
The first fully democratic Presidential election since 1960 occurred on 11 March 2007. The election was the final transfer from military to civilian rule following the military coup in 2005. This was the first time the president was selected by ballot in the country's history. The election was won by Sidi Ould Cheikh Abdallahi, who was ousted by a military coup in 2008 and replaced by general Mohamed Ould Abdel Aziz.
The Irish presidential election determines who serves as the President of Ireland, the head of state of Ireland. The last election took place on 27 October 2018. Where only one candidate is nominated, that candidate is declared elected without a ballot; this has occurred on six occasions.

Prior to the coup d'état of August 2005, Mauritania was a one party dominant state with the Democratic and Social Republican Party in power. Opposition parties were allowed, but widely considered to have no real chance of gaining power.

Latvia elects on national level a legislature. The Saeima has 100 members, elected for a four-year term by proportional representation with a 5% threshold. An unmodified Sainte-Laguë method is used to allocate seats. The parliamentary elections are held on the first Saturday of October. Locally, Latvia elects municipal councils, consisting of 7 to 60 members, depending on the size of the municipality, also by proportional representation for a four-year term.

Elections in Benin take place within the framework of a multi-party democracy and a presidential system. Both the President and the National Assembly are directly elected by voters, with elections organised by the Autonomous National Electoral Commission (CENA).

An Algerian Constitution was first adopted by a referendum in 1963, following the Algerian War of Independence (1954–62); originally, it was to be drafted by a constitutional assembly led by Ferhat Abbas, but this body was sidelined by Algeria's first President, Ahmed Ben Bella. In its 1963 form, the constitution declared Algeria a one-party state ruled by the former resistance movement, the National Liberation Front (FLN). This constitution was suspended by the military coup d'état of 1965. After years of ruling by executive fiat as leader of the Revolutionary Council, Houari Boumédienne issued a second constitution in 1976, emphasizing the importance of socialism and - formally - restoring political institutions to their primacy over the military establishment.

Colonel Ely Ould Mohamed Vall was a Mauritanian political and military figure. Following a coup d'état in August 2005, he served as the transitional military leader of Mauritania until 19 April 2007, when he relinquished power to an elected government.
This electoral calendar 2006 lists the national/federal direct elections held in 2006 in the de jure and de facto sovereign states and their dependent territories. Referendums are included, although they are not elections. By-elections are not included.

The President of Chile, officially known as the President of the Republic of Chile is the head of state and the head of government of Chile. The President is responsible for both the Chilean government and state administration. Although its role and significance has changed over the history of Chile, as well as its position and relations with other actors in the national political organization, it is one of the most prominent political figures. It is also considered as one of the institutions that make up the "Historic Constitution of Chile", and is essential to the country's political stability.

The 1992 Constitution of Mali was approved by a referendum on 12 January 1992 after being drawn up by a national conference in August 1991. The constitution provides for multi party democracy within a semi-presidential system.

The Constitution of the Republic of Chad is the supreme law of Chad. Chad's seventh constitution, it was adopted in 1996, six years after President Idriss Déby rose to power following a successful rebellion against President Hissène Habré, this formal document establishes the framework of the Chadian state and government and enumerates the rights and freedoms of its citizens. In its current form, the contents of the Constitution include a preamble, 16 parts and 225 articles.

The Constitution of Azerbaijan was adopted on 12 November 1995 by popular referendum. This Constitution was the first Constitution of independent Azerbaijan, the Azerbaijan Democratic Republic founded in 1918 and existed 23 months until 1920 was not able to adopt its constitution. Therefore, the history of Constitution building in Azerbaijan generally starts from the period of Azerbaijan being part of Soviet Union. The first Constitution of Azerbaijan SSR was adopted in 1921 and was in accordance with the Constitution of USSR. The last Constitution of Azerbaijan SSR was adopted on 21 April 1978 and also was in line and form of USSR Constitution. The first Constitution of independent Azerbaijan consists of 5 chapters, 12 sections and 147 articles. It was amended on 24 August 2002 and again on 18 March 2009. It carries the "highest legal force" in Azerbaijan as per article 147. The most recent amendments to the Constitution were approved after the Constitutional referendum held on 26 September 2016. In 2002, 31 amendments were made to 22 articles; in 2009, 41 amendments were made to 29 articles; and in 2016, 23 articles were amended and new 6 new articles were added.

The current Constitution of Mauritania was adopted on 12 July 1991. There have been several constitutions since Mauritania's independence in 1960.

The Constitution of Liberia is the supreme law of the Republic of Liberia. The current constitution, which came into force on 6 January 1986, replaced the Liberian Constitution of 1847, which had been in force since the independence of Liberia. Much like the 1847 Constitution, the Constitution creates a system of government heavily modeled on the Federal Government of the United States.
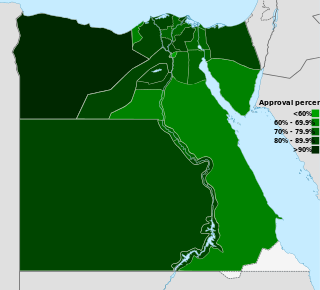
A constitutional referendum was held in Egypt on 19 March 2011, following the 2011 Egyptian revolution. More than 14 million (77%) were in favour, while around 4 million (23%) opposed the changes; 41% of 45 million eligible voters turned out to vote.
A committee formed in February 2011 by the Egyptian military following suspension of the constitution during the 2011 Egyptian revolution. The committee's purpose is to review the constitution of Egypt, to be ratified by a referendum.

A constitutional referendum was held in the Republic of the Congo on 25 October 2015 regarding a proposal to change the constitution, primarily to modify the rules regarding presidential terms.














