
Djibouti is a country in the Horn of Africa. It is bordered by Eritrea in the north, Ethiopia in the west and south, and Somalia in the southeast. To the east is its coastline on the Red Sea and the Gulf of Aden. Rainfall is sparse, and most of the territory has a semi-arid to arid environment. Lake Assal is a saline lake which lies 155 m (509 ft) below sea level, making it the lowest point on land in Africa and the third-lowest point on Earth after the Sea of Galilee and the Dead Sea. Djibouti has the fifth smallest population in Africa. Djibouti's major settlements include the capital Djibouti City, the port towns of Tadjoura and Obock, and the southern cities of Ali Sabieh and Dikhil. It is the forty-six country by area in Africa and 147st largest country in the world by land area, covering a total of 23,200 km2 (9,000 sq mi), of which 23,180 km2 (8,950 sq mi) is land and 20 km2 (7.7 sq mi) is water.

Eritrea is located in the Horn of Africa and is bordered on the northeast and east by the Red Sea, on the west and northwest by Sudan, on the south by Ethiopia, and on the southeast by Djibouti. The country has a high central plateau that varies from 1,800 to 3,000 meters (5,906–9,843 ft) above sea level. A coastal plain, western lowlands, and some 350 islands comprise the remainder of Eritrea's land mass.

Somalia is a country located in the Horn of Africa which officially consists of the intra-46th meridian east territory, the seven federal member states, namely Galmudug, Hirshabelle, Jubaland, South West, Puntland, and the municipality of Benadir. It is bordered by Ethiopia to the west, the Gulf of Aden to the north, the Somali Sea and Guardafui Channel to the east, and Kenya to the southwest. With a land area of 637,657 square kilometers, Somalia's terrain consists mainly of plateaus, plains and highlands. Its coastline is more than 3,333 kilometers in length, the longest of mainland Africa. It has been described as being roughly shaped "like a tilted number seven".

A rain shadow is an area of significantly reduced rainfall behind a mountainous region, on the side facing away from prevailing winds, known as its leeward side.

The climate of India consists of a wide range of weather conditions across a vast geographic scale and varied topography. Based on the Köppen system, India encompasses a diverse array of climatic subtypes. These range from arid and semi-arid regions in the west to highland, sub-arctic, tundra, and ice cap climates in the northern Himalayan regions, varying with elevation. The northern lowlands experience subtropical conditions, with some areas at higher altitudes, like Srinagar, touching continental climates. In contrast, much of the south and the east exhibit tropical climate conditions, which support lush rainforests in these territories. Many regions have starkly different microclimates, making it one of the most climatically diverse countries in the world. The country's meteorological department follows the international standard of four seasons with some local adjustments: winter, summer, monsoon or rainy season, and a post-monsoon period.

Djibouti is the capital of Djibouti. It is located in the coastal Djibouti Region on the Gulf of Tadjoura.
Arta Region is one of the six regions of Djibouti. It was officially created in 2003 by the regrouping of districts of the regions of Dikhil and Djibouti. It is situated in the south-central of the country, bordering the Tadjoura Region to the north, and the Djibouti Region to the north-east, and Dikhil Region the Ali Sabieh Region to the south, the country of Somaliland lies to the east.
Karachi has a semi-arid climate, formerly a hot desert climate, albeit a moderate version of this climate, influenced by monsoons. Karachi has a tropical climate, despite being located slightly above the Tropic of Cancer. It is situated in the monsoon region of Pakistan. It is located on the coast bordering the Arabian Sea, and as a result, has a relatively mild climate. However, in more recent years, rainfall has become more abundant. For this reason, the city may be classed as semi-arid (BSh), since it has a mild climate with a short but defined wet season, along with a lengthy dry season.

The geography of South America contains many diverse regions and climates. Geographically, South America is generally considered a continent forming the southern portion of the landmass of the Americas, south and east of the Colombia–Panama border by most authorities, or south and east of the Panama Canal by some. South and North America are sometimes considered a single continent or supercontinent, while constituent regions are infrequently considered subcontinents.
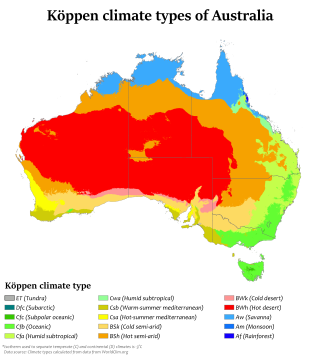
Australia's climate is governed mostly by its size and by the hot, sinking air of the subtropical high pressure belt. This moves north-west and north-east with the seasons. The climate is variable, with frequent droughts lasting several seasons, thought to be caused in part by the El Niño-Southern Oscillation. Australia has a wide variety of climates due to its large geographical size. The largest part of Australia is desert or semi-arid. Only the south-east and south-west corners have a temperate climate and moderately fertile soil. The northern part of the country has a tropical climate, varying between grasslands and desert. Australia holds many heat-related records: the continent has the hottest extended region year-round, the areas with the hottest summer climate, and the highest sunshine duration.

The climate of the United States varies due to changes in latitude, and a range of geographic features, including mountains and deserts. Generally, on the mainland, the climate of the U.S. becomes warmer the farther south one travels, and drier the farther west, until one reaches the West Coast.

The climate of Argentina varies from region to region, as the vast size of the country and wide variation in altitude make for a wide range of climate types. Summers are the warmest and wettest season in most of Argentina, except for most of Patagonia, where it is the driest season. The climate is warm in the north, cool in the center, and cold in the southern parts, that experience frequent frost and snow. Because the southern parts of the country are moderated by the surrounding oceans, the cold is less intense and prolonged than areas at similar latitudes in the northern hemisphere. Spring and autumn are transition seasons that generally feature mild weather.
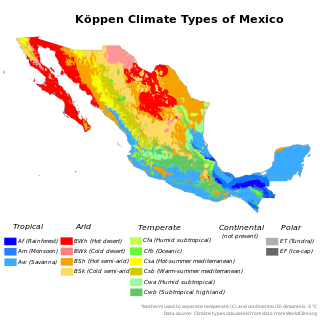
The climate of Mexico is very diverse. The Tropic of Cancer effectively divides the country into temperate and tropical zones. Land that is north of the twenty-fourth parallel experiences lower temperatures during the winter months. South of the twenty-fourth parallel, temperatures are fairly consistent all year round and vary solely as a function of elevation. The north of the country usually receives less precipitation than the south.

The Climate of Venezuela is characterized for being tropical and megathermal as a result of its geographical location near the Equator, but because of the topography and the dominant wind direction, several climatic types occur which can be the same as found in temperate latitudes, and even polar regions. Latitude exerts little influence on the Venezuelan climate. While the coastal cities of Maracaibo, Barcelona, Porlamar and Maiquetia can get extremely hot, cities in valleys such as Mérida, Caracas, Los Teques and San Cristobal have cooler climates, and the highest towns of Mucuchies and Apartaderos have cold (tundra) climates.
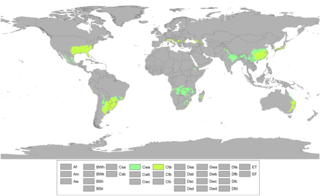
A humid subtropical climate is a temperate climate type characterized by hot and humid summers, and cool to mild winters. These climates normally lie on the southeast side of all continents, generally between latitudes 25° and 40° and are located poleward from adjacent tropical climates, and equatorward from either humid continental or oceanic climates. It is also known as warm temperate climate in some climate classifications.

The climate of Los Angeles is mild to hot year-round, and mostly dry. It is classified as borderline Mediterranean and semi-arid. The city is characterized by seasonal changes in rainfall—with a dry summer and a winter rainy season. Under the Köppen climate classification, the coastal areas are classified as BSh and Csb, while the inland areas are classified as BSh and Csa.
Multan is a city located in the southern part of Punjab, province in Pakistan. Multan features a hot semi arid climate with very hot and rainy summers and cold winters. The city witnesses some of the most extreme temperatures in the country. Dust storms are a common occurrence within the city. The closest major city is Bahawalpur. The area around the city is a flat plain and is ideal for agriculture, with many citrus and mango farms. There are many canals that cut across the Multan District, providing water from nearby farms. This makes the land very fertile. However usually land close to the Chenab River are flooded in the monsoon season.

Cyprus has a subtropical climate, Mediterranean and semi-arid type according to Köppen climate classification, with very mild winters on sea level and warm to hot summers. Snow is possible only in the Troodos mountains in the central part of the island. Rain occurs mainly in winter, with summer being generally dry.

Turkey's climate is varied and generally temperate, with the regions bordering the Mediterranean and Black Sea heavily affected by the coasts, and the interior being drier and more continental.

The climate of Spain is highly diverse and varies considerably across the country's various regions. Spain is a very climatically diverse country, sometimes described as the most varied in Europe, and has 13 different Köppen climates.



















