
LaTeX is a software system for typesetting documents. LaTeX markup describes the content and layout of the document, as opposed to the formatted text found in WYSIWYG word processors like Microsoft Word, LibreOffice Writer and Apple Pages. The writer uses markup tagging conventions to define the general structure of a document, to stylise text throughout a document, and to add citations and cross-references. A TeX distribution such as TeX Live or MiKTeX is used to produce an output file suitable for printing or digital distribution.
Mathematical Markup Language (MathML) is a mathematical markup language, an application of XML for describing mathematical notations and capturing both its structure and content, and is one of a number of mathematical markup languages. Its aim is to natively integrate mathematical formulae into World Wide Web pages and other documents. It is part of HTML5 and standardised by ISO/IEC since 2015.

Adobe FrameMaker is a document processor designed for writing and editing large or complex documents, including structured documents. It was originally developed by Frame Technology Corporation, which was bought by Adobe.
OpenType is a format for scalable computer fonts. Derived from TrueType, it retains TrueType's basic structure but adds many intricate data structures for describing typographic behavior. OpenType is a registered trademark of Microsoft Corporation.
Mellel is a word processor for Mac OS X, developed since 2002 and marketed as especially suited for technical and academic writers, and for writers with long, complex documents. It is made by Mellel AAR, a small software company. New features are added to the program every few months, many of which come from user suggestions. Its closest competitor is Nisus Writer Pro.

Lucida is an extended family of related typefaces designed by Charles Bigelow and Kris Holmes and released from 1984 onwards. The family is intended to be extremely legible when printed at small size or displayed on a low-resolution display – hence the name, from 'lucid'.
TeXShop is a free LaTeX and TeX editor and previewer for macOS. It is licensed under the GNU GPL.

Mathcad is computer software for the verification, validation, documentation and re-use of mathematical calculations in engineering and science, notably mechanical, chemical, electrical, and civil engineering. Released in 1986 on DOS, it introduced live editing (WYSIWYG) of typeset mathematical notation in an interactive notebook, combined with automatic computations. It was originally developed by Mathsoft, and since 2006 has been a product of Parametric Technology Corporation.

Adobe Captivate is an authoring tool that is used for creating eLearning content such as software demonstrations, software simulations, branched scenarios, and randomized quizzes in HTML5 format.

FontForge is a FOSS font editor which supports many common font formats. Developed primarily by George Williams until 2012, FontForge is free software and is distributed under a mix of the GNU General Public License Version 3 and the 3-clause BSD license. It is available for operating systems including Linux, Windows, and macOS, and is localized into 12 languages.
The Extensible Metadata Platform (XMP) is an ISO standard, originally created by Adobe Systems Inc., for the creation, processing and interchange of standardized and custom metadata for digital documents and data sets.

Cambria is a transitional serif typeface commissioned by Microsoft and distributed with Windows and Office. It was designed by Dutch typeface designer Jelle Bosma in 2004, with input from Steve Matteson and Robin Nicholas. It is intended as a serif font that is suitable for body text, that is very readable printed small or displayed on a low-resolution screen and has even spacing and proportions.
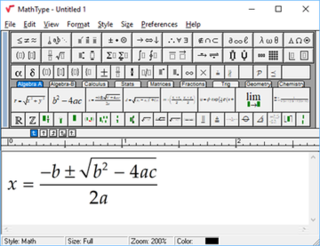
MathType is a software application created by Design Science that allows the creation of mathematical notation for inclusion in desktop and web applications.

Mathomatic is a free, portable, general-purpose computer algebra system (CAS) that can symbolically solve, simplify, combine and compare algebraic equations, and can perform complex number, modular, and polynomial arithmetic, along with standard arithmetic. It does some symbolic calculus (derivative, extrema, Taylor series, and polynomial integration and Laplace transforms), numerical integration, and handles all elementary algebra except logarithms. Trigonometric functions can be entered and manipulated using complex exponentials, with the GNU m4 preprocessor. Not currently implemented are general functions like f(x), arbitrary-precision and interval arithmetic, and matrices.
This is a comparison of word processing software.

The STIX Fonts project or Scientific and Technical Information Exchange (STIX), is a project sponsored by several leading scientific and technical publishers to provide, under royalty-free license, a comprehensive font set of mathematical symbols and alphabets, intended to serve the scientific and engineering community for electronic and print publication. The STIX fonts are available as fully hinted OpenType/CFF fonts. There is currently no TrueType version of the STIX fonts available, but the STIX Mission Statement includes the intention to create one in the future. However, there exists an unofficial conversion of STIX Fonts to TrueType, suitable for use with software without OpenType support.
A mathematical markup language is a computer notation for representing mathematical formulae, based on mathematical notation. Specialized markup languages are necessary because computers normally deal with linear text and more limited character sets. A formally standardized syntax also allows a computer to interpret otherwise ambiguous content, for rendering or even evaluating. For computer-interpretable syntaxes, the most popular are TeX/LaTeX, MathML, OpenMath and OMDoc.

MathJax is a cross-browser JavaScript library that displays mathematical notation in web browsers, using MathML, LaTeX and ASCIIMathML markup. MathJax is released as open-source software under the Apache License.











