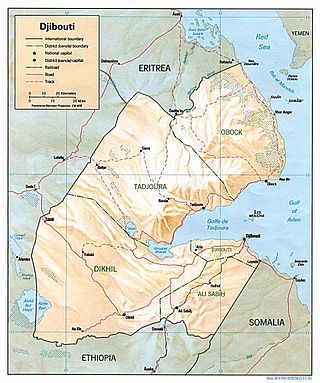
Djibouti is a country in the Horn of Africa bordered by Somalia to the east, Eritrea to west and the Red Sea to the north, Ethiopia to the west and south, and the Gulf of Aden to the east.

Eritrea is located in the Horn of Africa and is bordered on the northeast and east by the Red Sea, on the west and northwest by Sudan, on the south by Ethiopia, and on the southeast by Djibouti. The country has a high central plateau that varies from 1,800 to 3,000 meters (5,906–9,843 ft) above sea level. A coastal plain, western lowlands, and some 350 islands comprise the remainder of Eritrea's land mass.

The Gulf of Aden is a deepwater gulf of the Indian Ocean between Yemen to the north, the Arabian Sea to the east, Djibouti to the west, and the Guardafui Channel, the Socotra Archipelago, Puntland in Somalia and Somaliland to the south. In the northwest, it connects with the Red Sea through the Bab-el-Mandeb strait, and it connects with the Arabian Sea to the east. To the west, it narrows into the Gulf of Tadjoura in Djibouti. The Aden Ridge lies along the middle of the gulf, and tectonic activity at the ridge is causing the gulf to widen by about 15 mm (0.59 in) per year.

The Bab-el-Mandeb, the Gate of Grief or the Gate of Tears, is a strait between Yemen on the Arabian Peninsula and Djibouti and Eritrea in the Horn of Africa. It connects the Red Sea to the Gulf of Aden and by extension the Indian Ocean.

Ismaïl Omar Guellé is a Djiboutian politician who has served as the President of Djibouti since 1999, making him one of the longest-serving rulers in Africa. He is often referred to by his initials, IOG.

Djibouti is the capital of Djibouti. It is located in the coastal Djibouti Region on the Gulf of Tadjoura.
The Djibouti national football team, nicknamed the "Riverains de la Mer Rouge", is the national football team of Djibouti. It is controlled by the Djiboutian Football Federation and is a member of the Confederation of African Football (CAF) and the Union of Arab Football Associations (UAFA). The Djibouti national football team's first win in a full FIFA-sanctioned international match was a 1–0 win vs. Somalia in the first round of the 2010 FIFA World Cup qualification.
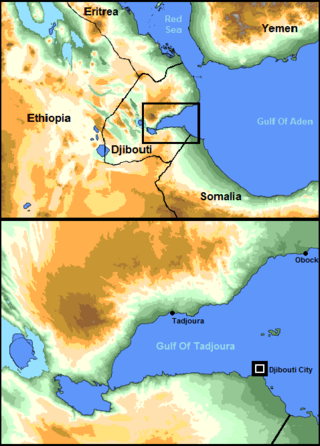
The Gulf of Tadjoura is a gulf or basin of the Indian Ocean in the Horn of Africa. It lies south of the straits of Bab-el-Mandeb, or the entrance to the Red Sea, at 11.7°N 43.0°E. The gulf has many fishing grounds, extensive coral reefs, and abundant pearl oysters. Most of its coastline is the territory of Djibouti, except for a short stretch on the southern shore, which is part of the territory of Somaliland.
Arta, ARTA, or Artà may refer to:
The wildlife of Djibouti, consisting of its flora and fauna, is in a harsh landscape with forest accounting for less than one percent of its area. Most species are found in the northern part of the country in the Day Forest National Park at an average elevation of 1,500 metres (4,900 ft), including the massif Goda, with a peak of 1,783 metres (5,850 ft). It covers an area of 3.5 square kilometres (1.4 sq mi) of Juniperus procera forest, with many of the trees rising to 20 metres (66 ft) height. This forest area is the main habitat of the critically endangered and endemic Djibouti spurfowl, and another recently noted vertebrate, Platyceps afarensis. The area also contains many species of woody and herbaceous plants, including boxwood and olive trees, which account for sixty percent of the identified species in the country.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to Djibouti:

Djibouti, officially the Republic of Djibouti, is a country in the Horn of Africa, bordered by Somalia to the south, Ethiopia to the southwest, Eritrea in the north, and the Red Sea and the Gulf of Aden to the east. The country has an area of 23,200 km2 (8,958 sq mi).

Tourism in Djibouti is one of the growing economic sectors of the country and is an industry that generates 53,000 and 73,000 arrivals per year, with its favorable beaches and climate and also including islands and beaches in the Gulf of Tadjoura and the Bab al-Mandab. The main tourist activities are scuba diving, fishing, trekking and hiking, discovering the nomadic way, bird watching, and sun, sea and sand.
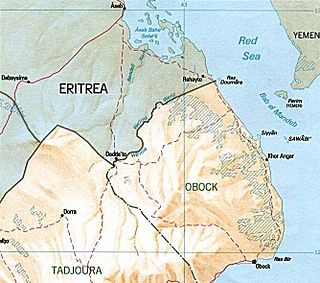
The Djiboutian–Eritrean border conflict was a border conflict between the forces of Djibouti and Eritrea occurred between June 10 and June 13, 2008. It was triggered by tension which began on April 16, 2008, when Djibouti reported that Eritrean armed forces had penetrated into Djibouti and dug trenches on both sides of the border. The crisis deepened when armed clashes broke out between the two armed forces in the border area on June 10, 2008. During the conflict, France provided logistical, medical and intelligence support to Djibouti, but did not participate in direct combat.

Djibouti–Eritrea relations refers to the current and historical relationship between neighboring states Djibouti and Eritrea.

All visitors to Djibouti must obtain either a visa on arrival to Djibouti, an electronic visa online or a visa from one of the Djiboutian diplomatic missions prior to arrival in Djibouti, unless they come from one of the visa exempt countries mentioned below.
The COVID-19 pandemic in Djibouti was a part of the worldwide pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2. The virus spread to Djibouti in March 2020. It is a novel infectious disease caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2. Model-based simulations for Djibouti indicate that the 95% confidence interval for the time-varying reproduction number R t has been rising since August 2020 and exceeded 1.0 until April 2021.

Kuriftu Resorts & Spa is a hotel chain in Ethiopia, serving Djibouti and Moucha Island. Founded, managed and operated by the Boston Partners Group in cooperation with Tadiwos Belete in 2002, the resort has various branches in Ethiopia; one of the main branch is located in Bishoftu, whereas the other in Bahir Dar, Adama, Langano and Semera.














