemical, physical, or biological agents on living organisms and the environment, including the prevention and amelioration of such effects. EBT has the potential to address concerns in the toxicological community about the limitations of current approaches to assessing the state of the science. These include concerns related to transparency in decision making, synthesis of different types of evidence, and the assessment of bias and credibility. Evidence-based toxicology has its roots in the larger movement towards evidence-based practices.

A pesticide, also called Plant Protection Product (PPP), which is a term used in regulatory documents, consists of several different components. The active ingredient in a pesticide is called “active substance” and these active substances either consist of chemicals or micro-organisms. The aims of these active substances are to specifically take action against organisms that are harmful to plants. In other words, active substances are the active components against pests and plant diseases.
Glyphosate-based herbicides are usually made of a glyphosate salt that is combined with other ingredients that are needed to stabilize the herbicide formula and allow penetration into plants. The glyphosate-based herbicide Roundup was first developed by Monsanto in the 1970s. It is used most heavily on corn, soy, and cotton crops that have been genetically modified to be resistant to the herbicide. Some products include two active ingredients, such as Enlist Duo which includes 2,4-D as well as glyphosate. As of 2010, more than 750 glyphosate products were on the market. The names of inert ingredients used in glyphosate formulations are usually not listed on the product labels.
Threshold dose is the minimum dose of drug that triggers minimal detectable biological effect in an animal. At extremely low doses, biological responses are absent for some of the drugs. The increase in dose above threshold dose induces an increase in the percentage of biological responses. Several benchmarks have been established to describe the effects of a particular dose of drug in a particular species, such as NOEL(no-observed-effect-level), NOAEL(no-observed-adverse-effect-level) and LOAEL(lowest-observed-adverse-effect-level). They are established by reviewing the available studies and animal studies. The application of threshold dose in risk assessment safeguards the participants in human clinical trials and evaluates the risks of chronic exposure to certain substances. However, the nature of animal studies also limits the applicability of experimental results in the human population and its significance in evaluating potential risk of certain substances. In toxicology, there are some other safety factors including LD50, LC50 and EC50.
References
- ↑ Benford, Diane; Bolger, P. Michael; Carthew, Philip; Coulet, Myriam; DiNovi, Michael; Leblanc, Jean-Charles; Renwick, Andrew G.; Setzer, Woodrow; Schlatter, Josef; Smith, Benjamin; Slob, Wout; Williams, Gary; Wildemann, Tanja (January 2010). "Application of the Margin of Exposure (MOE) approach to substances in food that are genotoxic and carcinogenic". Food and Chemical Toxicology. 48: S2–S24. doi:10.1016/j.fct.2009.11.003. PMID 20113851.
- ↑ "Margin of Exposure approach developed by EFSA". EFSA. Retrieved 20 November 2015.
- ↑ Lachenmeier, Dirk W.; Przybylski, Maria C.; Rehm, Jürgen (15 September 2012). "Comparative risk assessment of carcinogens in alcoholic beverages using the margin of exposure approach". International Journal of Cancer. 131 (6): E995–E1003. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.690.3319 . doi:10.1002/ijc.27553. PMID 22447328. S2CID 7021565.