| Look up maxillary in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
Maxillary means "related to the maxilla (upper jaw bone)". Terms containing "maxillary" include:
| Look up maxillary in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
Maxillary means "related to the maxilla (upper jaw bone)". Terms containing "maxillary" include:

Paranasal sinuses are a group of four paired air-filled spaces that surround the nasal cavity. The maxillary sinuses are located under the eyes; the frontal sinuses are above the eyes; the ethmoidal sinuses are between the eyes and the sphenoidal sinuses are behind the eyes. The sinuses are named for the facial bones in which they are located.
Sinus may refer to:

In mammalian oral anatomy, the canine teeth, also called cuspids, dog teeth, or fangs, eye teeth, vampire teeth, or vampire fangs, are the relatively long, pointed teeth. They can appear more flattened however, causing them to resemble incisors and leading them to be called incisiform. They developed and are used primarily for firmly holding food in order to tear it apart, and occasionally as weapons. They are often the largest teeth in a mammal's mouth. Individuals of most species that develop them normally have four, two in the upper jaw and two in the lower, separated within each jaw by incisors; humans and dogs are examples. In most species, canines are the anterior-most teeth in the maxillary bone.
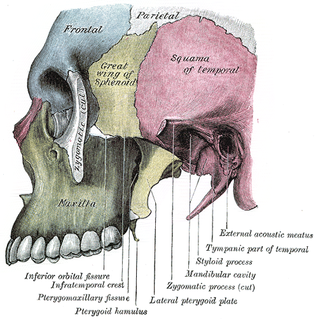
The maxilla in vertebrates is the upper fixed bone of the jaw formed from the fusion of two maxillary bones. In humans, the upper jaw includes the hard palate in the front of the mouth. The two maxillary bones are fused at the intermaxillary suture, forming the anterior nasal spine. This is similar to the mandible, which is also a fusion of two mandibular bones at the mandibular symphysis. The mandible is the movable part of the jaw.

Incisors are the front teeth present in most mammals. They are located in the premaxilla above and on the mandible below. Humans have a total of eight. Opossums have 18, whereas armadillos have none.

A snake skeleton consists primarily of the skull, vertebrae, and ribs, with only vestigial remnants of the limbs.

The pyramid-shaped maxillary sinus is the largest of the paranasal sinuses, and drains into the middle meatus of the nose through the osteomeatal complex.

A palatal expander is a device in the field of orthodontics which is used to widen the upper jaw (maxilla) so that the bottom and upper teeth will fit together better. This is a common orthodontic procedure. Although the use of an expander is most common in children and adolescents 8-18 years of age, it can also be used in adults, although expansion is slightly more uncomfortable and takes longer. A patient who would rather not wait several months for the end result by a palatal expander may be able to opt for a surgical separation of the maxilla. Use of a palatal expander is most often followed by braces to then straighten the teeth.
The superior alveolar artery may refer to:

The maxillary central incisor is a human tooth in the front upper jaw, or maxilla, and is usually the most visible of all teeth in the mouth. It is located mesial to the maxillary lateral incisor. As with all incisors, their function is for shearing or cutting food during mastication (chewing). There is typically a single cusp on each tooth, called an incisal ridge or incisal edge. Formation of these teeth begins at 14 weeks in utero for the deciduous (baby) set and 3–4 months of age for the permanent set.

The foramen rotundum is a circular hole in the sphenoid bone of the skull. It connects the middle cranial fossa and the pterygopalatine fossa. It allows for the passage of the maxillary nerve (V2), a branch of the trigeminal nerve.

In human anatomy, the pterygopalatine fossa is a fossa in the skull. A human skull contains two pterygopalatine fossae—one on the left side, and another on the right side. Each fossa is a cone-shaped paired depression deep to the infratemporal fossa and posterior to the maxilla on each side of the skull, located between the pterygoid process and the maxillary tuberosity close to the apex of the orbit. It is the indented area medial to the pterygomaxillary fissure leading into the sphenopalatine foramen. It communicates with the nasal and oral cavities, infratemporal fossa, orbit, pharynx, and middle cranial fossa through eight foramina.

The maxillary artery supplies deep structures of the face. It branches from the external carotid artery just deep to the neck of the mandible.

FDI World Dental Federation notation is the world's most commonly used dental notation. It is designated by the International Organization for Standardization as standard ISO 3950 "Dentistry — Designation system for teeth and areas of the oral cavity".
Dental anatomy is a field of anatomy dedicated to the study of human tooth structures. The development, appearance, and classification of teeth fall within its purview. Tooth formation begins before birth, and the teeth's eventual morphology is dictated during this time. Dental anatomy is also a taxonomical science: it is concerned with the naming of teeth and the structures of which they are made, this information serving a practical purpose in dental treatment.
In anatomy, a hiatus is a natural fissure in a structure. Examples include:
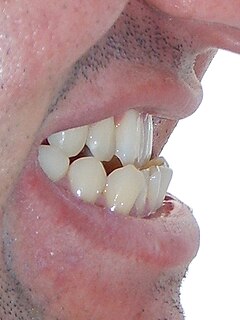
Maxillary hypoplasia, or maxillary deficiency, is an underdevelopment of the bones of the upper jaw. It is associated with Crouzon syndrome, Angelman syndrome, as well as fetal alcohol syndrome. It can also be associated with cleft lip and cleft palate. Some people could develop it due to poor dental extractions.

Stenaulorhynchus is an extinct genus of hyperodapedontid rhynchosaur known from the Middle Triassic deposits of Tanganyika Territory, Tanzania. It was found in the Lifua Member of the Manda Formation in the Karoo Supergroup. It was named and first described by Sidney Henry Haughton in 1932. The type species is Stenaulorhynchus stockleyi, a beaked herbivore measuring 1–6 meters in length.

Siamodon is an extinct genus of iguanodontian ornithopod dinosaur from Early Cretaceous deposits of northeastern Thailand.

In human anatomy, the mouth is the first portion of the alimentary canal that receives food and produces saliva. The oral mucosa is the mucous membrane epithelium lining the inside of the mouth.