Related Research Articles

Drawing is a visual art that uses an instrument to mark paper or another two-dimensional surface. The instruments used to make a drawing are pencils, crayons, pens with inks, brushes with paints, or combinations of these, and in more modern times, computer styluses with graphics tablets or gamepads in VR drawing software.

Computer-aided design (CAD) is the use of computers to aid in the creation, modification, analysis, or optimization of a design. This software is used to increase the productivity of the designer, improve the quality of design, improve communications through documentation, and to create a database for manufacturing. Designs made through CAD software help protect products and inventions when used in patent applications. CAD output is often in the form of electronic files for print, machining, or other manufacturing operations. The terms computer-aided drafting (CAD) and computer-aided design and drafting (CADD) are also used.

Technical drawing, drafting or drawing, is the act and discipline of composing drawings that visually communicate how something functions or is constructed.

Oblique projection is a simple type of technical drawing of graphical projection used for producing two-dimensional (2D) images of three-dimensional (3D) objects.

A drawing pin or [thumb] tack, also called a push-pin, is a short, small pin or nail with a flat, broad head that can be pressed into place with pressure from the thumb, often used for hanging light articles on a wall or noticeboard.

Body proportions is the study of artistic anatomy, which attempts to explore the relation of the elements of the human body to each other and to the whole. These ratios are used in depictions of the human figure and may become part of an artistic canon of body proportion within a culture. Academic art of the nineteenth century demanded close adherence to these reference metrics and some artists in the early twentieth century rejected those constraints and consciously mutated them.

The Omega Nebula, also known as the Swan Nebula, Checkmark Nebula, Lobster Nebula, and the Horseshoe Nebula is an H II region in the constellation Sagittarius. It was discovered by Philippe Loys de Chéseaux in 1745. Charles Messier catalogued it in 1764. It is by some of the richest starfields of the Milky Way, figuring in the northern two-thirds of Sagittarius.

Solomon "Sol" LeWitt was an American artist linked to various movements, including conceptual art and minimalism.

A figure drawing is a drawing of the human form in any of its various shapes and postures, using any of the drawing media. The term can also refer to the act of producing such a drawing. The degree of representation may range from highly detailed, anatomically correct renderings to loose and expressive sketches. A life drawing is a drawing of the human figure, traditionally nude, from observation of a live model. Creating life drawings, or life studies, in a life class, has been a large element in the traditional training of artists in the Western world since the Renaissance.
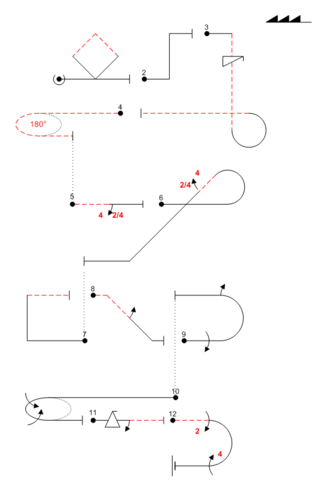
The Aresti Catalog is the Fédération Aéronautique Internationale (FAI) standards document enumerating the aerobatic manoeuvers permitted in aerobatic competition. Designed by Spanish aviator Colonel José Luis Aresti Aguirre (1919–2003), each figure in the catalog is represented by lines, arrows, geometric shapes and numbers representing the precise form of a manoeuver to be flown.

Chainmail is a medieval miniature wargame created by Gary Gygax and Jeff Perren. Gygax developed the core medieval system of the game by expanding on rules authored by his fellow Lake Geneva Tactical Studies Association (LGTSA) member Jeff Perren, a hobby-shop owner with whom he had become friendly. Guidon Games released the first edition of Chainmail in 1971.

In art and design, negative space is the empty space around and between the subject(s) of an image. Negative space may be most evident when the space around a subject, not the subject itself, forms an interesting or artistically relevant shape, and such space occasionally is used to artistic effect as the "real" subject of an image.

An art model poses, often nude, for visual artists as part of the creative process, providing a reference for the human body in a work of art. As an occupation, modeling requires the often strenuous 'physical work' of holding poses for the required length of time, the 'aesthetic work' of performing a variety of interesting poses, and the 'emotional work' of maintaining a socially ambiguous role. While the role of nude models is well-established as a necessary part of artistic practice, public nudity remains transgressive, and models may be vulnerable to stigmatization or exploitation. Artists may also have family and friends pose for them, in particular for works with costumed figures.
A three-turn is a figure skating element which involves both a change in direction and a change in edge. For example, when a skater executes a forward outside three-turn, the skater begins on a forward outside edge and finishes on a backwards inside edge. There are eight three-turns in all; one for each possible combination of direction, skating foot, and edge.

A figure study is a drawing or painting of the human body made in preparation for a more composed or finished work; or to learn drawing and painting techniques in general and the human figure in particular. By preference, figure studies are done from a live model, but may also include the use of other references and the imagination of the artist. The live model may be clothed, or nude, but is usually nude for student work in order to learn human anatomy, or by professionals who establish the underlying anatomy before adding clothing in the final work.
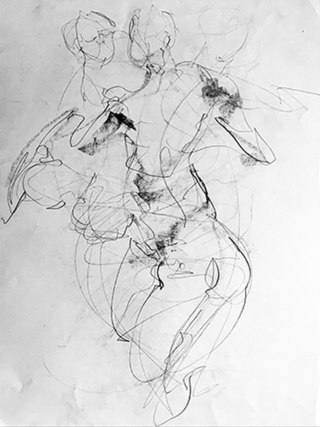
A gesture drawing is a laying in of the action, form, and pose of a model/figure. Typical situations involve an artist drawing a series of poses taken by a model in a short amount of time, often as little as 10 seconds, or as long as 5 minutes. Gesture drawing is often performed as a warm-up for a life drawing session, but is a skill that may be cultivated for its own sake.

Crossovers are a basic stroking technique in figure skating for gaining impetus while skating along a curve or circle. They may be performed while skating either forwards or backwards.

Disney's twelve basic principles of animation were introduced by the Disney animators Ollie Johnston and Frank Thomas in their 1981 book The Illusion of Life: Disney Animation.[a] The principles are based on the work of Disney animators from the 1930s onwards, in their quest to produce more realistic animation. The main purpose of these principles was to produce an illusion that cartoon characters adhered to the basic laws of physics, but they also dealt with more abstract issues, such as emotional timing and character appeal.

An artistic canon of body proportions, in the sphere of visual arts, is a formally codified set of criteria deemed mandatory for a particular artistic style of figurative art. The word canon was first used for this type of rule in Classical Greece, where it set a reference standard for body proportions, to produce a harmoniously formed figure appropriate to depict gods or kings. Other art styles have similar rules that apply particularly to the representation of royal or divine personalities.

John Henry Vanderpoel, born Johannes (Jan) van der Poel, was a Dutch-American artist and teacher, best known as an instructor of figure drawing. His book The Human Figure, a standard art school resource featuring numerous drawings based on his teaching at the School of the Art Institute of Chicago, was published in 1907.
References
- ↑ Albert, Greg (1994). Basic Figure Drawing Techniques . North Light Books. pp. 18–21. ISBN 9780891345510.
- ↑ Nicolaides, Kimon. The Natural Way to Draw. Boston: Houghton Mifflin Co. ISBN 0-395-20548-4.