Related Research Articles

Malaria is a mosquito-borne infectious disease that affects humans and other animals. Malaria causes symptoms that typically include fever, tiredness, vomiting, and headaches. In severe cases, it can cause jaundice, seizures, coma, or death. Symptoms usually begin ten to fifteen days after being bitten by an infected mosquito. If not properly treated, people may have recurrences of the disease months later. In those who have recently survived an infection, reinfection usually causes milder symptoms. This partial resistance disappears over months to years if the person has no continuing exposure to malaria.

Plasmodium is a genus of unicellular eukaryotes that are obligate parasites of vertebrates and insects. The life cycles of Plasmodium species involve development in a blood-feeding insect host which then injects parasites into a vertebrate host during a blood meal. Parasites grow within a vertebrate body tissue before entering the bloodstream to infect red blood cells. The ensuing destruction of host red blood cells can result in malaria. During this infection, some parasites are picked up by a blood-feeding insect, continuing the life cycle.

Primaquine is a medication used to treat and prevent malaria and to treat Pneumocystis pneumonia. Specifically it is used for malaria due to Plasmodium vivax and Plasmodium ovale along with other medications and for prevention if other options cannot be used. It is an alternative treatment for Pneumocystis pneumonia together with clindamycin. It is taken by mouth.

Plasmodium vivax is a protozoal parasite and a human pathogen. This parasite is the most frequent and widely distributed cause of recurring malaria. Although it is less virulent than Plasmodium falciparum, the deadliest of the five human malaria parasites, P. vivax malaria infections can lead to severe disease and death, often due to splenomegaly. P. vivax is carried by the female Anopheles mosquito; the males do not bite.

Plasmodium ovale is a species of parasitic protozoon that causes tertian malaria in humans. It is one of several species of Plasmodium parasites that infect humans, including Plasmodium falciparum and Plasmodium vivax which are responsible for most cases of malaria in the world. P. ovale is rare compared to these two parasites, and substantially less dangerous than P. falciparum.

Plasmodium malariae is a parasitic protozoan that causes malaria in humans. It is one of several species of Plasmodium parasites that infect other organisms as pathogens, also including Plasmodium falciparum and Plasmodium vivax, responsible for most malarial infection. Found worldwide, it causes a so-called "benign malaria", not nearly as dangerous as that produced by P. falciparum or P. vivax. The signs include fevers that recur at approximately three-day intervals – a quartan fever or quartan malaria – longer than the two-day (tertian) intervals of the other malarial parasites.
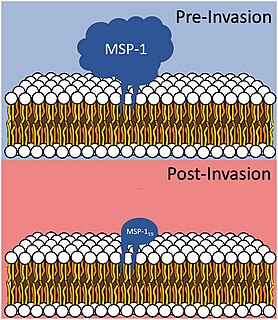
Merozoitesurface proteins are both integral and peripheral membrane proteins found on the surface of a merozoite, an early life cycle stage of a protozoan. Merozoite surface proteins, or MSPs, are important in understanding malaria, a disease caused by protozoans of the genus Plasmodium. During the asexual blood stage of its life cycle, the malaria parasite enters red blood cells to replicate itself, causing the classic symptoms of malaria. These surface protein complexes are involved in many interactions of the parasite with red blood cells and are therefore an important topic of study for scientists aiming to combat malaria.

Plasmodium knowlesi is a parasite that causes malaria in humans and other primates. It is found throughout Southeast Asia, and is the most common cause of human malaria in Malaysia. Like other Plasmodium species, P. knowlesi has a life cycle that requires infection of both a mosquito and a warm-blooded host. While the natural warm-blooded hosts of P. knowlesi are likely various Old World monkeys, humans can be infected by P. knowlesi if they are fed upon by infected mosquitoes. P. knowlesi is a eukaryote in the phylum Apicomplexa, genus Plasmodium, and subgenus Plasmodium. It is most closely related to the human parasite Plasmodium vivax as well as other Plasmodium species that infect non-human primates.

A malaria vaccine is a vaccine that is used to prevent malaria. The only approved use of a vaccine outside the EU, as of 2022, is RTS,S, known by the brand name Mosquirix. In October 2021, the WHO for the first time recommended the large-scale use of a malaria vaccine for children living in areas with moderate-to-high malaria transmission. Four injections are required for full protection.
Pregnancy-associated malaria (PAM) or placental malaria is a presentation of the common illness that is particularly life-threatening to both mother and developing fetus. PAM is caused primarily by infection with Plasmodium falciparum, the most dangerous of the four species of malaria-causing parasites that infect humans. During pregnancy, a woman faces a much higher risk of contracting malaria and of associated complications. Prevention and treatment of malaria are essential components of prenatal care in areas where the parasite is endemic – tropical and subtropical geographic areas. Placental malaria has also been demonstrated to occur in animal models, including in rodent and non-human primate models.

RTS,S/AS01 is a recombinant protein-based malaria vaccine. In October 2021, the vaccine was endorsed by the World Health Organization (WHO) for "broad use" in children, making it the first malaria vaccine candidate, and first vaccine to address parasitic infection, to receive this recommendation.
Jane M. Carlton is a biologist at New York University whose research centers on the genomics of two groups of single-celled parasites: those which cause malaria, and trichomonads, which include the common sexually transmitted parasite Trichomonas vaginalis.
Plasmodium coatneyi is a parasitic species that is an agent of malaria in nonhuman primates. P. coatneyi occurs in Southeast Asia. The natural host of this species is the rhesus macaque and crab-eating macaque, but there has been no evidence that zoonosis of P. coatneyi can occur through its vector, the female Anopheles mosquito.
Sanaria is a biotechnology company developing vaccines protective against malaria and other infectious diseases as well as related products for use in malaria research. Sanaria’s vaccines are based on the use of the sporozoite (SPZ) stage of the malaria parasite, Plasmodium, as an immunogen, and as a platform technology for liver-vectored gene delivery. SPZ are normally introduced into humans by mosquito bite where they migrate to the liver and further develop to liver stages, and eventually back into the blood stream where the parasite infects red blood cells (RBC) and causes malaria. Plasmodium falciparum is the species responsible for more than 95% deaths caused by malaria. The WHO estimates there were 241 million clinical cases and 627,000 deaths in 2020 alone.
Ruth Sonntag Nussenzweig was an Austrian-Brazilian immunologist specializing in the development of malaria vaccines. In a career spanning over 60 years, she was primarily affiliated with New York University (NYU). She served as C.V. Starr Professor of Medical and Molecular Parasitology at Langone Medical Center, Research Professor at the NYU Department of Pathology, and finally Professor Emerita of Microbiology and Pathology at the NYU Department of Microbiology.

Plasmodium cynomolgi is an apicomplexan parasite that infects mosquitoes and Asian Old World monkeys. In recent years, a number of natural infections of humans have also been documented. This species has been used as a model for human Plasmodium vivax because Plasmodium cynomolgi shares the same life cycle and some important biological features with P. vivax.
Yagya Dutta Sharma is an Indian molecular biologist, professor and head of the department of biotechnology at the All India Institute of Medical Sciences, Delhi. An elected fellow of all three major Indian science academies — Indian National Science Academy, Indian Academy of Sciences, and National Academy of Sciences, India — Sharma is known for his research on the molecular biology of malaria. The Council of Scientific and Industrial Research, the apex agency of the Government of India for scientific research, awarded him the Shanti Swarup Bhatnagar Prize for Science and Technology for his contributions to medical sciences in 1994.
William Erle "Bill" Collins was an American parasitologist.
Jessica Kissinger is a Distinguished Research Professor at the Franklin College of Arts and Sciences, University of Georgia and director of the Institute of Bioinformatics. Her research focus is on the evolution, assembly and data curation of protozoan parasite genomes, particularly Cryptosporidium, Toxoplasma gondii and Plasmodium.

Sanjeev Krishna,, is a British physician and parasitologist whose research focuses on affordable diagnosis and treatment of diseases such as COVID-19, malaria, Ebola, African trypanosomiasis, leishmaniasis, and colorectal cancer. Krishna is Professor of Medicine and Molecular Parasitology at St George's, University of London and St George's Hospital.
References
- ↑ "Mary R. Galinski, Ph.D." Emory University. Retrieved November 4, 2019.
- ↑ "Mary Galinski, PhD". Emory University. Retrieved November 4, 2019.
- ↑ Samantha Slappey (March 13, 2014). "Malaria researcher and global health advocate to speak at Vanguard Lecture Series". University of Georgia. Retrieved November 4, 2019.
- ↑ Kay Hinton (Spring 2010). "Mosquito-Borne Killer". Emory Magazine.
- ↑ Terry Hastings (November 19, 2012). "UGA partners with Emory, Georgia Tech and CDC Foundation on malaria research center". University of Georgia. Retrieved November 4, 2019.
- ↑ Brittini Ray (March 18, 2014). "Emory professor presents dangers, effects of malaria". The Red & Black. Retrieved November 4, 2019.
- ↑ Kay Hinton (Autumn 2016). "Malaria Math". Emory Magazine.