Marjan Minnesma | |
|---|---|
 Minnesma (2015) | |
| Born | Marjan Minnesma 1966 (age 57–58) |
| Nationality | Dutch |
| Occupation | Activist |
| Known for | Co-founding Urgenda Foundation |
Marjan Minnesma (born 1966) is a Dutch activist. [1] [2]
Marjan Minnesma | |
|---|---|
 Minnesma (2015) | |
| Born | Marjan Minnesma 1966 (age 57–58) |
| Nationality | Dutch |
| Occupation | Activist |
| Known for | Co-founding Urgenda Foundation |
Marjan Minnesma (born 1966) is a Dutch activist. [1] [2]
Marjan Minnesma was born and raised in Amsterdam. [1] She holds a degree in international law on climate change. [3]
In 2022, she received Goldman Environmental Prize for suing the Dutch government over its carbon emissions plans. [3] She won this lawsuit, becoming first woman to successfully sue a government over carbon emissions. [4]
Minnesma is the founder of Urgenda Foundation, [5] which aims to help enforce national, European and international environment treaties.

A carbon footprint (or greenhouse gas footprint) is a calculated value or index that makes it possible to compare the total amount of greenhouse gases that an activity, product, company or country adds to the atmosphere. Carbon footprints are usually reported in tonnes of emissions (CO2-equivalent) per unit of comparison. Such units can be for example tonnes CO2-eq per year, per kilogram of protein for consumption, per kilometer travelled, per piece of clothing and so forth. A product's carbon footprint includes the emissions for the entire life cycle. These run from the production along the supply chain to its final consumption and disposal.
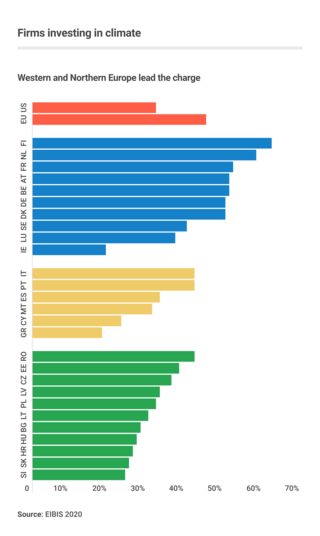
Business action on climate change is a topic which since 2000 includes a range of activities relating to climate change, and to influencing political decisions on climate change-related regulation, such as the Kyoto Protocol. Major multinationals have played and to some extent continue to play a significant role in the politics of climate change, especially in the United States, through lobbying of government and funding of climate change deniers. Business also plays a key role in the mitigation of climate change, through decisions to invest in researching and implementing new energy technologies and energy efficiency measures.

The CDP is an international non-profit organisation based in the United Kingdom, Japan, India, China, Germany, Brazil and the United States that helps companies, cities, states, regions and public authorities disclose their environmental impact. It aims to make environmental reporting and risk management a business norm, driving disclosure, insight, and action towards a sustainable economy. In 2022, nearly 18,700 organizations disclosed their environmental information through CDP.

The Virgin Earth Challenge was a competition offering a $25 million prize for whoever could demonstrate a commercially viable design which results in the permanent removal of greenhouse gases out of the Earth's atmosphere to contribute materially in global warming avoidance. The prize was conceived by Richard Branson, and was announced in London on 9 February 2007 by Branson and former US Vice President Al Gore.

Carbon emission trading (also called carbon market, emission trading scheme (ETS) or cap and trade) is a type of emissions trading scheme designed for carbon dioxide (CO2) and other greenhouse gases (GHGs). A form of carbon pricing, its purpose is to limit climate change by creating a market with limited allowances for emissions. Carbon emissions trading is a common method that countries use to attempt to meet their pledges under the Paris Agreement, with schemes operational in China, the European Union, and other countries.

Climate change is impacting the environment and human population of the United Kingdom (UK). The country's climate is becoming warmer, with drier summers and wetter winters. The frequency and intensity of storms, floods, droughts and heatwaves is increasing, and sea level rise is impacting coastal areas. The UK is also a contributor to climate change, having emitted more greenhouse gas per person than the world average. Climate change is having economic impacts on the UK and presents risks to human health and ecosystems.
The climate change policy of the United States has major impacts on global climate change and global climate change mitigation. This is because the United States is the second largest emitter of greenhouse gasses in the world after China, and is among the countries with the highest greenhouse gas emissions per person in the world. Cumulatively, the United States has emitted over a trillion metric tons of greenhouse gases, more than any country in the world.

Individual action on climate change is about personal choices that everyone can make to reduce the greenhouse gas emissions of their lifestyles. Such personal choices are related to the way people travel, their diet, shopping habits, consumption of goods and services, number of children they have and so on. Individuals can also get active in local and political advocacy work around climate action. People who wish to reduce their carbon footprint, can for example reduce their air travel for holidays, use bicycles instead of cars on a daily basis, eat a plant-based diet, and use consumer products for longer. Avoiding meat and dairy products has been called "the single biggest way" how individuals can reduce their environmental impacts.

Marie Corinne Lyne Le Quéré is a Canadian scientist. She is Royal Society Research Professor of Climate Change Science at the University of East Anglia and former Director of Tyndall Centre for Climate Change Research. She is the chair of the French High Council on Climate and member of the UK Climate Change Committee. Her research focuses on the interactions between the carbon cycle and climate change.

The climate movement is a global social movement focused on pressuring governments and industry to take action addressing the causes and impacts of climate change. Environmental non-profit organizations have engaged in significant climate activism since the late 1980s and early 1990s, as they sought to influence the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC). Climate activism has become increasingly prominent over time, gaining significant momentum during the 2009 Copenhagen Summit and particularly following the signing of the Paris Agreement in 2016.

Climate change litigation, also known as climate litigation, is an emerging body of environmental law using legal practice to set case law precedent to further climate change mitigation efforts from public institutions, such as governments and companies. Finding that climate change politics provides insufficient climate change mitigation for their tastes, activists and lawyers have increased efforts to use national and international judiciary systems to advance the effort. Climate litigation typically engages in one of five types of legal claims: Constitutional law, administrative law, private law, fraud or consumer protection, or human rights.

Climate change in Suriname is leading to warmer temperatures and more extreme weather events in Suriname. As a relatively poor country, its contributions to global climate change have been limited. Because of the large forest cover, the country has been running a carbon negative economy since 2014.
Elisabeth Holland is an American climate scientist who focuses on how the carbon and nitrogen cycles interact with earth systems. She has become a key player in the international climate debate. She is currently a professor of climate change at the University of the South Pacific. She is also the director of the Pacific Center for Environmental and Sustainable Development.

State of the Netherlands v Urgenda Foundation (2019) is climate change litigation heard by the Supreme Court of the Netherlands related to government efforts to curtail carbon dioxide emissions. The case was brought against the Dutch government in 2013, arguing the government, by not meeting a minimum carbon dioxide emission-reduction goal established by scientists to avert harmful climate change, was endangering the human rights of Dutch citizens as set by national and European Union laws.
Urgenda is a nonprofit foundation (stichting) in the Netherlands which aims to help enforce national, European and international environment treaties. In 2013, Urgenda filed a lawsuit against the state of the Netherlands – respectively also against the government – at the court of The Hague, to force them to make more effective policies that reduce the amount of emissions, with the aim to protect the people of the Netherlands against the effects of climate change and pollution.
The environmental policy of the Joe Biden administration includes a series of laws, regulations, and programs introduced by United States President Joe Biden since he took office in January 2021. Many of the actions taken by the Biden administration reversed the policies of his predecessor, Donald Trump. Biden's climate change policy focuses on reducing greenhouse gas emissions, similar to the efforts taken by the Obama administration. Biden promised to end and reverse deforestation and land degradation by 2030. The main climate target of the Biden administration is to reduce greenhouse gas emissions by the United States to net zero by 2050. A climate team was created to lead the effort.
Tessa Khan is an environmental lawyer who lives in the United Kingdom. She co-founded and is co-director of the Climate Litigation Network, which supports legal cases related to climate change mitigation and climate justice.

Milieudefensie v Royal Dutch Shell (2021) is a human rights law and tort law case heard by the district court of The Hague in the Netherlands in 2021 related to efforts by several NGO's to curtail carbon dioxide emissions by multinational corporations. It was brought by the Dutch branch of Friends of the Earth and a group of other NGO's against the oil corporation, Shell plc. In May 2021, the court ordered Shell to reduce its global carbon emissions from its 2019 levels by 45% by 2030, relating not only to the emissions from its operations, but also those from the products it sells. It is considered to be the first major climate change litigation ruling against a corporation.
Kimiko Hirata is a Japanese climate activist. As a founder of the Kiko Network, a non-governmental organization, she has campaigned for emissions reductions for more than 20 years. As of December 2022, her grassroots work has led to the cancellation of 17 planned coal-power plants. Hirata also led landmark coal divestment campaigns against Mizuho Financial Group and Mitsubishi UFJ. She currently serves as executive director for the Tokyo-based think tank, Climate Integrate, which focuses on accelerating decarbonization.
Alexandra Narváez Trujillo is an Ecuadorian scientist and Indigenous leader who advocates for the protection of her community's lands and cultures. She is a professor at the School of Biological Sciences at the Pontifical Catholic University of Ecuador, where she has conducted research on the bioactivity of Ecuadorian fungal endophytes. In addition to her scientific career, Narváez is an Indigenous leader and activist in Ecuador, and has played a crucial role in her community's efforts to defend their rights to land and cultural survival in the Amazon rainforest. She has received numerous awards and honors for her contributions to science and Indigenous activism, including the 2022 Goldman Environmental Prize.