Related Research Articles

Tourette syndrome or Tourette's syndrome is a common neurodevelopmental disorder that begins in childhood or adolescence. It is characterized by multiple movement (motor) tics and at least one vocal (phonic) tic. Common tics are blinking, coughing, throat clearing, sniffing, and facial movements. These are typically preceded by an unwanted urge or sensation in the affected muscles known as a premonitory urge, can sometimes be suppressed temporarily, and characteristically change in location, strength, and frequency. Tourette's is at the more severe end of a spectrum of tic disorders. The tics often go unnoticed by casual observers.
Coprolalia is involuntary swearing or the involuntary utterance of obscene words or socially inappropriate and derogatory remarks. Coprolalia comes from the Greek κόπρος (kópros), meaning "dung, feces", and λαλιά (laliā́) "speech", from λαλεῖν (laleîn) "to talk".

A tic is a sudden, repetitive, nonrhythmic motor movement or vocalization involving discrete muscle groups. Tics can be invisible to the observer, such as abdominal tensing or toe crunching. Common motor and phonic tics are, respectively, eye blinking and throat clearing.
The Jumping Frenchmen of Maine were a group of 19th-century lumberjacks who exhibited a rare disorder of unknown origin. The syndrome entails an exaggerated startle reflex which may be described as an uncontrollable "jump"; individuals with this condition can exhibit sudden movements in all parts of the body. Jumping Frenchmen syndrome shares some symptoms with other startle disorders.
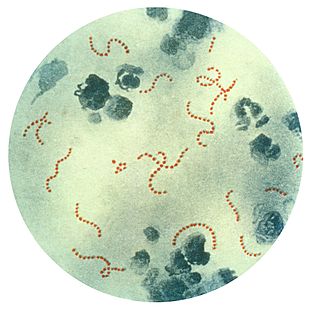
Pediatric autoimmune neuropsychiatric disorders associated with streptococcal infections (PANDAS) is a controversial hypothetical diagnosis for a subset of children with rapid onset of obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) or tic disorders. Symptoms are proposed to be caused by group A streptococcal (GAS), and more specifically, group A beta-hemolytic streptococcal (GABHS) infections. OCD and tic disorders are hypothesized to arise in a subset of children as a result of a post-streptococcal autoimmune process. The proposed link between infection and these disorders is that an autoimmune reaction to infection produces antibodies that interfere with basal ganglia function, causing symptom exacerbations, and this autoimmune response results in a broad range of neuropsychiatric symptoms.

Tic disorders are defined in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM) based on type and duration of tics. Tic disorders are defined similarly by the World Health Organization.
Stereotypic movement disorder (SMD) is a motor disorder with onset in childhood involving restrictive and/or repetitive, nonfunctional motor behavior, that markedly interferes with normal activities or results in bodily injury. To be classified as SMD, the behavior in question must not be due to the direct effects of a substance, autism, or another medical condition. The cause of this disorder is not known.
Societal and cultural aspects of Tourette syndrome include legal advocacy and health insurance issues, awareness of notable individuals with Tourette syndrome, and treatment of TS in the media and popular culture.
Tourette syndrome is an inherited neurodevelopmental disorder that begins in childhood or adolescence, characterized by the presence of motor and phonic tics. The management of Tourette syndrome has the goal of managing symptoms to achieve optimum functioning, rather than eliminating symptoms; not all persons with Tourette's require treatment, and there is no cure or universally effective medication. Explanation and reassurance alone are often sufficient treatment; education is an important part of any treatment plan.
Causes and origins of Tourette syndrome have not been fully elucidated. Tourette syndrome is an inherited neurodevelopmental disorder that begins in childhood or adolescence, characterized by the presence of multiple motor tics and at least one phonic tic, which characteristically wax and wane. Tourette's syndrome occurs along a spectrum of tic disorders, which includes transient tics and chronic tics.
Arthur K. Shapiro, M.D., was an American psychiatrist and expert on Tourette syndrome. His "contributions to the understanding of Tourette syndrome completely changed the prevailing view of this disorder"; he has been described as "the father of modern tic disorder research" and is "revered by his colleagues as the first dean of modern Tourette syndrome researchers".
Tourettism refers to the presence of Tourette-like symptoms in the absence of Tourette syndrome, as the result of other diseases or conditions, known as "secondary causes".
Sensory phenomena are general feelings, urges or bodily sensations. They are present in many conditions including autism spectrum disorders, epilepsy, neuropathy, obsessive–compulsive disorder, pain conditions, tardive syndromes, and tic disorders.
Habit reversal training (HRT) is a "multicomponent behavioral treatment package originally developed to address a wide variety of repetitive behavior disorders".
The obsessive–compulsive spectrum is a model of medical classification where various psychiatric, neurological and/or medical conditions are described as existing on a spectrum of conditions related to obsessive–compulsive disorder (OCD). "The disorders are thought to lie on a spectrum from impulsive to compulsive where impulsivity is said to persist due to deficits in the ability to inhibit repetitive behavior with known negative consequences, while compulsivity persists as a consequence of deficits in recognizing completion of tasks." OCD is a mental disorder characterized by obsessions and/or compulsions. An obsession is defined as "a recurring thought, image, or urge that the individual cannot control". Compulsion can be described as a "ritualistic behavior that the person feels compelled to perform". The model suggests that many conditions overlap with OCD in symptomatic profile, demographics, family history, neurobiology, comorbidity, clinical course and response to various pharmacotherapies. Conditions described as being on the spectrum are sometimes referred to as obsessive–compulsive spectrum disorders.

Tourette syndrome is an inherited neurological disorder that begins in childhood or adolescence, characterized by the presence of multiple physical (motor) tics and at least one vocal (phonic) tic.

Ecopipam is a dopamine antagonist which is under development for the treatment of Lesch-Nyhan syndrome, Tourette's syndrome, speech disorders, and restless legs syndrome. It is taken by mouth.
James Frederick Leckman, M.D., is a child psychiatrist and psychoanalyst and the Neison Harris Professor of Child Psychiatry, Psychiatry, Psychology and Pediatrics at the Yale School of Medicine, recognized for his research in Tourette syndrome (TS) and obsessive–compulsive disorder (OCD).
Echophenomenon is "automatic imitative actions without explicit awareness" or pathological repetitions of external stimuli or activities, actions, sounds, or phrases, indicative of an underlying disorder.
A premonitory urge is a sensory phenomenon associated with Tourette syndrome and other tic disorders. Premonitory urges are "uncomfortable feelings or sensations preceding tics that usually are relieved by [a particular] movement".
References
- 1 2 Woods DW, Himle MB, Conelea CA. Behavior therapy: other interventions for tic disorders. Adv Neurol. 2006;99:234–40. PMID 16536371
- ↑ Singer HS. "Tourette's syndrome: from behaviour to biology". Lancet Neurol. 2005 Mar;4(3):149–59. doi : 10.1016/S1474-4422(05)01012-4 PMID 15721825
- ↑ Andrén P, Jakubovski E, Murphy TL, et al. (July 2021). "European clinical guidelines for Tourette syndrome and other tic disorders-version 2.0. Part II: psychological interventions". Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 31 (3): 403–423. doi:10.1007/s00787-021-01845-z. PMC 8314030 . PMID 34313861.