Related Research Articles

The Eastern Highlands, also known as the Manica Highlands, is a mountain range on the border of Zimbabwe and Mozambique. The Eastern Highlands extend north and south for about 300 kilometres (190 mi) through Zimbabwe's Manicaland Province and Mozambique's Manica Province.

Brachystegia spiciformis, commonly known as zebrawood, or msasa, is a medium-sized African tree having compound leaves and racemes of small fragrant green flowers. The tree is broad and has a distinctive amber and wine red colour when the young leaves sprout during spring (August–September). It grows in savanna, both open woodland and closed woodland of Southern and Eastern Africa, mostly Tanzania, Zambia, Zimbabwe, Malawi and Mozambique. The word msasa is commonly used as a proper name in African place names. The word also means 'rough plant' in Swahili. Other common names: mundu, myombo, mtondo (Tanzania), muputu (Zambia). The plant is known in the Venda language as mutsiwa, which means 'the one that is left behind'. An outlying population of Brachystegia has recently been discovered in the Soutpansberg mountains of northern South Africa. This tree is a protected species in South Africa.
Chipinge District is a district in Manicaland Province of eastern Zimbabwe. The administrative headquarters is Chipinge.

Brachystegia tamarindoides, known as mu'unze and also as the mountain acacia, is a medium-sized tree with smooth grey bark, bluish-green leaves and small creamy-white flowers that produce copious amounts of pollen and nectar. It is almost always very close to upturned umbrella shaped with a partially developed flat top, making it easy to recognise in mixed woodland. In this it differs from most of the other Brachystegia species that have variable shapes. The leaves are feathery in appearance, with around 10-12 leaflets arrayed along each leaf stalk.

Miombo woodland is a tropical and subtropical grasslands, savannas, and shrublands biome located in central and southern tropical Africa. It includes three woodland savanna ecoregions characterized by the dominant presence of Brachystegia and Julbernardia species of trees, and has a range of climates ranging from humid to semi-arid, and tropical to subtropical or even temperate. The trees characteristically shed their leaves for a short period in the dry season to reduce water loss and produce a flush of new leaves just before the onset of the wet season with rich gold and red colours masking the underlying chlorophyll, reminiscent of autumn colours in the temperate zone.

Brachystegia is a genus of tree of the subfamily Detarioideae that is native to tropical Africa.

The Bvumba Mountains or Vumba Mountains straddle the Zimbabwe–Mozambique border, and lie some 10 km southeast of the city of Mutare. The Bvumba rise to Castle Beacon at 1,911 metres, and are, together with the Chimanimani Mountains to the south and Nyanga Mountains to the north, part of the Eastern Highlands of the Manicaland and adjacent Manica provinces. They are referred to as the "Mountains of the Mist", as so often the early morning starts with a mist which clears by mid-morning. Although lying mostly within Zimbabwe, the mountains extend north-eastward to Mount Vumba in Mozambique. They are capped by cool, green hills which shelter country hotels, a casino and golf course at the Leopard Rock Hotel and a Botanical Garden with one of the best views in Africa. The mountains are also known for their coffee plantations.

The wildlife of Zimbabwe occurs foremost in remote or rugged terrain, in national parks and private wildlife ranches, in miombo woodlands and thorny acacia or kopje. The prominent wild fauna includes African buffalo, African bush elephant, black rhinoceros, southern giraffe, African leopard, lion, plains zebra, and several antelope species.

The Eastern miombo woodlands (AT0706) are an ecoregion of grassland and woodland in northern Mozambique, southern Tanzania, and southeastern Malawi.

The wildlife of Mozambique consists of the flora and fauna of this country in southeastern Africa. Mozambique has a range of different habitat types and an ecologically rich and diverse wildlife. This includes 236 species of mammal, 740 species of bird and 5,692 species of vascular plant. The Maputaland-Pondoland-Albany hotspot, with significantly high levels of biodiversity, stretches from the southern tip of Mozambique into northeastern South Africa.

The Southern Zanzibar–Inhambane coastal forest mosaic, also known as the Southern Swahili coastal forests and woodlands, is a tropical moist broadleaf forest ecoregion of eastern Africa. It is a southern variation of Northern Zanzibar-Inhambane coastal forest mosaic. The ecoregion supports habitats of forest, savanna and swamps. The southern portion of the ecoregion is not as well studied due to the 1977-1992 civil war in Mozambique.
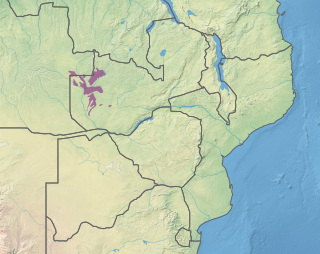
The Zambezian evergreen dry forests, also known as the Zambezian Cryptosepalum dry forest, is a tropical dry broadleaf forest ecoregion of Southern Africa. It consists of several areas of thick forest in western Zambia and adjacent Angola. It is one of the largest areas of tropical evergreen forest outside the equatorial zone.

Northern Zanzibar–Inhambane coastal forest mosaic, also known as the Northern Swahili coastal forests and woodlands, is a tropical moist broadleaf forest ecoregion of coastal East Africa. The ecoregion includes a variety of habitats, including forest, savanna and swamps.

The Chimanimani Mountains are a mountain range on the border of Zimbabwe and Mozambique. The mountains are in the southern portion of the Eastern Highlands, or Manica Highlands, a belt of highlands that extend north and south along the international border, between the Zambezi and Save rivers.

Chimanimani National Park is a protected area next to Chimoio, capital of Manica Province in Mozambique. It is located in the Chimanimani Mountains on the border with Zimbabwe. Together with Zimbabwe's Chimanimani National Park, it forms the Chimanimani Transfrontier Park. It was designated a national reserve in 2003. In 2020 it was designated a national park.
Mount Chiperone is a mountain in northern Mozambique. It lies in Milange District of Zambézia Province, 40 km SSW of the town of Milange.
The Cheringoma Plateau is a low plateau in Sofala Province of Mozambique. It lies mostly within Cheringoma, Muanza, and Marromeu districts.

The Southern miombo woodlands is a tropical grasslands and woodlands ecoregion extending across portions of Malawi, Mozambique, Zambia, and Zimbabwe.

The Victoria Basin forest–grassland mosaic is an ecoregion that lies mostly in Uganda and extends into neighboring countries. The ecoregion is centered north and west of Lake Victoria, with an outlier on the border of Ethiopia and South Sudan.

The dry miombo woodlands is an ecoregion in Africa. It has an area of 1,185,632 square kilometres (457,775 sq mi), covering portions of Tanzania, Mozambique, Malawi, Zambia, Zimbabwe, and Angola.
References
- 1 2 UNEP-WCMC (2024). Protected Area Profile for Maronga from the World Database on Protected Areas. Retrieved 7 June 2024.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Müller, Thomas & Sitoe, Almeida & Mabunda, Rito. Assessment of the Forest Reserve Network in Mozambique.
- 1 2 Ghiurghi, Andrea & Dondeyne, S. & Bannerman, J. (2010). Chimanimani national reserve: management plan. 10.13140/2.1.1734.6240.