
Encephalitis is inflammation of the brain. The severity can be variable with symptoms including reduction or alteration in consciousness, headache, fever, confusion, a stiff neck, and vomiting. Complications may include seizures, hallucinations, trouble speaking, memory problems, and problems with hearing.
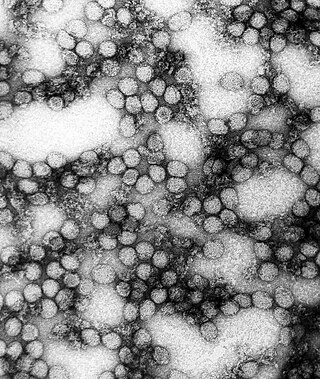
Flavivirus, renamed Orthoflavivirus in 2023, is a genus of positive-strand RNA viruses in the family Flaviviridae. The genus includes the West Nile virus, dengue virus, tick-borne encephalitis virus, yellow fever virus, Zika virus and several other viruses which may cause encephalitis, as well as insect-specific flaviviruses (ISFs) such as cell fusing agent virus (CFAV), Palm Creek virus (PCV), and Parramatta River virus (PaRV). While dual-host flaviviruses can infect vertebrates as well as arthropods, insect-specific flaviviruses are restricted to their competent arthropods. The means by which flaviviruses establish persistent infection in their competent vectors and cause disease in humans depends upon several virus-host interactions, including the intricate interplay between flavivirus-encoded immune antagonists and the host antiviral innate immune effector molecules.

Arbovirus is an informal name for any virus that is transmitted by arthropod vectors. The term arbovirus is a portmanteau word. Tibovirus is sometimes used to more specifically describe viruses transmitted by ticks, a superorder within the arthropods. Arboviruses can affect both animals and plants. In humans, symptoms of arbovirus infection generally occur 3–15 days after exposure to the virus and last three or four days. The most common clinical features of infection are fever, headache, and malaise, but encephalitis and viral hemorrhagic fever may also occur.

Geographic Resources Analysis Support System is a geographic information system (GIS) software suite used for geospatial data management and analysis, image processing, producing graphics and maps, spatial and temporal modeling, and visualizing. It can handle raster, topological vector, image processing, and graphic data.

Bunyavirales is an order of segmented negative-strand RNA viruses with mainly tripartite genomes. Member viruses infect arthropods, plants, protozoans, and vertebrates. It is the only order in the class Ellioviricetes. The name Bunyavirales derives from Bunyamwera, where the original type species Bunyamwera orthobunyavirus was first discovered. Ellioviricetes is named in honor of late virologist Richard M. Elliott for his early work on bunyaviruses.

A transport network, or transportation network, is a network or graph in geographic space, describing an infrastructure that permits and constrains movement or flow. Examples include but are not limited to road networks, railways, air routes, pipelines, aqueducts, and power lines. The digital representation of these networks, and the methods for their analysis, is a core part of spatial analysis, geographic information systems, public utilities, and transport engineering. Network analysis is an application of the theories and algorithms of graph theory and is a form of proximity analysis.
A GIS software program is a computer program to support the use of a geographic information system, providing the ability to create, store, manage, query, analyze, and visualize geographic data, that is, data representing phenomena for which location is important. The GIS software industry encompasses a broad range of commercial and open-source products that provide some or all of these capabilities within various information technology architectures.
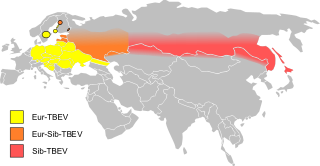
Tick-borne encephalitis (TBE) is a viral infectious disease involving the central nervous system. The disease most often manifests as meningitis, encephalitis or meningoencephalitis. Myelitis and spinal paralysis also occurs. In about one third of cases sequelae, predominantly cognitive dysfunction, persist for a year or more.

Tick-borne encephalitis virus (TBEV) is a positive-strand RNA virus associated with tick-borne encephalitis in the genus Flavivirus.

Solomon 'Sol' Katz was an American software developer who pioneered geospatial computer software and left behind a large body of work in the form of computer applications and format specifications while at the U.S. Bureau of Land Management. This early archive provided both source code and applications freely available to the community, including the Windows application PC-MOSS, where MOSS is the earliest known Open Source Geographic Information System. Katz was also a frequent contributor to many geospatial list servers.
A Web Map Service (WMS) is a standard protocol developed by the Open Geospatial Consortium in 1999 for serving georeferenced map images over the Internet. These images are typically produced by a map server from data provided by a GIS database.

Viral encephalitis is inflammation of the brain parenchyma, called encephalitis, by a virus. The different forms of viral encephalitis are called viral encephalitides. It is the most common type of encephalitis and often occurs with viral meningitis. Encephalitic viruses first cause infection and replicate outside of the central nervous system (CNS), most reaching the CNS through the circulatory system and a minority from nerve endings toward the CNS. Once in the brain, the virus and the host's inflammatory response disrupt neural function, leading to illness and complications, many of which frequently are neurological in nature, such as impaired motor skills and altered behavior.
This is a comparison of notable GIS software. To be included on this list, the software must have a linked existing article.
The Open Source Geospatial Foundation (OSGeo), is a non-profit non-governmental organization whose mission is to support and promote the collaborative development of open geospatial technologies and data. The foundation was formed in February 2006 to provide financial, organizational and legal support to the broader Libre/Free and open-source geospatial community. It also serves as an independent legal entity to which community members can contribute code, funding and other resources.

The Geospatial Data Abstraction Library (GDAL) is a computer software library for reading and writing raster and vector geospatial data formats, and is released under the permissive X/MIT style free software license by the Open Source Geospatial Foundation. As a library, it presents a single abstract data model to the calling application for all supported formats. It may also be built with a variety of useful command line interface utilities for data translation and processing. Projections and transformations are supported by the PROJ library.
Powassan virus (POWV) is a Flavivirus transmitted by ticks, found in North America and in the Russian Far East. It is named after the town of Powassan, Ontario, where it was identified in a young boy who eventually died from it. It can cause encephalitis, inflammation of the brain. No approved vaccine or antiviral drug exists. Prevention of tick bites is the best precaution.

Tick-borne encephalitis vaccine is a vaccine used to prevent tick-borne encephalitis (TBE). The disease is most common in Central and Eastern Europe, and Northern Asia. More than 87% of people who receive the vaccine develop immunity. It is not useful following the bite of an infected tick. It is given by injection into a muscle.
GIS Live DVD is a type of the thematic Live CD containing GIS/RS applications and related tutorials, and sample data sets. The general sense of a GIS Live DVD is to demonstrate the power of FLOSS GIS and encourage users to start on FLOSS GIS. However, a disc can be used for GIS data processing and training, too. A disc usually includes some selected Linux-based or Wine (software)-enabled Windows applications for GIS and Remote Sensing use. Using this disc the end users can execute GIS functions to get experience in free and open source software solutions or solve some simple business operations. The set-up and the operating behaviour of the applications can also be studied prior to building real FLOSS GIS-based systems. Recently a LiveDVD image is stored and booted from USB.
Patricia (Pat) Anne Nuttall, OBE is a British virologist and acarologist known for her research on tick-borne diseases. Her discoveries include the fact that pathogens can be transmitted between vectors feeding on a host without being detectable in the host's blood. She is also a science administrator who served as the director of the Natural Environment Research Council (NERC) Centre for Ecology & Hydrology (2001–11). As of 2015, she is professor of arbovirology in the Department of Zoology of the University of Oxford.

Duccio Rocchini is an Italian professor. Since 2019, he has been serving as a full professor at the University of Bologna and holds an honorary professorship at the Czech University of Life Sciences Prague.













