
Color or colour is the visual perception based on the electromagnetic spectrum. Though color is not an inherent property of matter, color perception is related to an object's light absorption, reflection, emission spectra and interference. For most humans, colors are perceived in the visible light spectrum with three types of cone cells (trichromacy). Other animals may have a different number of cone cell types or have eyes sensitive to different wavelength, such as bees that can distinguish ultraviolet, and thus have a different color sensitivity range. Animal perception of color originates from different light wavelength or spectral sensitivity in cone cell types, which is then processed by the brain.

Brown is a color. It can be considered a composite color, but it is mainly a darker shade of orange. In the CMYK color model used in printing and painting, brown is usually made by combining the colors orange and black. In the RGB color model used to project colors onto television screens and computer monitors, brown combines red and green.
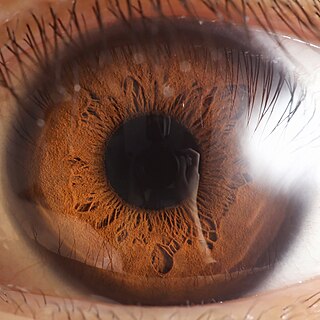
The iris is a thin, annular structure in the eye in most mammals and birds, responsible for controlling the diameter and size of the pupil, and thus the amount of light reaching the retina. In optical terms, the pupil is the eye's aperture, while the iris is the diaphragm. Eye color is defined by the iris.

Darkness is defined as a lack of illumination, an absence of visible light, or a surface that absorbs light, such as a black one.
In computing, on the X Window System, X11 color names are represented in a simple text file, which maps certain strings to RGB color values. It was traditionally shipped with every X11 installation, hence the name, and is usually located in <X11root>/lib/X11/rgb.txt. The web colors list is descended from it but differs for certain color names.

Complementary colors are pairs of colors which, when combined or mixed, cancel each other out by producing a grayscale color like white or black. When placed next to each other, they create the strongest contrast for those two colors. Complementary colors may also be called "opposite colors".
Color theory, or more specifically traditional color theory, is the historical body of knowledge describing the behavior of colors, namely in color mixing, color contrast effects, color harmony, color schemes and color symbolism. Modern color theory is generally referred to as Color science. While there is no clear distinction in scope, traditional color theory tends to be more subjective and have artistic applications, while color science tends to be more objective and have functional applications, such as in chemistry, astronomy or color reproduction. Color theory dates back at least as far as Aristotle's treatise On Colors. A formalization of "color theory" began in the 18th century, initially within a partisan controversy over Isaac Newton's theory of color and the nature of primary colors. By the end of the 19th century, a schism had formed between traditional color theory and color science.

Grey or gray is an intermediate color between black and white. It is a neutral or achromatic color, meaning literally that it is "without color", because it can be composed of black and white. It is the color of a cloud-covered sky, of ash, and of lead.

Eye color is a polygenic phenotypic trait determined by two factors: the pigmentation of the eye's iris and the frequency-dependence of the scattering of light by the turbid medium in the stroma of the iris.
In many languages, the colors described in English as "blue" and "green" are colexified, i.e., expressed using a single umbrella term. To render this ambiguous notion in English, linguists use the blend word grue, from green and blue, a term coined by the philosopher Nelson Goodman – with a rather different meaning – in his 1955 Fact, Fiction, and Forecast to illustrate his "new riddle of induction".

Horses exhibit a diverse array of coat colors and distinctive markings. A specialized vocabulary has evolved to describe them.

Basic Color Terms: Their Universality and Evolution is a book by Brent Berlin and Paul Kay. Berlin and Kay's work proposed that the basic color terms in a culture, such as black, brown, or red, are predictable by the number of color terms the culture has. All cultures have terms for black/dark and white/bright. If a culture has three color terms, the third is red. If a culture has four, it has either yellow or green.
Color analysis (also known as personal color analysis,seasonal color analysis, or skin—tone matching is a subjective belief within the fashion and Cosmetic industry to describe a method of determining the Color of clothing, makeup, Hairstyle that purportedly harmonizes with a person's skin complexion, eye color, and hair color for use in wardrobe planning and style consulting that claims to be favorable.

There are three types of color mixing models, depending on the relative brightness of the resultant mixture: additive, subtractive, and average. In these models, mixing black and white will yield white, black and gray, respectively. Physical mixing processes, e.g. mixing light beams or oil paints, will follow one or a hybrid of these 3 models. Each mixing model is associated with several color models, depending on the approximate primary colors used. The most common color models are optimized to human trichromatic color vision, therefore comprising three primary colors.

The Martin–Schultz scale is a standard color scale commonly used in physical anthropology to establish more or less precisely the eye color of an individual; it was created by the anthropologists Rudolf Martin and Bruno K Schultz in the first half of the 20th century. The scale consists of 20 colors that correspond to the different eye colors observed in nature due to the amount of melanin in the iris :

Variations of gray or grey include achromatic grayscale shades, which lie exactly between white and black, and nearby colors with low colorfulness. A selection of a number of these various colors is shown below.

Shades of black are colors that differ only slightly from pure black. These colors have a low lightness. From a photometric point of view, a color which differs slightly from black always has low relative luminance. Variations of black include what are commonly termed off-black colors, which may be considered part of a neutral color scheme, usually in interior design as a part of a background for brighter colors. Black and dark gray colors are powerful accent colors that suggest weight, dignity, formality, and solemnity.











