Dieting is the practice of eating food in a regulated way to decrease, maintain, or increase body weight, or to prevent and treat diseases such as diabetes and obesity. As weight loss depends on calorie intake, different kinds of calorie-reduced diets, such as those emphasising particular macronutrients, have been shown to be no more effective than one another. As weight regain is common, diet success is best predicted by long-term adherence. Regardless, the outcome of a diet can vary widely depending on the individual.

"Junk food" is a term used to describe food that is high in calories from macronutrients such as sugar and/or fat, and possibly sodium, making it hyperpalatable, but with insufficient dietary fiber, protein, or micronutrients such as vitamins and minerals. It is also known as HFSS food. The term junk food is a pejorative dating back to the 1950s. Many variations of junk food can be easily found in most supermarkets and fast food restaurants. Due to easy accessibility, commercially-oriented packaging, and often-low prices, people are most likely to consume it.

A healthy diet is a diet that maintains or improves overall health. A healthy diet provides the body with essential nutrition: fluid, macronutrients such as protein, micronutrients such as vitamins, and adequate fibre and food energy.

Childhood obesity is a condition where excess body fat negatively affects a child's health or well-being. As methods to determine body fat directly are difficult, the diagnosis of obesity is often based on BMI. Due to the rising prevalence of obesity in children and its many adverse health effects it is being recognized as a serious public health concern. The term overweight rather than obese is often used when discussing childhood obesity, as it is less stigmatizing, although the term overweight can also refer to a different BMI category. The prevalence of childhood obesity is known to differ by sex and gender.
A fat tax is a tax or surcharge that is placed upon fattening food, beverages or on overweight individuals. It is considered an example of Pigovian taxation. A fat tax aims to discourage unhealthy diets and offset the economic costs of obesity.
A food environment is the "physical presence of food that affects a person's diet, a person's proximity to food store locations, the distribution of food stores, food service, and any physical entity by which food may be obtained, or a connected system that allows access to food".
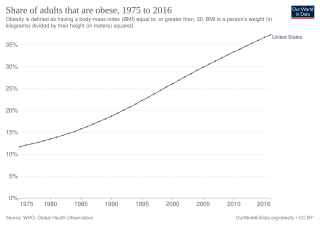
Obesity is common in the United States and is a major health issue associated with numerous diseases, specifically an increased risk of certain types of cancer, coronary artery disease, type 2 diabetes, stroke, and cardiovascular disease, as well as significant increases in early mortality and economic costs.
Based in Washington, D.C., Leadership for Healthy Communities is a $10-million national program of the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation designed to engage and support local and state government leaders nationwide in their efforts to advance public policies that support healthier communities and prevent childhood obesity. The program places an emphasis on policies with the greatest potential for increasing sustainable opportunities for physical activity and healthy eating among children at highest risk for obesity, including African-American, Latino, American Indian and Alaska Native, Asian-American and Pacific Islander children living in lower-income communities. The foundation's primary goal is the reversal of the childhood obesity epidemic by 2015.
Research into food choice investigates how people select the food they eat. An interdisciplinary topic, food choice comprises psychological and sociological aspects, economic issues and sensory aspects.

Obesity in the Middle East and North Africa is a notable health issue. Out of the fifteen fattest nations in the world as of 2014, 5 were located in the Middle East and North Africa region.
The term "Freshman 15" is an expression commonly used in the United States and Canada to refer to weight gain during a student's first year in college. Although the 15 refers to a 15 lb weight gain, the expression can apply more generally. In Australia and New Zealand, it is sometimes referred to as "First Year Fatties", "Fresher Spread", or "Fresher Five", the latter referring to a gain of 5 kg (11 lb).

Criticism of fast food includes claims of negative health effects, animal cruelty, cases of worker exploitation, children-targeted marketing and claims of cultural degradation via shifts in people's eating patterns away from traditional foods. Fast food chains have come under fire from consumer groups, such as the Center for Science in the Public Interest, a longtime fast food critic over issues such as caloric content, trans fats and portion sizes. Social scientists have highlighted how the prominence of fast food narratives in popular urban legends suggests that modern consumers have an ambivalent relationship with fast food, particularly in relation to children.

Social class differences in food consumption refers to how the quantity and quality of food varies according to a person's social status or position in the social hierarchy. Various disciplines, including social, psychological, nutritional, and public health sciences, have examined this topic. Social class can be examined according to defining factors — education, income, or occupational status — or subjective components, like perceived rank in society.

Sugar-sweetened beverages (SSB) are any beverage with added sugar. They have been described as "liquid candy". Consumption of sugar-sweetened beverages have been linked to weight gain and an increased risk of cardiovascular disease mortality. According to the CDC, consumption of sweetened beverages is also associated with unhealthy behaviors like smoking, not getting enough sleep and exercise, and eating fast food often and not enough fruits regularly.
Barry Michael Popkin is an American nutrition and obesity researcher at the Carolina Population Center and the W.R. Kenan Jr. Distinguished Professor of Nutrition at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill School of Public Health, where he is the director of the Global Food Research Program. He developed the concept of "nutrition transition". He is the author of over 650 journal articles and a book, The World is Fat, translated into a dozen languages.
Childhood obesity is defined as a body mass index (BMI) at or above the 96th percentile for children of the same age and sex. It can cause a variety of health problems, including high blood pressure, high cholesterol, heart disease, diabetes, breathing problems, sleeping problems, and joint problems later in life. Children who are obese are at a greater risk for social and psychological problems as well, such as peer victimization, increased levels of aggression, and low self-esteem. Many environmental and social factors have been shown to correlate with childhood obesity, and researchers are attempting to use this knowledge to help prevent and treat the condition. When implemented early, certain forms of behavioral and psychological treatment can help children regain and/or maintain a healthy weight.

Obesity and the environment aims to look at the different environmental factors that researchers worldwide have determined cause and perpetuate obesity. Obesity is a condition in which a person's weight is higher than what is considered healthy for their height, and is the leading cause of preventable death worldwide. Obesity can result from several factors such as poor nutritional choices, overeating, genetics, culture, and metabolism. Many diseases and health complications are associated with obesity. Worldwide, the rates of obesity have nearly tripled since 1975, leading health professionals to label the condition as a modern epidemic in most parts of the world. Current worldwide population estimates of obese adults are near 13%; overweight adults total approximately 39%.
Jamie Sue Stang is an American dietitian and nutritionist. She is an associate professor in the Division of Epidemiology and Community Health at the University of Minnesota School of Public Health.
Dianne Neumark-Sztainer is a University of Minnesota Regents Professor in the Division of Epidemiology and Community Health at the School of Public Health. She is a scholar on adolescent and young adult eating and weight-related health.
Eliana Perrin is an American pediatrician, researcher, and Bloomberg Distinguished Professor of Primary Care with joint appointments with tenure in the Department of Pediatrics in the School of Medicine and in the School of Nursing at Johns Hopkins University. She was elected a member of the American Pediatric Society in 2021.








