
Guinea is a country on the coast of West Africa and is bordered by Guinea-Bissau, Senegal, Mali, Ivory Coast, Liberia, and Sierra Leone.

Liberia is a Sub-Saharan nation in West Africa located at 6 °N, 9 °W. It borders the north Atlantic Ocean to the southwest and three other African nations on the other three sides.
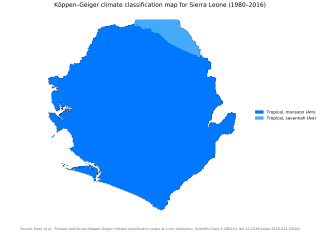
Sierra Leone is located on the west coast of Africa, between the 7th and 10th parallels north of the equator. Sierra Leone is bordered by Guinea to the north and northeast, Liberia to the south and southeast, and the Atlantic Ocean to the west.

The Gulf of Guinea is the northeasternmost part of the tropical Atlantic Ocean between Cape Lopez in Gabon, north and west to Cape Palmas in Liberia. The intersection of the Equator and Prime Meridian is in the gulf.
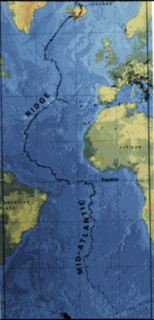
The Mid-Atlantic Ridge (MAR) is a mid-ocean ridge, a divergent tectonic plate or constructive plate boundary located along the floor of the Atlantic Ocean, and part of the longest mountain range in the world. In the North Atlantic it separates the Eurasian and North American plates, and in the South Atlantic it separates the African and South American plates. The ridge extends from a junction with the Gakkel Ridge northeast of Greenland southward to the Bouvet Triple Junction in the South Atlantic. Although the Mid-Atlantic Ridge is mostly an underwater feature, portions of it have enough elevation to extend above sea level. The section of the ridge that includes Iceland is known as the Reykjanes Ridge. The ridge has an average spreading rate of about 2.5 centimetres (0.98 in) per year.

Pepper Coast, also known as the Grain Coast, was the name given by European traders to a coastal area of western Africa, between Cape Mesurado and Cape Palmas. It encloses the present republic of Liberia.
Greenville is the capital of Sinoe County in southeastern Liberia and lies on a lagoon near the Sinoe River and the Atlantic Ocean. It is located about 150 miles southeast of Monrovia. As of the 2008 national census, the population stood at 16,434.

Harbel is a town in Margibi County, Liberia. It lies along the Farmington River, about 15 miles upstream from the Atlantic Ocean. It was named for the founder of The Firestone Tire & Rubber Company, Harvey S. Firestone, and his wife, Idabelle. Since 1926, Harbel has been home to a massive natural rubber plantation which is still operated by the Firestone subsidiary of Bridgestone.
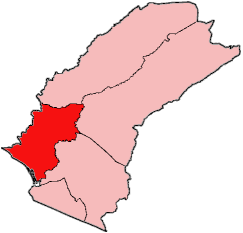
Tewor District is one of five districts located in Grand Cape Mount County, Liberia.
The Berrys River is a 12.9-mile (20.8 km) long river located in southeastern New Hampshire in the United States. It is a tributary of the Isinglass River, part of the Cocheco River/Piscataqua River watershed leading to the Atlantic Ocean.
The Ela River is a 10.6-mile (17.1 km) long river located in eastern New Hampshire in the United States. It is a tributary of the Cocheco River, part of the Piscataqua River watershed leading to the Atlantic Ocean.

The Mad River is a 5.2-mile-long (8.4 km) river in eastern New Hampshire in the United States. It is a tributary of the Cocheco River, part of the Piscataqua River watershed leading to the Atlantic Ocean.
The Rattlesnake River is a 3.6-mile-long (5.9 km) river in eastern New Hampshire in the United States. It is a tributary of the Cocheco River, part of the Piscataqua River watershed leading to the Atlantic Ocean.

The Saint Paul River is a river of western Africa. Its headwaters are in southeastern Guinea. Its upper portion in Guinea is known as the Diani River or Niandi River, and forms part of the boundary between Guinea and Liberia.

The Cestos River, also known as Nuon or Nipoué river, is a Liberian river that rises in the Nimba Range of Guinea and flows south along the Côte d'Ivoire border, then southwest through tracks of Liberian rain forest to empty into a bay on the Atlantic Ocean where the city River Cess is located. The pygmy hippopotamus is known to inhabit lands along stretches of the river. It forms the northern third of the international boundary between Liberia and Côte d'Ivoire.
The Firestone hydroelectric power station is a hydroelectric power station in Liberia on the Farmington River. Built in 1942, it was the first power generating dam built in the country. Located in Harbel, Margibi County, it is operated by the Firestone Plantations Company.

The Saint John River is one of the six main rivers in the West African nation of Liberia. With its headwaters in neighboring Guinea, the river flows generally southwest through Liberia and empties into the Atlantic Ocean at Bassa Cove near Edina in Grand Bassa County. The 175-mile-long (282 km) river has a drainage basin covering 5,700 square miles (15,000 km2).

West Point is a township of the Liberian capital city of Monrovia, located on a peninsula which juts out into the Atlantic Ocean between the Mesurado and Saint Paul rivers. Home to approximately 75,000 people, West Point is one of Monrovia's most densely populated slums.

The Farmington River is a river in Liberia. It empties into the Atlantic Ocean near the town of Marshall.

















